
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 species of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of Chlamydomonas is that it contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of Chlamydomonas are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains.

Brown algae are a large group of multicellular algae comprising the class Phaeophyceae. They include many seaweeds located in colder waters of the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and polar regions. Many brown algae, such as members of the order Fucales, commonly grow along rocky seashores. Most brown algae live in marine environments, where they play an important role both as food and as a potential habitat. For instance, Macrocystis, a kelp of the order Laminariales, may reach 60 m (200 ft) in length and forms prominent underwater kelp forests that contain a high level of biodiversity. Another example is Sargassum, which creates unique floating mats of seaweed in the tropical waters of the Sargasso Sea that serve as the habitats for many species. Some members of the class, such as kelps, are used by humans as food.
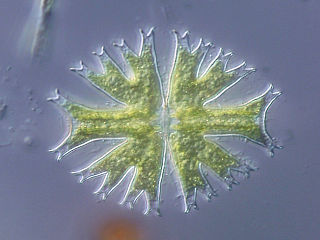
Desmidiales, commonly called the desmids, are an order in the Charophyta, a division of green algae in which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged. Desmids consist of single-celled microscopic green algae. Because desmids are highly symmetrical, attractive, and come in a diversity of forms, they are popular subjects for microscopists, both amateur and professional.

A coenocyte is a multinucleate cell which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without their accompanying cytokinesis, in contrast to a syncytium, which results from cellular aggregation followed by dissolution of the cell membranes inside the mass. The word syncytium in animal embryology is used to refer to the coenocytic blastoderm of invertebrates. A coenocytic colony is referred to as a coenobium, and most coenobia are composed of a distinct number of cells, often as a multiple of two.

Caulerpa taxifolia is a species of green seaweed, an alga of the genus Caulerpa, native to tropical waters of the Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean, and Caribbean Sea. The species name taxifolia arises from the resemblance of its leaf-like fronds to those of the yew (Taxus).

Caulerpa is a genus of seaweeds in the family Caulerpaceae. They are unusual because they consist of only one cell with many nuclei, making them among the biggest single cells in the world.

Caulerpa racemosa is a species of edible green alga, a seaweed in the family Caulerpaceae. It is commonly known as sea grapes and is found in many areas of shallow sea around the world. Despite the name, it is not related to grapes. There are a number of different forms and varieties, and one that appeared in the Mediterranean Sea in 1990, which is giving cause for concern as an invasive species.

Halimeda is a genus of green macroalgae. The algal body (thallus) is composed of calcified green segments. Calcium carbonate is deposited in its tissues, making it inedible to most herbivores. However one species, Halimeda tuna, was described as pleasant to eat with oil, vinegar, and salt.

Codium is a genus of edible green macroalgae under the order Bryopsidales. The genus name is derived from a Greek word that pertains to the soft texture of its thallus. One of the foremost experts on Codium taxonomy was Paul Claude Silva at the University of California, Berkeley. Silva was able to describe 36 species for the genus, and in honor of his work on Codium, the species C. silvae was named after the late professor.

Ectocarpales is a very large order in the brown algae. The order includes families with pseudoparenchymatous (Splachnidiaceae) or true parenchymatous (Scytosiphonaceae) tissue. Pseudoparenchymatous refers to a filamentous alga with cells packed very close together to give an appearance of parenchymatous tissue, the latter being composed of cells which can truly divide in three dimensions, unusual among the algae. Filamentous algae are composed of cells that divide along a single plane, allowing only elongation to form filaments of one or more rows of cells. Algae that can divide in two planes can form sheet-like thalli or bodies. Cells that can divide in a third plane potentially allow for the organism to develop a more complex body plan, and diversification of body plans into an erect thallus of some sort and a holdfast for attaching the upright portion to the substrate.

Polysiphonia, known as red hair algae, is a genus of filamentous red algae with about 19 species on the coasts of the British Isles and about 200 species worldwide, including Crete in Greece, Antarctica and Greenland. Its members are known by a number of common names. It is in the order Ceramiales and family Rhodomelaceae.

Udoteaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Bryopsidales.

Bryopsis, often referred to a hair algae, is a genus of marine green algae in the family Bryopsidaceae. Species in the genus are macroscopic, siphonous marine green algae that are made up of units of single tubular filaments. They can form dense tufts up to 40 cm in height. Each cell is made of up an erect thallus that is often branched into pinnules. Approximately 60 species have been identified in this genus since its initial discovery in 1809. The ecological success of Bryopsis has also been attributed to its associations with endophytic bacteria that reside in the cytoplasm of their cells.
Lobocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiosiphonaceae. It contains the single species Lobocharacium coloradoense. It has been isolated from a pond in Colorado, United States.
Rhipiliopsis is a genus of green algae in the family Rhipiliaceae. Johnson-sea-linkia is a synonym.
Struvea is a genus of green macroalgae in the family Boodleaceae.

Udotea is a genus of green algae in the family Udoteaceae.

Halimeda tuna is a species of calcareous green seaweed in the order Bryopsidales. It is found on reefs in the Atlantic Ocean, the Indo-Pacific region and the Mediterranean Sea. Halimeda tuna is the type species of the genus Halimeda and the type locality is the Mediterranean Sea. The specific name "tuna" comes from the Taíno language, meaning "cactus" and referring to the resemblance of the thallus to the growth form of an Opuntia cactus.

Caulerpa prolifera is a species of green alga, a seaweed in the family Caulerpaceae. It is the type species of the genus Caulerpa, the type location being Alexandria, Egypt. It grows rapidly and forms a dense mass of vegetation on shallow sandy areas of the sea.

Acetabularia acetabulum is a species of green alga in the family Polyphysaceae. It is found in the Mediterranean Sea at a depth of one to two metres.

















