| Administrative divisions of Cuba | |
|---|---|
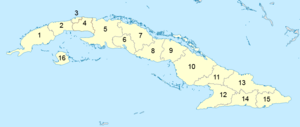 Provinces (1–15) and special municipality (16) of Cuba | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | Republic of Cuba |
| Number | 15 provinces 1 special municipality |
| Populations | 81,486 (Isla de la Juventud) – 2,130,517 (La Habana) |
| Areas | 281.18 square miles (728.3 km2) (La Habana) – 5,951.31 square miles (15,413.8 km2) (Camagüey Province) |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |
Administratively, Cuba is divided into 15 provinces and one special municipality (the Isla de la Juventud). The current structure has been in place since August 2010, when the then-La Habana Province was divided into Artemisa Province and Mayabeque Province.


