Brașov County is a county (județ) of Romania, in Transylvania, with the capital city at Brașov. The county incorporates within its boundaries most of the Medieval "lands" (țări) Burzenland and Făgăraș.

Sibiu County is a county (județ) of Romania, in the historical region Transylvania, with the capital city Sibiu.

Satu Mare County is a county (județ) of Romania on the border with Hungary and Ukraine. The capital city is Satu Mare. Besides Romanians, Satu Mare features a significant ethnic minority of Hungarians (34.5%).

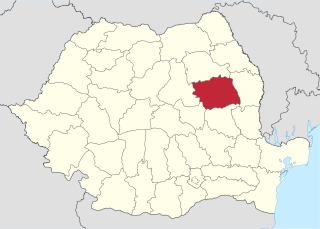
Mureș County is a county (județ) of Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania, with the administrative centre in Târgu Mureș. The county was established in 1968, after the administrative reorganization that re-introduced the historical judeţ (county) system, still used today. This reform eliminated the previous Mureș-Magyar Autonomous Region, which had been created in 1952 within the People's Republic of Romania. Mureș county has a vibrant multicultural fabric that includes Hungarian-speaking Székelys and Transylvanian Saxons, with a rich heritage of fortified churches and towns.
Bacău County is a county (județ) of Romania, in Moldavia, with its capital city at Bacău. It has one commune, Ghimeș-Făget, in Transylvania.

Frumoasa is a commune in Harghita County, Romania. It lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania.

Durostor County was a county (județ) of the Kingdom of Romania, in Southern Dobruja, with the seat at Silistra.

Cernăuți County was a county (județ) of Romania, in Bukovina, with the capital city at Cernăuți. The area was incorporated into the Soviet Union in 1940 and again in 1944, and has been part of Ukraine since 1991.

Storojineț County was a county (județ) of Romania, in Bukovina, with the capital city at Storojineț. The area was incorporated into the Soviet Union in 1940 and again in 1944, and has been part of Ukraine since 1991.

Odorhei County was a county in the Kingdom of Romania. The county seat was Odorheiu Secuiesc.

Târnava-Mică County was a county in the Kingdom of Romania, the successor to Kis-Küküllő County of the KIngdom of Hungary. Its capital was Diciosânmartin until 1926, and afterwards at Blaj.

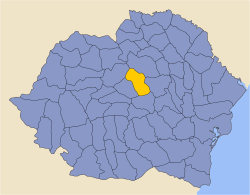
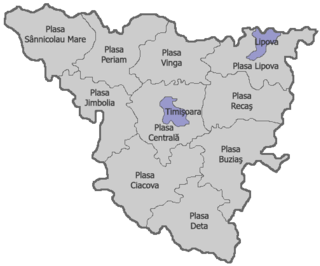
Timiș-Torontal was a county in the Kingdom of Romania. Its capital was Timișoara. The territory of the county had been transferred to Romania in 1920 from the Kingdom of Hungary under the Treaty of Trianon.

Câmpulung County is one of the historic counties of the Kingdom of Romania, in the historical region of Bukovina. The county seat was Câmpulung Moldovenesc.

Caraș County is one of the historic counties Romania in the historic region of the Banat. The county seat was Oravița. The county was founded in 1926, following the division of the former Caraş-Severin County.

Făgăraș County is one of the historic counties of Transylvania, Romania. The county seat was Făgăraș.

Năsăud County is one of the historic counties of Transylvania, Romania. The county seat was Bistrița.

Rădăuți County is one of the historic counties of Bukovina, Romania. The county seat was Rădăuți.

Someș County is one of the historic counties of Transylvania, Romania. The county seat was Dej.

Târnava-Mare County is one of the historical counties of the Kingdom of Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania. The county seat was Sighișoara.

Trei Scaune County is one of the historical counties of the Kingdom of Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania. The county seat was Sfântu Gheorghe.