
Vetulicolia is a group of bilaterian marine animals encompassing several extinct species from the Cambrian, and possibly Ediacaran, periods. As of 2023, the majority of workers favor placing Vetulicolians in the stem group of the Chordata, but some continue to favor a more crownward placement as a sister group to the Tunicata. It was initially erected as a monophyletic clade with the rank of phylum in 2001, with subsequent work supporting its monophyly. However, more recent research suggests that vetulicolians may be paraphyletic and form a basal evolutionary grade of stem chordates.

The Maotianshan Shales (帽天山页岩) are a series of Early Cambrian sedimentary deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their Konservat Lagerstätten, deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shales form one of some forty Cambrian fossil locations worldwide exhibiting exquisite preservation of rarely preserved, non-mineralized soft tissue, comparable to the fossils of the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. They take their name from Maotianshan Hill in Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China.

Yunnanozoon lividum is an extinct species of bilaterian animal from the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang biota of Yunnan province, China. Its affinities have been long the subject of controversy.

Vetulicola is an extinct genus of marine animal discovered from the Cambrian of China. It is the eponymous member of the enigmatic phylum Vetulicolia, which is of uncertain affinities but may belong to the deuterostomes. The name was derived from Vetulicola cuneata, the first species described by Hou Xian-guang in 1987 from the Lower Cambrian Chiungchussu Formation in Chengjiang, China.

Pomatrum is an extinct vetulicolian, the senior synonym of Xidazoon; the latter taxon was described by Shu, et al. (1999) based on fossils found in the Qiongzhusi (Chiungchussu) Formation, Yu'anshan Member, Lower Cambrian, Haikou, (Kunming), about 50 km west of Chengjiang, China.

Didazoonidae is a vetulicolian family within the order Vetulicolata. It is charaterized by a relatively thin-walled, non-biomineralized body and a large, round anterior opening surrounded by an oral disc. It may be paraphyletic, even if the phylum Vetulicolia is monophyletic.

Ambulacraria, or Coelomopora, is a clade of invertebrate phyla that includes echinoderms and hemichordates; a member of this group is called an ambulacrarian. Phylogenetic analysis suggests the echinoderms and hemichordates separated around 533 million years ago. The Ambulacraria are part of the deuterostomes, a clade that also includes the many Chordata, and the few extinct species belonging to the Vetulicolia.

Deuterostomes are bilaterian animals of the superphylum Deuterostomia, typically characterized by their anus forming before the mouth during embryonic development. Deuterostomia is further divided into four phyla: Chordata, Echinodermata, Hemichordata, and the extinct Vetulicolia known from Cambrian fossils. The extinct clade Cambroernida is thought to be a member of Deuterostomia.

Banffozoa is an extinct class of bilaterians. Most workers place it in the Vetulicolia, but the protostome-like features of some members have motivated ongoing debate. Banffozoa consists of the order Banffiata as well as a dwarf "Form A" that has not been formally described or named. Skeemella has been placed incertae sedis in this class, but has more recently been placed with the Banffidae. Banffozoa may be paraphyletic even if Vetulicolia is monophyletic.
Archaeopriapulida is a group of priapulid worms known from Cambrian lagerstätte. The group is closely related to, and very similar to, the modern Priapulids. It is unclear whether it is mono- or polyphyletic. Despite a remarkable morphological similarity to their modern cousins, they fall outside of the priapulid crown group, which is not unambiguously represented in the fossil record until the Carboniferous. In addition to well-preserved body fossils, remains of several archaeopriapulid taxa are known to have been preserved primarily as organic microfossils, such as isolated scalids and pharyngeal teeth. They are probably closely related or paraphyletic to the palaeoscolecids; the relationship between these basal worms is somewhat unresolved.

The palaeoscolecids are a group of extinct ecdysozoan worms resembling armoured priapulids. They are known from the Lower Cambrian to the lower Ludfordian ; they are mainly found as disarticulated sclerites, but are also preserved in many of the Cambrian lagerstätten. They take their name from the typifying genus Palaeoscolex. Other genera include Cricocosmia from the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang biota. Their taxonomic affinities within Ecdysozoa have been the subject of debate.

Vetulicola cuneata is a species of extinct marine animal from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang biota of China. It was described by Hou Xian-guang in 1987 from the Lower Cambrian Chiungchussu Formation, and became the first animal under an eponymous phylum Vetulicolia.

Rotadiscus is a genus of discoidal animal known from the Cambrian Chengjiang biota and classified with the eldonioids.

Phlogites is a member of the extinct ambulacrarian stem group Cambroernida, occupying an intermediate position between the basal Herpetogaster and the more derived Eldonioidea. It is known from the Lower Cambrian Haikou Chengjiang deposits of China.

Vetulicola rectangulata is a species of extinct animal from the Early Cambrian of the Chengjiang biota of China. Regarded as a deuterostome, it has characteristic rectangular anterior body on which the posterior tail region is attached. It was described by Luo Huilin and Hu Shi-xue in 1999.

Cincta is an extinct class of echinoderms that lived only in the Middle Cambrian epoch. Homostelea is a junior synonym. The classification of cinctans is controversial, but they are probably part of the echinoderm stem group.

Beidazoon venustum is a deuterostome from the deuterostome group Vetulicolia. It originates from the lower Cambrian Chengjiang biota of Yunnan Province, China. Beidazoon was a marine organism discovered by Degan Shu in 2005.

Ctenocystoidea is an extinct clade of echinoderms, which lived during the Cambrian and Ordovician periods. Unlike other echinoderms, ctenocystoids had bilateral symmetry, or were only very slightly asymmetrical. They are believed to be one of the earliest-diverging branches of echinoderms, with their bilateral symmetry a trait shared with other deuterostomes. Ctenocystoids were once classified in the taxon Homalozoa, also known as Carpoidea, alongside cinctans, solutes, and stylophorans. Homalozoa is now recognized as a polyphyletic group of echinoderms without radial symmetry. Ctenocystoids were geographically widespread during the Middle Cambrian, with one species surviving into the Late Ordovician.

Banffidae is a family of extinct banffozoan animals from North America and China. It includes Banffia, Heteromorphus, and possibly Skeemella. The family may be paraphyletic. A Heteromorphus-like dwarf "Form A" is allied with this group at the class level, but has not been formally described or assigned to this family.
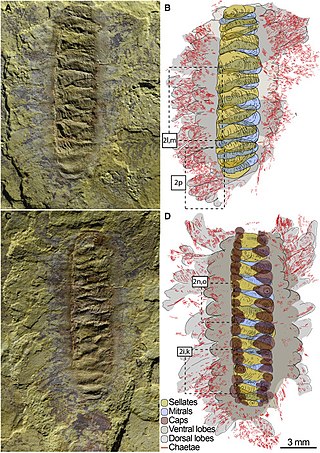
Wufengella is a genus of extinct camenellan "tommotiid" that lived during the Early Cambrian. Described in 2022, the only species Wufengella bengtsonii was discovered from the Maotianshan Shales of Chiungchussu (Qiongzhusi) Formation in Yunnan, China. The fossil indicates that the animal was an armoured worm that close to the common ancestry of the phyla Phonorida, Brachiozoa and Bryozoa, which are collectively grouped into a clade called Lophophorata.




















