Related Research Articles
Nepal is a landlocked country where transportation is difficult due to the mountainous terrain. Modern transportation in Nepal has just started in the 20th century.
The Trans-Asian Railway(TAR) is a project to create an integrated freight railway network across Europe and Asia. The project is of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP).

Pakistan Railways is the national, state-owned railway company of Pakistan with its headquarters in Lahore. Founded in 1861 as the North Western State Railway and headquartered in Lahore, it owns 7,789 kilometres of operational track across Pakistan, stretching from Peshawar to Karachi, offering both freight and passenger services, covering 488 operational stations across Pakistan.

Biratnagar is a metropolitan city in Nepal, which serves as the capital of Koshi Province. With a Metropolitan Urban Agglomeration population of 244,750 as per the 2021 census, it is the largest city and fastest growing city in the province and also the headquarters of Morang district. As per the preliminary report of 2022 Nepal census, Biratnagar Metropolitan has an estimated city population of 243,927 excluding the suburban areas which are now very well connected to the old town. It is the administrative center of the Greater Birat Development Area which incorporates the cities of Biratnagar and its suburbs and towns of-Itahari-Gothgau-Biratchowk-Dharan primarily located on the Koshi Highway in Eastern Nepal, with an estimated total urban agglomerated population of 804,300 people in 159,332 households including the town of Ithari. Biratnagar is located 399 km (248 mi) east of the capital, Kathmandu, and 6 km (3.7 mi) north of the bordering town of Jogbani in the Indian state of Bihar. It is one of the major entry point in Nepal for Businessmen as well as Tourists who come to visit Nepal for various purposes.

Birgunj is a metropolitan city in Parsa District in Madhes Pradesh in southern Nepal. It lies 135 km (84 mi) south of the capital Kathmandu, attached in the north to Raxaul on the border of the Indian state of Bihar. As an entry point to Nepal from Patna, Birganj is known as the "Gateway of Nepal". It is also called the "Commercial Capital of Nepal". The town has significant economic importance for Nepal as most of the trade with India is via Birganj and the Indian town of Raxaul. The Tribhuvan Highway links Birgunj to Nepal's capital, Kathmandu.

Raxaul is a sub-divisional town in the East Champaran district of the Indian state of Bihar. It is situated at the India-Nepal border with Birgunj city (Nepal). Raxaul is a major railway junction.
The Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region is a Government of India ministry, established in September 2001, which functions as the nodal Department of the Central Government to deal with matters related to the socio-economic development of the eight States of Northeast India: Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura and Sikkim. It acts as a facilitator between the Central Ministries/ Departments and the State Governments of the North Eastern Region in the economic development including removal of infrastructural bottlenecks, provision of basic minimum services, creating an environment for private investment and to remove impediments to lasting peace and security in the North Eastern Region.

Janakpurdham or Janakpur, is a capital city of Madhesh Province. This sub-metropolitan city is a central hub for Maithili language, religious and cultural tourism in Nepal.

Mahendra Highway or NH01, also called East-West Highway, runs across the Terai geographical region of Nepal, from Mechinagar in the east to Bhim Datta in the west, cutting across the entire width of the country. It is the longest highway in Nepal and was constructed in cooperation with various countries. The highway is named after King Mahendra Shah.

The Nepal Railway Company Ltd., reporting mark: NRW / ने. रे) is a state-owned company under Department of Railways (DORW) which operates passenger train services in Nepal. It is the only train service provider in the country. Currently it operates passenger transport service on the 52 kilometres (32 mi) line from Jainagar, India to Bhangaha, Nepal. It is sort of equivalent to the Sajha Yatayat for road transportation.
Gede is the last railway station on the Indian side of the Bangladesh–India border in Krishnaganj CD Block in Nadia district in the Indian state of West Bengal. The corresponding station on the Bangladesh side is Darshana. It is the terminal station on the Sealdah–Gede section of Kolkata Suburban Railway system. There is a border checkpoint at Gede.
Mahisasan is a border railway station and a defunct railway transit facility point on the India–Bangladesh border in Karimganj district in the Indian state of Assam. The corresponding station on the Bangladesh side is Shahbajpur in Sylhet District. The border station is linked to Karimganj 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) away. The Mahisasan–Shahbajpur route has not been operational since December, 1996 due to lack of traffic.

The Nepal Government Railway (NGR) was Nepal's first railway. Established in 1927 and closed in 1965, it linked Amlekhganj with Raxaul across the border in India in the south. The 2 ft 6 in narrow gauge railway was 47 km long.

