
Raúl Modesto Castro Ruz is a Cuban politician who is currently serving as the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba, the most senior position in the socialist state, succeeding his brother Fidel Castro in April 2011. He has also been a member of the Politburo of the Communist Party of Cuba, the highest decision-making body since 1975. In February 2008, he was appointed the President of the Council of State and President of the Council of Ministers. He stepped down as President on 19 April 2018, but remains the first secretary of the Communist Party, holding ultimate power and authority over state and government.

Even before attaining its independence from Spain, Cuba had several constitutions either proposed or adopted by insurgents as governing documents for territory they controlled during their war against Spain. Cuba has had several constitutions since winning its independence. The current constitution was drafted in 1976 and has since been amended. Cuba is, in 2018, engaged in a major revision of its Constitution, and the revisions are being widely discussed by the people and by academics.

Elections in Portugal gives information on election and election results in Portugal.

Elections in Cuba involve nomination of municipal candidates by voters in nomination assemblies, nomination of provincial and national candidates by candidacy commissions, voting by secret ballot, and recall elections. Cuba is a one-party state with the Communist Party of Cuba as the "leading force of society and of the state" under the national constitution, although elections are nominally non-partisan.

A constitutional referendum was held in Bolivia on 25 January 2009, postponed from the initially planned dates of 4 May 2008 and then 7 December 2008. Drafted by the Constituent Assembly in 2007, the new constitution was approved in the referendum according to an exit poll by Ipsos Apoyo for La Razón and ATB, a Bolivian television network. Furthermore, it required early elections to be held on 6 December 2009.

On 30 September 2007 an election for a Constituent Assembly was held in Ecuador following the referendum on this issue successfully held on 15 April 2007. 130 delegates were elected: 24 members from national lists, 100 representing the provinces and six for emigrants living outside Ecuador.

A constitutional referendum was held in Ecuador on 28 September 2008 to ratify or reject the constitution drafted by the Ecuadorian Constituent Assembly elected in 2007. The new constitution was approved by 69% of voters.
The Ecuadorian Constituent Assembly was a 2007–2008 constitutional assembly in Ecuador, which drafted the 2008 Constitution of Ecuador, approved via the Ecuadorian constitutional referendum, 2008.
François Ibovi is a Congolese politician who held a succession of key posts in the government of Congo-Brazzaville beginning in 1997. Closely associated with President Denis Sassou Nguesso, he was Minister of Communication from 1997 to 2002, Minister of Territorial Administration from 2002 to 2007, First Vice-President of the National Assembly from 2007 to 2012, and Minister of Health from 2012 to 2016.
A parliamentary election to the National Assembly of People's Power was held in Cuba on 20 January 2008. According to the Cuban electoral system, one candidate was nominated for each of the 614 seats in the Assembly, and candidates were elected if they received at least 50% of the vote. The candidates are otherwise proposed by nominating assemblies, which comprise representatives of workers, youth, women, students and farmers as well as members of the Committees for the Defense of the Revolution, after initial mass meetings soliciting a first list of names. The final list of candidates is drawn up by the National Candidature Commission taking into account criteria such as candidates' merit, patriotism, ethical values and revolutionary history.
Prensa Latina, legal name Agencia de Noticias Latinoamericana S.A., is the official state news agency of Cuba, founded in March 1959 shortly after the Cuban Revolution.

An indirect presidential election was held in Cuba on 24 February 2008, in which the National Assembly of People's Power elected a new President of Cuba and the members of the Council of State. The election followed the January 2008 parliamentary election. In the election, Raúl Castro, who had been Acting President since July 2006, was elected as President, succeeding his older brother, Fidel Castro.
José Ramón Machado Ventura, M.D. is a Cuban revolutionary and politician who was the First Vice President of the Council of State of Cuba from 2008 to 2013. With the election of Raúl Castro as President of Cuba on 24 February 2008, Machado was elected to succeed him as First Vice President. He has been Second Secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba since 2011.
Cuban-Pacific relations are diplomatic, economic, cultural and other relations between the Republic of Cuba and countries situated in Oceania. In the 2000s, Cuba has been strengthening its relations with Pacific nations, which have, for the most part, responded favourably to Cuban medical aid in particular. The first Cuba-Pacific Islands ministerial meeting was held in September 2008 in Havana, with government members from ten Pacific countries—Kiribati, Tuvalu, Nauru, Solomon Islands, Fiji, Tonga, Vanuatu, Samoa, the Federated States of Micronesia and Papua New Guinea—attending. The meeting was a consolidation rather than a starting point of Cuban-Pacific relations.
Alejandro Castro Espín is a Cuban political and military figure. He has the rank of colonel in the Interior Ministry of Cuba. He is the only son of Raúl Castro, the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba, and Vilma Espín, one of the main leaders of the Cuban Revolution; he is a nephew of Fidel Castro.
Indirect parliamentary elections were held in Cuba on 28 December 1981.

The Cuban Revolution was not only fought by armed rebels on the battlefield but also through the propaganda campaigns designed and orchestrated by Fidel Castro and his rebel comrades. Propaganda in Cuba during revolution included Castro's use of personal interviews with journalists, radio broadcasts and publicity seeking operations that contributed significantly to the victory of the rebels over Fulgencio Batista's and provided insight into the successful propaganda campaign established by Castro after gaining power. The limited yet successful revolutionary propaganda apparatus transitioned into what Castro has called "one of the most potent weapons in his foreign policy arsenal." Today the Cuban government maintains an intricate propaganda machine that includes a global news agency, magazines, newspapers, broadcasting facilities, publishing houses, front groups, and other miscellaneous organizations that all stem from the modest beginnings of Castro's revolutionary propaganda machine.

Parliamentary elections were held in Cuba on 11 March 2018 to elect members of the National Assembly of People's Power, alongside provincial elections. Prior to the elections, President Raúl Castro declared he would not be seeking a new term, and a new President of the Council of State will be elected by the National Assembly. His deputy, Miguel Díaz-Canel, was subsequently elected as the new president. However, Castro remained the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba, the most senior position in the country.
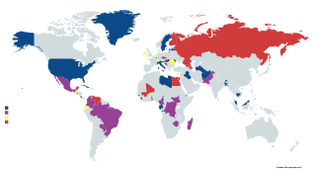
This national electoral calendar for the year 2018 lists the national/federal direct elections to be held in 2018 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included. Specific dates are given where they have been known.










