
Passiflora edulis, commonly known as passion fruit, is a vine species of passion flower native to the region of southern Brazil through Paraguay to northern Argentina. It is cultivated commercially in tropical and subtropical areas for its sweet, seedy fruit.

Carpobrotus edulis is a ground-creeping plant with succulent leaves in the genus Carpobrotus, native to South Africa. Its common names include hottentot-fig, sour fig, ice plant, highway ice plant, or vygie.

The Aizoaceae, or fig-marigold family, is a large family of dicotyledonous flowering plants containing 135 genera and about 1,800 species. Several genera are commonly known as 'ice plants' or 'carpet weeds'. The Aizoaceae are also referred to as vygies in South Africa. Some of the unusual Southern African genera—such as Conophytum, Lithops, Titanopsis and Pleiospilos —resemble gemstones, rocks or pebbles, and are sometimes referred to as 'living stones' or 'mesembs'.

Boletus edulis is a basidiomycete fungus, and the type species of the genus Boletus. Widely distributed in the Northern Hemisphere across Europe, Asia, and North America, it does not occur naturally in the Southern Hemisphere, although it has been introduced to southern Africa, Australia, New Zealand, and Brazil. Several closely related European mushrooms formerly thought to be varieties or forms of B. edulis have been shown using molecular phylogenetic analysis to be distinct species, and others previously classed as separate species are conspecific with this species. The western North American species commonly known as the California king bolete is a large, darker-coloured variant first formally identified in 2007.
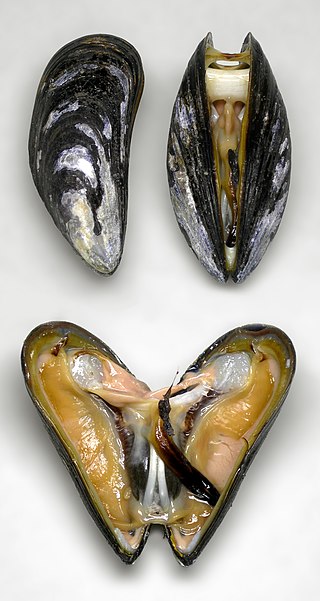
The blue mussel, also known as the common mussel, is a medium-sized edible marine bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae, the only extant family in the order Mytilida, known as "true mussels". Blue mussels are subject to commercial use and intensive aquaculture. A species with a large range, empty shells are commonly found on beaches around the world.

The Passifloraceae are a family of flowering plants, containing about 750 species classified in around 27 genera.

Pinus edulis, the Colorado pinyon, two-needle piñon, pinyon pine, or simply piñon, is a pine in the pinyon pine group native to the Southwestern United States, used for its edible pine nuts.

Heart of palm is a vegetable harvested from the inner core and growing bud of certain palm trees, most notably the coconut, juçara, açaí palm, palmetto, and peach palm. Heart of palm may be eaten on its own, and often it is eaten in a salad.

Ostrea edulis, commonly known as the European flat oyster, is a species of oyster native to Europe. In Great Britain and Ireland, regional names include Colchester native oyster, mud oyster, or edible oyster. In France, Ostrea edulis are known as huîtres plates except for those that come from the Belon River estuary in Brittany, France, which are known as Belons.

Inga is a genus of small tropical, tough-leaved, nitrogen-fixing trees and shrubs, subfamily Mimosoideae. Inga's leaves are pinnate, and flowers are generally white. Many of the hundreds of species are used ornamentally.

Dacryodes edulis is a fruit tree in the family Burseraceae native to Africa. Its various regional names include safou, messa, plum (Cameroon), atanga, ube, elumi/rukuki (Nigeria), African pear, bush pear, African plum, nsafu, bush butter tree, or butterfruit.

Inga edulis, known as ice-cream bean, ice-cream-bean, joaquiniquil, cuaniquilguama or guaba, is a fruit native to South America. It is in the mimosoid tribe of the legume family Fabaceae. It is widely grown, especially by Indigenous Amazonians, for shade, food, timber, medicine, and production of the alcoholic beverage cachiri. It is popular in Peru, Ecuador, Pernambuco-Brazil, Venezuela, Guyana and Colombia. The taxonomic name Inga is derived from its name with the Tupí people of South America (ingá) while the species name edulis is Latin for "edible". The common name "ice-cream bean" alludes to the sweet flavor and smooth texture of the pulp.

Aria edulis, the whitebeam or common whitebeam, is a species of deciduous tree in the family Rosaceae.

The Chilean mussel or Chilean blue mussel, Mytilus chilensis, is a species of blue mussel native to the coasts of Chile from Biobío Region to Cape Horn. Genomic evidence has confirmed that the native Chilean blue mussel is genetically distinct from the Northern Hemisphere M. edulis, M. galloprovincialis and M. trossulus and also genetically different from Mytilus platensis,the other species of smooth shelled mussel from South America.

Etiella zinckenella, the pulse pod borer moth, is a moth of the family Pyralidae. It is found in southern and eastern Europe and in the tropics and subtropics of Africa and Asia. They have also been introduced to North America and Australia. It is usually a minor pest for many legumes, but can be a serious pest.

Boletus pinophilus, commonly known as the pine bolete or pinewood king bolete, is a basidiomycete fungus of the genus Boletus found throughout Europe and western Asia. Described by Italian naturalist Carlo Vittadini in 1835, B. pinophilus was for many years considered a subspecies or form of the porcini mushroom B. edulis before genetic studies confirmed its distinct status. In 2008, B. pinophilus in western North America were reclassified as a new species, B. rex-veris. B. pinophilus is edible, and may be preserved and cooked.

Phyllostachys edulis, the mōsō bamboo, or tortoise-shell bamboo, or mao zhu, , is a temperate species of giant timber bamboo native to China and Taiwan and naturalised elsewhere, including Japan where it is widely distributed from south of Hokkaido to Kagoshima. The edulis part of the Latin name refers to its edible shoots. This bamboo can reach heights of up to 28 m (92 ft). This particular species of bamboo is the most common species used in the bamboo textile industry of China and other countries, for the production of rayon. Moso is less cold-hardy than many phyllostachys, surviving at a reduced height down to 5 degrees Fahrenheit (-15 °C).

Corixinae is a subfamily of aquatic bugs in the family Corixidae. There are at least 130 described species in Corixinae.
Corisella decolor is a species of water boatman in the family Corixidae. It is found in North America.
Processa edulis is a species of caridean shrimp found in shallow water in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It mostly inhabits seagrass beds and eelgrass flats, hiding by day and feeding at night. A common name for it is nika shrimp.


















