
Algae is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as Chlorella, Prototheca and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to 50 metres (160 ft) in length. Most are aquatic and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a division of green algae which includes, for example, Spirogyra and stoneworts. Algae that are carried by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton.

The sea lettuces comprise the genus Ulva, a group of edible green algae that is widely distributed along the coasts of the world's oceans. The type species within the genus Ulva is Ulva lactuca, lactuca being Latin for "lettuce". The genus also includes the species previously classified under the genus Enteromorpha, the former members of which are known under the common name green nori.

Sargassum is a genus of brown macroalgae (seaweed) in the order Fucales of the Phaeophyceae class. Numerous species are distributed throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world, where they generally inhabit shallow water and coral reefs, and the genus is widely known for its planktonic (free-floating) species. Most species within the class Phaeophyceae are predominantly cold-water organisms that benefit from nutrients upwelling, but the genus Sargassum appears to be an exception. Any number of the normally benthic species may take on a planktonic, often pelagic existence after being removed from reefs during rough weather. Two species have become holopelagic—reproducing vegetatively and never attaching to the seafloor during their lifecycles. The Atlantic Ocean's Sargasso Sea was named after the algae, as it hosts a large amount of Sargassum.

Caulerpa taxifolia is a species of green seaweed, an alga of the genus Caulerpa, native to tropical waters of the Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean, and Caribbean Sea. The species name taxifolia arises from the resemblance of its leaf-like fronds to those of the yew (Taxus).

Caulerpa is a genus of seaweeds in the family Caulerpaceae. They are unusual because they consist of only one cell with many nuclei, making them among the biggest single cells in the world.

Ulva lactuca, also known by the common name sea lettuce, is an edible green alga in the family Ulvaceae. It is the type species of the genus Ulva. A synonym is U. fenestrata, referring to its "windowed" or "holed" appearance.

Halimeda is a genus of green macroalgae. The algal body (thallus) is composed of calcified green segments. Calcium carbonate is deposited in its tissues, making it inedible to most herbivores. However one species, Halimeda tuna, was described as pleasant to eat with oil, vinegar, and salt.
Prymnesium parvum is a species of haptophyte. The species is of concern because of its ability to produce the phycotoxin prymnesin. It is a flagellated alga that is normally found suspended in the water column. It was first identified in North America in 1985, but it is not known if it was introduced artificially or missed in previous surveys. Toxin production mainly kills fish and appears to have little effect on cattle or humans. This distinguishes it from a red tide, which is an algal bloom whose toxins lead to harmful effects in people. Although no harmful effects are known, it is recommended not to consume dead or dying fish exposed to a P. parvum bloom.

Heterosigma akashiwo is a species of microscopic algae of the class Raphidophyceae. It is a swimming marine alga that episodically forms toxic surface aggregations known as harmful algal bloom. The species name akashiwo is from the Japanese for "red tide".

Bryopsis is a genus of marine green algae in the family Bryopsidaceae. It is frequently a pest in aquariums, where it is commonly referred to as hair algae.

Udotea is a genus of green algae in the family Udoteaceae.

Turbinaria is a genus of brown algae (Phaeophyceae) found primarily in tropical marine waters. It generally grows on rocky substrates. In tropical Turbinaria species that are often preferentially consumed by herbivorous fishes and echinoids, there is a relatively low level of phenolics and tannins.
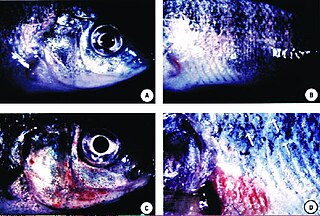
Predatory dinoflagellates are predatory heterotrophic or mixotrophic alveolates that derive some or most of their nutrients from digesting other organisms. About one half of dinoflagellates lack photosynthetic pigments and specialize in consuming other eukaryotic cells, and even photosynthetic forms are often predatory.

Peyssonnelia is a genus of thalloid red alga, named after naturalist Jean-André Peyssonnel (1694–1759) It includes the algae commonly known as rumoi-iwanokawa, mayoi-iwanokawa and akase-iwanokawa. Specimens can reach around 20 cm in size. Peyssonnelia produces tetraspores.

Halimeda tuna is a species of calcareous green seaweed in the order Bryopsidales. It is found on reefs in the Atlantic Ocean, the Indo-Pacific region and the Mediterranean Sea. Halimeda tuna is the type species of the genus Halimeda and the type locality is the Mediterranean Sea. The specific name "tuna" comes from the Taíno language, meaning "cactus" and referring to the resemblance of the thallus to the growth form of an Opuntia cactus.

Gobiodon histrio, the Broad-barred goby, is a species of goby native to the Indian Ocean from the Red Sea to the western Pacific Ocean to southern Japan, Samoa and the Great Barrier Reef. This species is a reef dweller, being found at depths of from 2 to 15 metres. It can reach a length of 3.5 centimetres (1.4 in) TL. This species can also be found in the aquarium trade.

Chaetophora elegans is the type species in the algae genus Chaetophora.
Lobophora variegata is a species of small thalloid brown alga which grows intertidally or in shallow water in tropical and warm temperate seas. It has three basic forms, being sometimes ruffled, sometimes reclining and sometimes encrusting, and each form is typically found in a different habitat. This seaweed occurs worldwide. It is the type species of the genus Lobophora, the type locality being the Antilles in the West Indies.
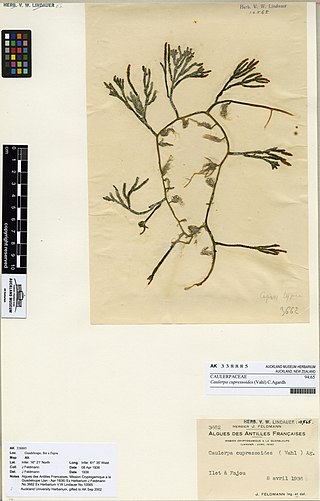
Caulerpa cupressoides, commonly known as cactus tree alga, is a species of seaweed in the Caulerpaceae family. Green alge of Caulerpa genus are salty and pungent in style and are consumed by several marine cultures around the world.


