Adapur is a block in East Champaran district of Bihar, India. Adapur railway station is located 40 kilometres (25 mi) north of Motihari, the district headquarters. The state capital Patna is 175 kilometres (109 mi) in south. Adapur is located on the India - Nepal border. There are many villagers Near Adapur town peoples come to buy their daily essential things.
The China–Nepal Railway is a planned railway between China and Nepal. The railway will link Kathmandu with Shigatse, Tibet, crossing the China–Nepal border at Gyirong–Rasuwa.

The India–Nepal border is an open international boundary running between the republics of India and Nepal. The 1,751 km (1,088.02 mi) long border includes the Himalayan territories as well as Indo-Gangetic Plain of the subcontinent. The current border was delimited after the Sugauli treaty of 1816 between Nepal and the British Raj. Following Indian independence, the prevailing border was recognised as the international border between the Kingdom of Nepal and the Dominion of India.

Department of Railways under Ministry of Physical Infrastructure and Transport is the authority to develop, maintain and plan railways in Nepal. It has its headquarter at Bishalnagar, Kathmandu. Currently it maintains three in-operation railway lines in the country: Raxaul–Sirsiya, Jainagar–Bhangaha and Bathnaha-Budhnagar. It is equivalent to Department of Road for road infrastructure. It has several lines planned.
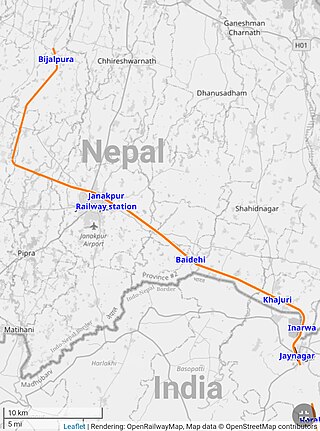
The Jaynagar–Janakpur–Bardibas railway line is a cross-border railway line between India and Nepal. The railway links Bijalpura with Jaynagar, crossing the India–Nepal border near Inarwa. An extension to Bardibas is being constructed. The line began as a 2 ft 6 in freight railway in 1937, and subsequently became a passenger railway. It closed in 2014 to allow it to be converted to 5 ft 6 in broad gauge, and reopened in 2022. At that time it was the only operational passenger railway line in Nepal.

The Raxaul–Kathmandu railway line is a proposed cross-border railway between India and Nepal. The governments of India and Nepal had issued a joint statement on expanding rail linkages with India's financial support, connecting the border city of Raxaul in India to Kathmandu in Nepal. Nepal signed a memorandum of understanding with India to prepare a detailed project report for a proposed railway linking the two towns, with an estimated cost around US$3 billion.
North Eastern Railway Connectivity Project is an multi phased railway connectivity project in Northeast India which comprises states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura and it also includes the state of Sikkim. These states come under Northeast Frontier Railway Zone of Indian Railways. This Railway project is considered as strategically important for India because it connects all the border states in this region and also close to ASEAN countries.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Starting of freight trains via restored Haldibari (India) – Chilahati (Bangladesh) rail link". pib.gov.in. Retrieved 2022-07-05.
- 1 2 3 4 "Assam as India's Gateway to ASEAN" (PDF). Asian Development Bank.
- ↑ "Rail Links with Bangladesh". www.pib.gov.in. Retrieved 2022-07-05.
- ↑ Chatterjee, Pradyot Kumar. "Trans-Asian rail connectivity: South Asian perspective". The Pioneer. Retrieved 2022-07-05.
- ↑ "Deuba, Modi flag off Kurtha-Jayanagar railway from Delhi". kathmandupost.com. Retrieved 2023-01-27.
- ↑ "India- Nepal railway service: The projects, route, cost in 10 points". The Times of India. April 1, 2022. Retrieved 2023-01-27.
- ↑ "Nepal, India sign accord on Kathmandu-Raxaul railway". kathmandupost.com. Retrieved 2023-01-27.
- ↑ "India And Nepal To Speed Up Raxaul-Kathmandu Rail Project". NDTV.com. Retrieved 2023-01-27.
- ↑ "India-Nepal to Get Closer, Thanks to New Railway Link and Inland Waterways!". The Better India. 2018-04-09. Retrieved 2023-01-27.
- ↑ "Biratnagar-Bathnah freight train to come into operational within two weeks". My Republica. Retrieved 2023-01-27.
- ↑ Shah, Narendra (2021-04-08). "IRCON invites tender for civil works at Biratnagar Station on Jogbani (India) to Biratnagar (Nepal) Railway Line". Metro Rail News. Retrieved 2023-01-27.
- ↑ "गोरखपुर से नेपाल जाना होगा आसान, सोनौली-भैरहवा रेल लाइन को मिली मंजूरी". Amar Ujala (in Hindi). Retrieved 2023-01-27.
- ↑ "Strengthening Indo-Nepal trade ties with improved connectivity". ThePrint. 2022-03-29. Retrieved 2023-01-27.