
Paullinia is a genus of flowering shrubs, small trees and lianas in the soapberry family, Sapindaceae and typical of tribe Paullinieae. It is native to tropical South America, Central America and the Caribbean.

Zanthoxylum is a genus of about 250 species of deciduous and evergreen trees, shrubs and climbers in the family Rutaceae that are native to warm temperate and subtropical areas worldwide. It is the type genus of the tribe Zanthoxyleae in the subfamily Rutoideae. Several of the species have yellow heartwood, to which their generic name alludes. Several species are cultivated for their use as spices, notably including Sichuan pepper.
Clusiella is a plant genus of the family Calophyllaceae. When Planchon and Triana first published it in 1860, based on Clusiella elegans, the genus was considered monotypic and remained as such for about 100 years.

Quapoya is a genus of flowering plants in the family Clusiaceae. It includes four species native to northern South America, ranging from Colombia and Peru to northern Brazil and Guyana.

Vismia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Hypericaceae. Members of the genus are small trees and shrubs found in tropical and subtropical areas of Central America and South America. Including the countries of Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panamá, Peru, Suriname, Trinidad-Tobago and Venezuela.

Columnea is a genus of around 200 species of epiphytic herbs and shrubs in the family Gesneriaceae, native to the tropics of the Americas and the Caribbean. The tubular or oddly shaped flowers are usually large and brightly colored – usually red, yellow, or orange – sometimes resembling a fish in shape. A common name is flying goldfish plants due to the unusual flower shape.

Protium is a genus of more than 140 species of flowering plants in the family Burseraceae. It is native to the Neotropics from northern Mexico to Paraguay and southern Brazil, and to Madagascar, the Indian subcontinent, Indochina, southern China, the Philippines, Java, and New Guinea. The genus had been included in Bursera, but is distinct.

Egletes is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. It is native to South America, Mesoamerica, and the West Indies, with the range of one species barely crossing the US border into the extreme southern part of Texas.

Esenbeckia is a genus of flowering plants in the rue family, Rutaceae. All species in the genus are native to the Americas, with the highest diversity in South America. They are commonly known as jopoy, the Mayan word for E. berlandieri, or gasparillo (Spanish).

Neea is a genus of plants in family Nyctaginaceae from the Caribbean region, Central and South America. Members of the genus are commonly called Nia, Neea, or saltwood.

Cupania is a genus of flowering plants in the family Sapindaceae. It includes 58 species native to the tropical Americas, ranging from Mexico and south Florida through Central America, the Caribbean, and South America to northern Argentina.
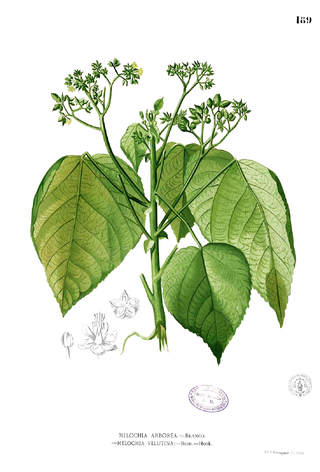
Melochia is a genus of flowering plants in the mallow family, Malvaceae. It comprises 54 species from the tropical and subtropical regions of the world, ranging from India eastwards through Malesia and the Pacific Islands to the Americas and the Caribbean.

Dichapetalum is a genus in the plant family Dichapetalaceae. The plants are tropical lianas native mainly to tropical regions of Africa, Asia, Malesia, the West Indies, Australia and Latin America. Some species are known to be poisonous due to the presence of toxic fluorinated compounds such as fluorocarboxylic acid and dichapetalins, a unique class of cytotoxic compounds that are only found within this genus.

Connarus is a genus of plants in the family Connaraceae.

Tetrapterys is a genus of flowering plants in the family Malpighiaceae, native to Latin America and the Caribbean, from Mexico through to Argentina, but excluding Chile. Small trees, shrubs or vines, they are known to be toxic to livestock if consumed for long periods of time, and T. mucronata and T. styloptera have hallucinogenic effects in humans similar to ayahuasca.














