
Hyoliths are animals with small conical shells, known as fossils from the Palaeozoic era. They are at least considered as lophotrochozoan, and possibly being lophophorates, a group which includes the brachiopods, while others consider them as being basal lophotrochozoans, or even molluscs.
The radula is an anatomical structure used by mollusks for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food enters the esophagus. The radula is unique to the mollusks, and is found in every class of mollusk except the bivalves, which instead use cilia, waving filaments that bring minute organisms to the mouth.
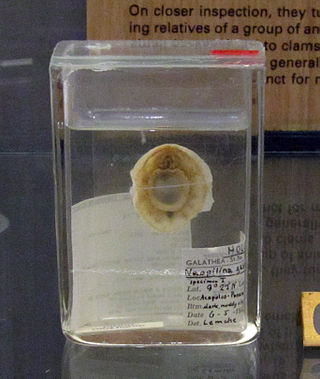
Monoplacophora, meaning "bearing one plate", is a polyphyletic superclass of molluscs with a cap-like shell, inhabiting deep sea environments. Extant representatives were not recognized as such until 1952; previously they were known only from the fossil record, and were thought to have become extinct 375 million years ago.
Strepsodiscus is an extinct genus of very primitive fossil snail-like molluscs from the early part of the Late Cambrian of North America. The coiled, slightly asymmetrical shells are about 3 cm in height. It is not known whether these are shells of gastropods or monoplacophorans, which are more primitive mollusks.

The Bellerophontidae are an extinct family of specialized globose bellerophontids, Paleozoic and early Triassic mollusks of the class Gastropoda.
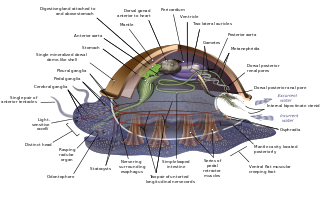
The evolution of the molluscs is the way in which the Mollusca, one of the largest groups of invertebrate animals, evolved. This phylum includes gastropods, bivalves, scaphopods, cephalopods, and several other groups. The fossil record of mollusks is relatively complete, and they are well represented in most fossil-bearing marine strata. Very early organisms which have dubiously been compared to molluscs include Kimberella and Odontogriphus.

Banffia is a genus of animals described from Middle Cambrian fossils. The genus commemorates Banff, Alberta, near where the first fossil specimens were discovered. Its placement in higher taxa is controversial. It is considered to be a member of the enigmatic phylum Vetulicolia.

Latouchella is an extinct genus of marine invertebrate animal, that is considered to be a mollusk and which may be a sea snail, a gastropod. It is a helcionellid from the Tommotian epoch of what is now Siberia. Its tightly coiled, spiral shell contains a number of low "walls" running up the front surface of the interior; these would have directed water currents within its shell. Between these walls are a series of furrows, parallel to the shell's aperture, giving casts of the internal structure the appearance of a railway line, with sleepers tying together paired rails that run towards the apex of the shell.

The Euomphalina comprise a major suborder of mainly Paleozoic archaeogastropods, shells of which are hyperstophic to depressed orthstrophic, commonly with an angulation at the outer upper whorl surface thought to be coincident with the exhalent channel; shell wall thick, outer layer calcitic, inner layers aragonitic but not nacreous; operculum calcareous and heavy. Their range is from the Upper Cambrian to the Triassic, and possibly as high as the Upper Cretaceous.

Yochelcionella is an extinct genus of basal molluscs which lived during the Tommotian epoch, the first epoch of the Cambrian period. This genus is often reconstructed to resemble snails.

Scenella is an extinct genus of fossil invertebrate animal which is generally considered to be a mollusc; at various times it has been suggested that this genus belongs with the gastropods, the monoplacophorans, or the helcionellids, although no firm association with any of these classes has been established. An affinity with the hydrozoa has been considered, although some authors oppose this hypothesis. A gastropod affinity is defended on the basis of six pairs of internal muscle scars, whilst the serially-repeated nature of these scars suggests to other authors a monoplacophoran affinity. However the specimens showing this scarring have not been convincingly shown to belong to the genus Scenella. A similarity to the Ediacaran Ovatoscutum has also been drawn.

Helcionellid or Helcionelliformes is an order of small fossil shells that are universally interpreted as molluscs, though no sources spell out why this taxonomic interpretation is preferred. These animals are first found about 540 to 530 million years ago in the late Nemakit-Daldynian age, which is the earliest part of the Cambrian period. A single species persisted to the Early Ordovician. These fossils are component of the small shelly fossils (SSF) assemblages.
The small shelly fauna, small shelly fossils (SSF), or early skeletal fossils (ESF) are mineralized fossils, many only a few millimetres long, with a nearly continuous record from the latest stages of the Ediacaran to the end of the Early Cambrian Period. They are very diverse, and there is no formal definition of "small shelly fauna" or "small shelly fossils". Almost all are from earlier rocks than more familiar fossils such as trilobites. Since most SSFs were preserved by being covered quickly with phosphate and this method of preservation is mainly limited to the late Ediacaran and early Cambrian periods, the animals that made them may actually have arisen earlier and persisted after this time span.

Plectronoceras is the earliest known shelled cephalopod, dating to the Late Cambrian. None of the fossils are complete, and none show the apex or aperture of the shell. Approximately half of its shell was filled with septa; 7 were recorded in a 2 centimetres (0.79 in) shell. Its shell contains transverse septa separated by about half a millimetre, with a siphuncle on its concave side. Its morphology matches closely to that hypothesised for the last common ancestor of all cephalopods.

Bellerophontoidea, common name "bellerophonts", is a superfamily of extinct planospirally-coiled globose molluscs. This superfamily is generally included within the Gastropoda, but may instead be a group of monoplacophorans. The taxon first appeared late in the Cambrian and continued until late in the Triassic.
The Kirengellids are a group of problematic Cambrian fossil shells of marine organisms. The shells bear a number of paired muscle scars on the inner surface of the valve.
The cephalopods have a long geological history, with the first nautiloids found in late Cambrian strata, and purported stem-group representatives present in the earliest Cambrian lagerstätten.
Watsonella is an extinct genus of mollusc known from early (Terreneuvian) Cambrian strata. It has been hypothesized to be close to the origin of bivalves. It contains a single species, Watsonella crosbyi.

Kutorginates (Kutorginata) are an extinct class of early rhynchonelliform ("articulate") brachiopods. The class contains only a single order, Kutorginida (kutorginides). Kutorginides were among the earliest rhynchonelliforms, restricted to the lower-middle part of the Cambrian Period.

Nenoxites is an extinct genus of Ediacaran ichnofossils described by Mikhail Fedonkin in 1973. The genus is monotypic; the only species to have been described is Nenoxites curvus.









