
Skinks are lizards belonging to the family Scincidae, a family in the infraorder Scincomorpha. With more than 1,500 described species across 100 different taxonomic genera, the family Scincidae is one of the most diverse families of lizards. Skinks are characterized by their smaller legs in comparison to typical lizards and are found in different habitats except arctic and subarctic regions.

Eulamprus is a genus of lizards, commonly known as water skinks, in the subfamily Sphenomorphinae of the family Scincidae. The genus is native to Australia.
Nangura spinosa, the Nangur spiny skink or Nangur skink, is a lizard known from two patches of dry-rainforest in South East Queensland, Australia. It was formerly placed in the monotypic genus Nangura but was moved to Concinnia following the molecular phylogenetic studies of O'Connor & Moritz (2003) and Skinner and co-authors (2013). It was returned to Nangura in 2018. This species is known only from two localities; the type locality, now in Nangura National Park, and a much smaller isolated population in Oakview National Park and adjacent Oakview State Forest. The total distribution spans just 42 square kilometers, within which this species occupies less than 4 square kilometers, with an estimated population size of less than 200 individuals. It is threatened by invasive species including cats, pigs, dogs, foxes and cane toads, by the invasive plant species Lantana camara, which increases fire risk and changes forest structure, and in some sites by logging and road maintenance. Consequently, it is listed as critically endangered under the Australian Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 It resembles Gnypetoscincus queenslandiae in its spiny scales and like that species it is live bearing. Along with minor differences in scalation, the Nangur spiny skink differs from other Australian Sphenomorphid skinks in its karyotype of 2n=28 chromosomes, where most others have 2n=30. It is also unlike related species in that it lives in burrows, which occur in small colonies through the dry rainforest habitat. There is some indication of parental care in this species, with adults sharing burrows with juveniles.

The Bermuda skink, longnose skink, or Bermuda rock lizard is a critically endangered species and the only endemic land-living vertebrate of Bermuda. It is a relatively small skink : adults reach an average snout-to-vent length of about 8 cm (3.1 in).

Axel Johann Einar Lönnberg was a Swedish zoologist and conservationist. Lönnberg was born in Stockholm. He was head of the Vertebrate Department of the Naturhistoriska Riksmuseet from 1904 to 1933.
Carinascincus palfreymani, known commonly as the Pedra Branca skink, as well as the Palfreyman's window-eyed skink, the Pedra Branca cool-skink, or the red-throated skink, is a species of skink in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Australia, and is restricted to the windswept Pedra Branca, an island off southern Tasmania of only 2.5 ha, where it is dependent on the seabird colonies. It is the only lizard species found on the island.

The Seychelles skink also known as the Mangouya, is a species of skink in the family Scincidae. It is endemic to the Seychelles.

Carinascincus metallicus, the metallic cool-skink or metallic skink is a species of skink in the family Scincidae. It is endemic to Australia, found in southern Victoria, as well as in Tasmania where it is the most widespread and common lizard, occurring on many offshore islands in Bass Strait as well as the mainland. It gives birth to live young. It is highly variable in colour and pattern, and may be a complex of closely related species.

Eulamprus quoyii, more commonly known as the eastern water skink, eastern water-skink, or golden water skink, is a viviparous species of diurnal skink. Eulamprus quoyii belongs to the family Scincidae and is considered a common garden animal in Australia. The skink is endemic to Australia and found only along the east coast of the country. It makes its home in creekside habitats along the east coast of Australia and in urban garden areas with high amounts of moisture. The species can be identified by the twin, long yellow stripes that run along its body from the top of the eye, as well as by several more specific character derived states. The pale yellow dorsolateral stripes are most likely where its common name, the golden water skink, is derived. Like other ectotherms, the skink can often be seen basking in the sun on rocky outcroppings in order to regulate its body temperature. Its diet mainly consists of both aquatic and terrestrial insects, tadpoles and small amounts of plant matter. The skink both hunts for food and scavenges when necessary and is considered an opportunistic feeder. It is prey to larger lizards, snakes, cats and birds and so will often be seen moving quickly into hiding when other organisms are present.

Concinnia is a genus of skinks in the subfamily Lygosominae.

Sphenomorphinae is a large subfamily of skinks, lizards within the family Scincidae. The genera in this subfamily were previously found to belong to the Sphenomorphus group in the large subfamily Lygosominae.
The eastern crevice-skink is a species of large skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to eastern Australia.
The Eastern Ranges rock-skink is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to eastern Australia.

The lemon-barred forest-skink is a species of skink found in Queensland in Australia.
Concinnia frerei, also known commonly as the stout bar-sided skink or the stout barsided skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Queensland in Australia.

The dark barsided skink is a species of skink found in Queensland and New South Wales in Australia.
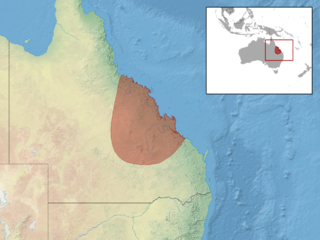
The stout barsided skink is a species of skink found in Queensland in Australia.

The bar-sided forest-skink or barred-sided skink is a species of skink found in New South Wales and Queensland in Australia.

The yellow-blotched forest-skink or rainforest water-skink is a species of skink found in Queensland in Australia.
The ghost skink is a species of skink endemic to Australia.














