
Gaultheria is a genus of about 283 species of shrubs in the family Ericaceae. The name commemorates Jean François Gaultier of Quebec, an honour bestowed by the Scandinavian Pehr Kalm in 1748 and taken up by Carl Linnaeus in his Species Plantarum. These plants are native to Asia, Australasia and North and South America. In the past, the Southern Hemisphere species were often treated as the separate genus Pernettya, but no consistent reliable morphological or genetic differences support recognition of two genera, and they are now united in the single genus Gaultheria.

The Styracaceae are a small family of flowering plants in the order Ericales, containing 12 genera and about 160 species of trees and shrubs. The family occurs in warm temperate and subtropical regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
Albisaurus was once thought to be a genus of dinosaur, but is now thought to be a non-dinosaurian archosaur. It was first described by Antonin Fritsch, a Czech palaeontologist, in 1893, but the remains are sparse. The validity of the species cannot be proven based on the fossil remains, and it is usually marked as a nomen dubium. It lived during the Turonian-Santonian stages of the Cretaceous period.

Allium nigrum, common name black garlic, broad-leaved leek, or broadleaf garlic, is a Middle Eastern species of wild onion. It lacks the onion or garlic scent shared by most of the other species in the group. The species is native to Turkey, Cyprus, Syria, Lebanon, and Israel but cultivated as an ornamental in many other places. It has become naturalized in some regions, including parts of the United States.

Cretornis is a pterosaur genus from the late Cretaceous period of what is now the Jizera Formation in the Czech Republic, dating to about 92 million years ago. It only contains a single species, Cretornis hlavaci.

Codonanthe is a genus of mainly epiphytic plants in the family Gesneriaceae, endemic to the Atlantic Forest of Brazil. The botanical name comes from the Ancient Greek for 'bellflower'. They have white or pale pink flowers and somewhat fleshy leaves. In 2013, the genus was reduced in size when more than half of the species were transferred to Codonanthopsis. They can be grown as houseplants, particularly in hanging baskets. Artificial crosses with Nematanthus hybrids have produced the hybrid genus × Codonatanthus.
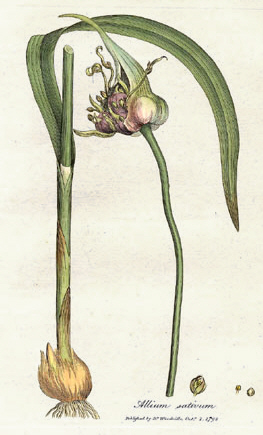
Allium is a genus of monocotyledonous flowering plants with hundreds of species, including the cultivated onion, garlic, scallion, shallot, leek, and chives. It is one of about 57 genera of flowering plants with more than 500 species. It is by far the largest genus in the Amaryllidaceae, and also in the Alliaceae in classification systems in which that family is recognized as separate.
Codonanthopsis elegans is a plant species in the family Gesneriaceae. It is endemic to Belize.
Stillingia uleana is a species of flowering plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. It was described in 1912. It is native to Brazil, in Bahia and Minas Gerais.
Mattauschia is an extinct genus of trematopid temnospondyls from the Late Carboniferous of the Czech Republic.

The Gesnerioideae are a subfamily of plants in the family Gesneriaceae: based on the type genus Gesneria. Although genera typically originate in the New World, some species have become widely distributed as ornamental plants.

Bohemiclavulus is a genus of synapsids that was discovered in the Slaný Formation of the Czech Republic. The type, and currently only, species is B. mirabilis.

An ant garden is a mutualistic interaction between certain species of arboreal ants and various epiphytic plants. It is a structure made in the tree canopy by the ants that is filled with debris and other organic matter in which epiphytes grow. The ants benefit from this arrangement by having a stable framework on which to build their nest while the plants benefit by obtaining nutrients from the soil and from the moisture retained there.

Codonanthopsis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Gesneriaceae. Its native range is from southern Mexico through tropical America to Bolivia and most of Brazil. Codonanthopsis species are generally trailing epiphytes with pale flowers. Most have a mutualistic relationship with tree-living ants: the plants provide the ants with food, including nectar, and give their nests structure and support, while the ants disperse the plants' seeds. The genus was considerably expanded in 2013 when species were transferred from Codonanthe. Some Codonanthopsis species are cultivated as houseplants, when they may be grown in hanging baskets.

Codonanthopsis crassifolia is a species of plant in the family Gesneriaceae.
Codonanthopsis calcarata is a species of flowering plant in the family Gesneriaceae. This species is native to Bolivia, Brazil North, Brazil West-Central, Colombia, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, and Venezuela. Codonanthopsis calcarata is an epiphyte, and mainly grows in wet tropical biomes. Codonanthopsis calcarata was first published in 2013.
Codonanthopsis caribaea is a species of flowering plant in the family Gesneriaceae. This species is native to Guadeloupe to North Venezuela, and is a epiphyte and mainly grows in wet tropical biomes. Codonanthopsis caribaea, along with other species in its genus, was first published in 2013.
Codonanthopsis dissimulata is a species of flowering plant in the family Gesneriaceae. This species is native to northern Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Peru, and Venezuela. Is an epiphyte and mainly grows in wet tropical biomes. The description was first published in 1978.
Codonanthopsis erubescens is a species of flowering plant in the family Gesneriaceae. This species is native to Ecuador and mainly grows in wet tropical biomes. Codonanthopsis erubescens was first published in 2013.
Codonanthopsis macradenia is a species of flowering plant in the family Gesneriaceae. This species is native to Belize, Colombia, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, and Panamá, and mainly grows in subtropical biomes. Codonanthopsis macradenia was first published in 2013.











