
Sozopol is an ancient seaside town located 35 km south of Burgas on the southern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. Today it is one of the major seaside resorts in the country, known for the Apollonia art and film festival that is named after one of the town's ancient names.

Bithynia was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor, adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwest, Paphlagonia to the northeast along the Pontic coast, and Phrygia to the southeast towards the interior of Asia Minor.

Heraclea Pontica, known in Byzantine and later times as Pontoheraclea, was an ancient city on the coast of Bithynia in Asia Minor, at the mouth of the river Lycus. It was founded by the Greek city-state of Megara in approximately 560–558 BC and was named after Heracles who the Greeks believed entered the underworld at a cave on the adjoining Archerusian promontory. The site is now the location of the modern city Karadeniz Ereğli, in the Zonguldak Province of Turkey.

Prusias I Cholus was a king of Bithynia, who reigned from c. 228 to 182 BC.
Comana Pontica, was an ancient city located in ancient Pontus, now in modern Turkey.
La Fée Absinthe is a brand of absinthe; a highly alcoholic, distilled spirit containing the herb wormwood. La Fée Absinthe was created by Green Utopia, which is owned and run by George Rowley.

The Yeşilırmak is a river in northern Turkey. From its source northeast of Sivas, it flows past Tokat and Amasya, crosses the Pontic Mountains and the Çarşamba Plain, reaching the Black Sea east of Samsun after 418 km (260 mi).

Ladik is a city of Samsun Province, Turkey on the site of the ancient Laodicea Pontica. The mayor is Selim Özbalci (AKP).

The Diocese of Pontus was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of northern and northeastern Asia Minor up to the border with the Sassanid Empire in Armenia. The diocese was established after the reforms of Diocletian, and its vicarius, headquartered at Amaseia, was subordinate to the Praetorian prefecture of the East. Its military forces, facing the Sassanid threat, were commanded by the dux Ponti et Armeniae until the middle of the 5th century, and by two separate duces afterwards, until Justinian I instituted a new magister militum per Armeniam for the Armenian frontier. Justinian's reforms also abolished the diocese in 535, and its vicar was made into the governor of Galatia I. The results however were not satisfactory, and the diocese was reestablished in 548, continuing to function until replaced by the themata of Armeniakon and Opsikion in the later 7th century. On the north east shore of the Black Sea, the cities Nitike, Pitiyus, and Dioscurias were part of the diocese until the 7th century. The diocese included 12 provinces: Bithynia, Honorias, Paphlagonia, Helenopontus, Pontus Polemoniacus, Galatia I and Galatia II (Salutaris), Cappadocia I and Cappadocia II, Armenia I, Armenia II, Armenia Maior and the autonomous Armenian principalities (Satrapiae) in the area of Sophene. In 536, Armenia III and Armenia IV were created.
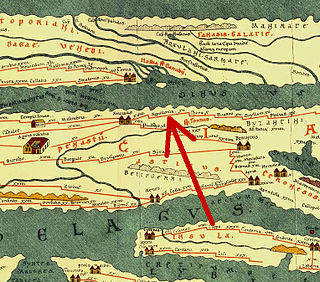
Via Pontica was an ancient Roman road in Thrace along the Black Sea, starting from Byzantium and passing through Deultum, Aquae Calidae, Apollonia, Mesembria, Odessos, Byzone, and Kaliakra ; and then through Kallatis, Tomis, and Istros.

Craniophora ligustri, the coronet, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. It is found in Europe, through the Palearctic to Japan.

Craniophora is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae.

Eteobalea intermediella is a moth of the family Cosmopterigidae. It is native to an area ranging from Central and Southern Europe, east to the Caucasus, Asia Minor, the Near and Middle East towards Central Asia. It is also present in North Africa. It has been introduced to the United States and Canada.

Craniophora harmandi is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in Japan, They emerge as adults between June and September in Japan. Nepal, and the western Himalaya to Taiwan "in the region with monsoonic influence."

Craniophora fujianensis is a moth of the family Noctuidae, named for the Fujian province where it was discovered in 2004. The species is found in Fujian and Hainan Provinces in China, but the nominate subspecies is found only in Fujian, and subspecies C. f. hainanensis is restricted to Hainan.

Craniophora praeclara is a moth of the family Noctuidae. Its distribution includes North Korea, Japan, China, and the Russian Far East.

The siege of Theodosia in 389 BC was the first of three sieges carried out against the city of Theodosia by the rulers of the Bosporan Kingdom, who attempted time and time again to annex the city to their dominions during the long Bosporan-Heracleote War. The first of these sieges was carried out by Satyros I, the father of Leukon I.

Craniophora fasciata is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Frederic Moore in 1884. It is found in Sri Lanka, Japan, Korea, Taiwan, Thailand and Australia.
Dia, also Diospolis (Διόσπολις), was a port city of ancient Bithynia on the Pontus Euxinus in Asia Minor. Marcian of Heraclea places it 60 stadia east of the mouth of the Hypius, which river is between the Sangarius River and Heraclea Pontica. The name in Marcian, Diaspolis, may be a mistake for Diospolis, which Ptolemy has. There are some very rare coins with the epigraph Dias (Διας), which Sestini assigns to this place.
Metroon, also called Aulia. was a town on the Black Sea coast of ancient Bithynia, described by Arrian as 80 stades east of Heraclea Pontica.















