
Amblypygi is an order of arachnid chelicerate arthropods also known as whip spiders or tailless whip scorpions, not to be confused with whip scorpions or vinegaroons that belong to the related order Thelyphonida. The name "amblypygid" means "blunt tail", a reference to a lack of the flagellum that is otherwise seen in whip scorpions. Amblypygids possess no silk glands or venomous fangs. They rarely bite if threatened, but can grab fingers with their pedipalps, resulting in thorn-like puncture injuries.

Uropygi is an arachnid order comprising invertebrates commonly known as whip scorpions or vinegaroons. They are often called uropygids. The name "whip scorpion" refers to their resemblance to true scorpions and possession of a whiplike tail, and "vinegaroon" refers to their ability when attacked to discharge an offensive, vinegar-smelling liquid, which contains acetic acid. The order may also be called Thelyphonida. Both names, Uropygi and Thelyphonida, may be used either in a narrow sense for the order of whip scorpions, or in a broad sense which includes the order Schizomida.

Cybaeidae is a family of spiders first described by Nathan Banks in 1892. The diving bell spider or water spider Argyroneta aquatica was previously included in this family, but is now in the family Dictynidae.

Plesiosiro is an extinct arachnid genus known exclusively from nine specimens from the Upper Carboniferous of Coseley, Staffordshire, United Kingdom. The genus is monotypic, represented only by the species Plesiosiro madeleyi described by Reginald Innes Pocock in his important 1911 monograph on British Carboniferous arachnids. It is the only known member of the order Haptopoda.
Austrochilidae is a small spider family with nine species in two genera. Austrochilus and Thaida are endemic to the Andean forest of central and southern Chile and adjacent Argentina.

The Entelegynae or entelegynes are a subgroup of araneomorph spiders, the largest of the two main groups into which the araneomorphs were traditionally divided. Females have a genital plate (epigynum) and a "flow through" fertilization system; males have complex palpal bulbs. Molecular phylogenetic studies have supported the monophyly of Entelegynae.

Atypoidea is a clade of mygalomorph spiders, one of the two main groups into which the mygalomorphs are divided. It has been treated at the rank of superfamily. It contains five families of spiders:

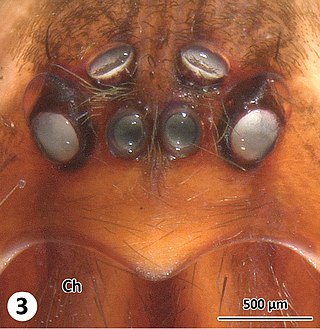
Damon medius is a species of arachnid of the family Phrynichidae.

Synspermiata is a clade of araneomorph spiders, comprising most of the former "haplogynes". They are united by having simpler genitalia than other araneomorph spiders, lacking a cribellum, and sharing an evolutionary history of synspermia – a particular way in which spermatozoa are grouped together when transferred to the female.
Sarax is a genus of amblypygids of the family Charinidae.

Acanthophrynus is a genus of tailless whipscorpion in the family Phrynidae containing a single species, Acanthophrynus coronatus. This species is sometimes kept as a pet.

Toxopidae is a small family of araneomorph spiders, first described in 1940. For many years it was sunk into Desidae as a subfamily, although doubts were expressed as to whether this was correct. A large-scale molecular phylogenetic study in 2016 led to the family being revived.
Phrynichus is a genus of tailless whipscorpions in the family Phrynichidae. There are about 16 described species in Phrynichus.

Avicularioidea is a clade of mygalomorph spiders, one of the two main clades into which mygalomorphs are divided. It has been treated at the rank of superfamily.

Paracharon is a genus of tailless whip scorpion. A single species, Paracharon caecus has been described. It is endemic to Guinea-Bissau in West Africa It is one of two living genera of the family Paracharontidae, alongside the South American Jorottui. It is a troglobite having no eyes, with P. caecus found living in termite nests.
Charinus is a genus of amblypygids (whip-spiders) of the family Charinidae.
Weygoldtia is a genus of amblypygids of the family Charinidae, described in 2018 by Gustavo Silva de Miranda, Alessandro P.L. Giupponi, Lorenzo Prendini and Nikolaj Scharff. The genus is named after the German arachnologist Peter Weygoldt, in recognition of his contributions to the study of Amblypygi.

Paracharontidae is an arachnid family within the order Amblypygi. Paracharontidae and the extinct Weygoldtinidae from the Carboniferous form the suborder Paleoamblypygi, the sister group to the remaining Amblypygi. The family contains two genera: Paracharon, containing the single species Paracharon caecus Hansen, 1921 from Guinea-Bissau in West Africa, and Jorottui with the single species Jorottui ipuanai from Colombia in northern South America. Paracharonopsis from the Eocene (Ypresian) aged Cambay amber of India was initially assigned to this family but this was later questioned and it has since been reassigned to Euamblypygi. Both living species are troglobites, having no eyes, with P. caecus living in termite nests, while J. ipuanai inhabits caves.
Catageus is a genus of amblypygids of the family Charontidae.













