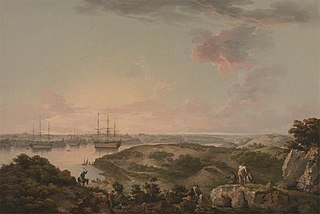The Battle of the Gabbard, was a naval battle fought from 2 to 3 June 1653 during the First Anglo-Dutch War. It took place near the Gabbard shoal off the coast of Suffolk, England, between fleets of the Commonwealth of England and the Dutch Republic. It resulted in a decisive English victory.

The Second Battle of Ushant was a naval battle fought between French and British squadrons near Ushant, an island off the coast of Brittany, on 12 December 1781, as part of the American Revolutionary War.

The Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports is a ceremonial official in the United Kingdom. The post dates from at least the 12th century, when the title was Keeper of the Coast, but may be older. The Lord Warden was originally in charge of the Cinque Ports, a group of five port towns on the southeast coast of England that was formed to collectively supply ships for The Crown in the absence at the time of a formal navy. Today the role is a sinecure and an honorary title, and fourteen towns belong to the Cinque Ports confederation. The title is one of the higher honours bestowed by the Sovereign; it has often been held by members of the Royal Family or prime ministers, especially those who have been influential in defending Britain at times of war.

Sherard Osborn was a Royal Navy admiral and Arctic explorer.

Royal Naval Dockyard, Halifax was a Royal Navy base in Halifax, Nova Scotia. Established in 1759, the Halifax Yard served as the headquarters for the Royal Navy's North American Station for sixty years, starting with the Seven Years' War. The Royal Navy continued to operate the station until it was closed in 1905. The station was sold to Canada in 1907 becoming His Majesty's Canadian Dockyard, a function it still serves today as part of CFB Halifax.

HMS Warwick was a 60-gun fourth-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built to the 1719 Establishment at Plymouth by Peirson Lock. The keel was laid down on 1 April 1730, and the ship was launched on 25 October 1733, and completed on 24 August 1734.

Admiral Sir Bartholomew Samuel Rowley was a British naval officer who served during the American, French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.

Malta Dockyard was an important naval base in the Grand Harbour in Malta in the Mediterranean Sea. The infrastructure which is still in operation is now operated by Palumbo Shipyards.

HMS Genoa was a Téméraire-class 74-gun ship of the line laid down for the French Navy as Brillant which the British captured incomplete while still on slip at the fall of Genoa in 1814. She was completed for the Royal Navy and served as HMS Genoa until 1838. On 20 October 1827 Genoa took part in the Battle of Navarino where her captain Walter Bathurst was killed.

The Admiral of the West, also known as Admiral of the Western Seas or Admiral of the Western Fleet, was formerly an English Navy appointment. The postholder was chiefly responsible for the command of the English navy's fleet based at Portsmouth, which operated in the English Channel, Irish Sea and Atlantic Ocean, from 1294 to 1412.

The Admiral of the South also known as Admiral of the Southern Fleet was a senior English Navy appointment. The post holder was chiefly responsible for the command of the navy's fleet that operated in the English Channel out of Portsmouth from 1294 to 1326.

The Victualling Department originally known as the Department of the Comptroller of Victualling and Transport Services or the Victualling Office, also known as the Department of the Director of Victualling was the British Admiralty department responsible for civil administration of Victualling Yards and the storing and supply of Naval Victuals for the Royal Navy from 1832 to 1964.

The Training Squadron was a formation of sailing ships employed for use of naval training from 1885 to 1899.
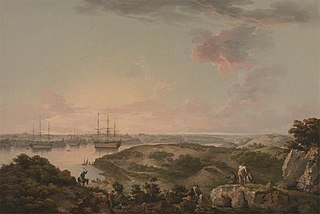
Port Mahon Dockyard was a Royal Navy Dockyard located at Port Mahon, Menorca, Spain. It was opened in 1708 and in 1802 the port was ceded back to Spain. However a resident commissioner of the Royal Navy was still appointed as late as 1814. The dockyard was administered by the Navy Board and was part of the Mediterranean Fleet.
Admiral Sir Gervase Alard, Bart. (1270–1340), was an English knight and naval commander who was appointed Admiral of the Cinque Ports Fleet and Admiral of the Western Fleet of the English Navy who served under King's Edward I, Edward II and Edward III of England from 1296 to 1340.
The Irish Squadron originally known as the Irish Fleet was a series of temporary naval formations assembled for specific military campaigns of the English Navy, the Navy Royal and later the Royal Navy from 1297 to 1731.
Admiral Sir John Perbroun or John de Perbroun, was an English Knight, MP, merchant, ship owner and naval commander who served as Admiral of the North under King Edward III of England from (1322–1324) and again from.
Admiral Sir Peter Bard was an English Knight and naval officer who held a number of important commands of the Navy Royal from 1314 to 1336. and Admiral of the West from 1314 to 1315 and again from 1338 to 1339. Vice-Admiral of the West in 1337. and Admiral of the Fleet of the Cinque Ports from 1335 to 1336.
Admiral Sir John Wells was a Royal Navy officer of the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. He was the son of Sarah Wells, who was mistress to Rear-Admiral Augustus Keppel. After joining the Royal Navy Wells was promoted to lieutenant in 1779 and commander in 1782. He was then given his first command, the sloop HMS Raven. He served in her on the Leeward Islands Station until he was captured by two French frigates in 1783. He was then promoted to post captain and given command of the frigate HMS Boreas upon his release later in the year. He left Boreas in 1784 and did not receive another command until 1797 when he commissioned the ship of the line HMS Lancaster.

Captain James Hawker was an English officer in the Royal Navy. After service on the Shrewsbury and Sheerness, he was appointed first lieutenant of the Colchester at the end of 1755, and was posted in 1768. With the Iris he fought a drawn battle with La Touche Treville in the more powerful frigate Hermione off New York in 1780. He commanded the Hero in Porto Praya under Commodore George Johnstone in 1781, after which he had no further service.