
The potato is a starchy root vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are tubers of the plant Solanum tuberosum, a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.

Ullucus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Basellaceae, with one species, Ullucus tuberosus, a plant grown primarily as a root vegetable, secondarily as a leaf vegetable. The name ulluco is derived from the Quechua word ulluku, but depending on the region, it has many different names. These include illaco, melloco, chungua or ruba, olluco or papalisa, or ulluma.

Russet Burbank is a potato cultivar with dark brown skin and few eyes that is the most widely grown potato in North America. A russet type, its flesh is white, dry, and mealy, and it is good for baking, mashing, and french fries (chips). It is a common and popular potato.

The Désirée potato is a red-skinned main-crop potato originally bred in the Netherlands in 1962. It has yellow flesh with a distinctive flavour and is a favourite with allotment-holders because of its resistance to drought, and is fairly resistant to disease. It is a versatile, fairly waxy variety which is firm and holds its shape, and is useful for all methods of cooking, from roasting to mashing and salads.

Potato leafroll virus (PLRV) is a member of the genus Polerovirus and family Solemoviridae. The phloem limited positive sense RNA virus infects potatoes and other members of the family Solanaceae. PLRV was first described by Quanjer et al. in 1916. PLRV is transmitted by aphids, primarily the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae. PLRV is one of the most important potato viruses worldwide but particularly devastating in countries with limited resources and management. It can be responsible for individual plant yield losses of over 50%. One estimate suggests that PLRV is responsible for an annual global yield loss of 20 million tons. Symptoms include chlorosis, necrosis and leaf curling.
Red Gold potato is an early variety of North American potato. It has a red skin with yellow flesh inside. It is resistant to potato leafroll virus and potato virus Y and moderately resistant to common scab, but is susceptible to potato virus A and potato virus S.
Potato mop-top virus (PMTV) is a plant pathogenic virus transmitted through the vector Spongospora subterranea that affects potatoes. PMTV belongs to family of Virgaviridae, and the genus Pomovirus. The virus was first identified in 1966 by Calvert and Harrison in Britain, and is now reported in many other potato cultivating regions of the world including U.S.A., Canada, China, Pakistan, Japan, South American countries and many parts of Europe. Many disease management systems have been found to be ineffective against the virus, although a combination of sanitation and vector controls seems to work well.

Red Norland is a red, early-maturing potato. Smaller tubers are commonly sold as “baby reds” and this variety is often served boiled or in potato salads. The progenitor variety, 'Norland', was released by the North Dakota Agricultural College in 1957. Since the release of 'Norland', other darker red skinned variants were selected, most notably 'Red Norland' and 'Dark Red Norland'. None of these three varieties is under plant variety protection. The darker red strains are now widely grown, and 'Norland' is rarely grown. 'Norland' and its selections are widely adapted, but have relatively low to intermediate yields.
Alturas is a russet potato variety released in 2002 by the USDA-ARS and the Agricultural Experiment Stations of Idaho, Oregon, and Washington and it is under plant variety protection. It is a processing potato that has cold-sweetening resistance, so it can be processed directly out of storage into French fries and other frozen potato products.

Bintje is a middle-early ripening potato variety bred in the Netherlands by the Frisian schoolmaster K.L. de Vries in 1904 from and marketed for the first time in 1910. The name of the potato, a diminutive of Benedict, was borrowed from one of his former students.
Superior is a white-skinned, white-fleshed, mid-season potato variety. It was released by the University of Wisconsin potato breeding program in 1962, and is not under plant variety protection. It is a progeny of a cross between 'B96-56' and 'M59.44' and was first grown in 1951. 'B96-56' was also a parent of Kennebec. Like the potato variety Atlantic, Superior is widely grown for potato chip manufacturing right off the field and marketable yields are fairly high.
MegaChip is a round white potato variety with good tuber size, and specific gravity for making potato chips.
Umatilla Russet is a moderately late maturing variety of potato especially suitable for frozen french fries processing. It was jointly released by the Agricultural Experiment Station of Oregon, Idaho, and Washington and the U.S. Department of Agriculture in 1998. 'Umatilla Russet' has been equal to or better than Russet Burbank in fry color in Oregon and regional trials. The potato was named by the state of Oregon after the Umatilla tribe, from which the city of Umatilla also takes its name.
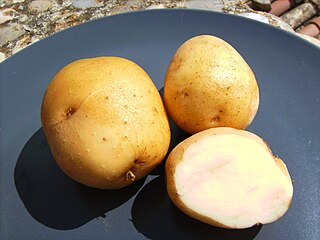
Kennebec is a medium- to late-maturing white potato. It was bred by the USDA and selected by Presque Isle Station, Maine, in 1941. Kennebec is not under plant variety protection. This fast-growing variety has high yields. It maintains good quality in storage and is grown for both fresh market use and for potato chip manufacturing.
The Ranger Russet is a late-maturing potato that is used for baking and processing into fries. It was originally bred by Joseph J. Pavek of the USDA in Aberdeen, Idaho, and released jointly by the USDA and the agricultural stations of Idaho, Washington, Oregon and Colorado in 1991. Ranger Russet is not under plant variety protection. It yields medium to high numbers of tubers with a short dormancy period.
Marcy is a late maturing white potato variety. It was originally bred in 1990 at Cornell University from a cross between the Atlantic variety and Q155-3 variety. It is mostly used for chipping but can be used for baking and boiling. It has good storability; chip color is good even after short to medium storage. Marcy has a high yielding crop.
Lenape (B5141-6) is a potato cultivar first released in 1967 and named after the Lenape Native American tribe, which had to be pulled from the market in 1970 after findings of its high glycoalkaloid content. It was bred by Wilford Mills of Pennsylvania State University in collaboration with the Wise Potato Chip Company. The Lenape potato was produced by crossing Delta Gold with a wild Peruvian potato known for its resistance to insects. It was selected for its high specific gravity and low sugar content which made it ideal for producing potato chips but it was also immune to potato virus A and resistant to common strains of late blight. It is of medium-late maturity and produces round, white tubers with shallow eyes.
Pike is a variety of potato bred by the Cornell and Pennsylvania Experimental Stations in March 1996. This clone originated from a cross made in 1981, between 'Allegany' and 'Atlantic potato' varieties. It is resistant to infection by golden nematode, common scab, golden necrosis, and foliage infection by Phytophthora. Pike is intended to be used agriculturally, specifically for use in potato chips.

Māori potatoes or taewa are varieties of potato cultivated by Māori people, especially those grown before New Zealand was colonised by the British.

Viral diseases of potato are a group of diseases caused by different types of Viruses that affect potato crops worldwide and, although they do not affect human or animal health since they are viruses that only infect vegetables, they are a source of great economic losses annually. About 28 viruses have been reported infecting potato crops. However, potato virus X (PVX), potato virus Y (PVY), and potato leafroll virus (PLRV) are the most important viruses worldwide. Some others are of economic importance only in some regions. Such is the case of potato virus M (PVM) in some Asian and European countries.











