
The spotted shag or pārekareka is a species of cormorant endemic to New Zealand. Though originally classified as Phalacrocorax punctatus, it is sufficiently different in appearance from typical members of that genus that for a time it was placed in a separate genus, Stictocarbo, along with a similar species, the Pitt shag. Subsequent genetic studies show that the spotted shag's lineage is nested within the typical shags.

The Agelenidae are a large family of spiders in the suborder Araneomorphae. Well-known examples include the common "grass spiders" of the genus Agelenopsis. Nearly all Agelenidae are harmless to humans, but the bite of the hobo spider may be medically significant, and some evidence suggests it might cause necrotic lesions, but the matter remains subject to debate. The most widely accepted common name for members of the family is funnel weaver.

The Coelopidae or kelp flies are a family of Acalyptratae flies, they are sometimes also called seaweed flies, although both terms are used for a number of seashore Diptera. Fewer than 40 species occur worldwide. The family is found in temperate areas, with species occurring in the southern Afrotropical, Holarctic, and Australasian regions.

The Margarodidae or ground pearls are a family of scale insects within the superfamily Coccoidea. Members of the family include the Polish cochineal and Armenian cochineal and the original ground pearl genus, Margarodes. Beginning in 1880, a number of distinct subfamilies were recognized, with the giant coccids being the first. Although Maskell proposed a new family, many continued to regard the monophlebids as a mere subfamily for many years, and the Margarodidae classification continued to be polyphyletic through the 20th Century. Since then, taking the advice of Koteja several subfamilies and tribes have been elevated into their own families such as Matsucoccidae and Xylococcidae. The pared-down family of Margarodidae is monophyletic.

Icerya purchasi is a scale insect that feeds on more than 80 families of woody plants, most notably on Citrus and Pittosporum. Originally described in 1878 from specimens collected in New Zealand as pests of kangaroo acacia and named by W.M. Maskell "after the Rev. Dr. Purchas who, [he] believe[d], first found it", it is now found worldwide where citrus crops are grown. The cottony cushion scale originates from Australia.
The long-billed wren is an extinct species of New Zealand wren formerly endemic to the South Island of New Zealand. It was the only species in the genus Dendroscansor. It shares the name "long-billed wren" with the Brazilian bird Cantorchilus longirostris.
Paratachardina pseudolobata, the lobate lac scale, is a polyphagous and pestiferous lac scale insect, which damages trees and woody shrubs in Cuba, Florida, the Bahamas and the Australian territory of Christmas Island. It was mistakenly identified as Paratachardina lobata (Chamberlin), an insect native to India and Sri Lanka, but was in 2007 recognized and named as a distinct species based on material from Florida; its native distribution is as yet unknown. The new lac insect was described based on all stages of the female, during the revision of the genus Paratachardina, wherein all its known species were redescribed.

William Miles Maskell was a New Zealand farmer, politician and entomologist.

Ramalina is a genus of greenish fruticose lichens that grow in the form of flattened, strap-like branches. Members of the genus are commonly called strap lichens or cartilage lichens. Apothecia are lecanorine.

John Evans Brown was a 19th-century Member of Parliament in New Zealand. Born in Pennsylvania, he came to New Zealand after spending time in Australia, where he was a farmer and US Consul. He farmed in Canterbury, where he was known as "Yankee" Brown. Three of his brothers in law, through his first wife, served as his fellow Members of Parliament. He married a second time, as his first wife died young, and moved back to the United States. On his father's land in Asheville, he came to considerable wealth due to the mining of mica.

Bemisia is a genus of whitefly in the family Aleyrodidae.

Monophlebidae is a family of scale insects commonly known as the giant scales or monophlebids. They occur in most parts of the world but more genera are found in the tropics than elsewhere.
Phenacoleachiidae is a family of scale insects commonly known as the phenacoleachiids. They are found only in the South Island of New Zealand, and on certain offshore islands. There are two species in a single genus.

Trigonospila brevifacies is a species of true fly in the family Tachinidae native to eastern Australia. This species is also found in New Zealand. Like the vast majority of tachinid flies, T. brevifacies is a parasitoid of other insects, specifically late larval stages of a number of species of Lepidoptera. It is also known as the Australian Leaf-Roller Fly or Leafroller Fly.

Batrachedra agaura is a species of moth in the family Batrachedridae. It is endemic to New Zealand. This species is distributed throughout the country. The species inhabits native forests, especially beech and kanuka forests or manuka scrubland. The larvae of this species are associated with sooty mold and sooty beech scale. It has been hypothesized that the larvae feed on sooty beech scale. However, they may also feed on the sooty mold itself. The adult female is lighter in appearance than the male, and the species shows considerable variation in patterns on the forewing. Adults are on the wing from October to February. They are nocturnal and occasionally attracted to light.

Callococcus is a genus of Australian scale insect that feeds on species of Leptospermum, Hypocalymma, Kunzea and some other members of the tribes Chamelaucieae and Leptospermeae in the myrtle family Myrtaceae. Callococcus leptospermi induces stem-swelling galls on some species of Leptospermum, and it is considered to be a potential biological control agent of Leptospermum laevigatum in South Africa. The other described species of Callococcus do not induce galls.

Ultracoelostoma assimile, commonly known as sooty beech scale, is a scale insect in the Margarodidae family. It is endemic to New Zealand. It was first described by William Miles Maskell in 1890.

Coelostomidiidae is a family of scales and mealybugs in the order Hemiptera. There are about 5 genera and 11 described species in Coelostomidiidae.
Callipappus is a genus of scale insects in the family Callipappidae in the order Hemiptera. There are five described species in the genus, all from Australia.
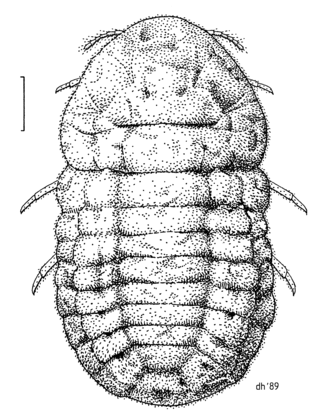
Coelostomidia zealandica is a scale insect endemic to New Zealand. The female is notably larger and very different in appearance from the small winged male.

















