Telecommunications in Bulgaria include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
Telecommunications in Cameroon include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
Telecommunications in the Dominican Republic include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
Telecommunications in Kuwait provides information about the telephone, Internet, radio, and television infrastructure in Kuwait.

Mass media in Mexico are regulated by the Secretariat of Communication and Transportation, a federal executive cabinet ministry and by the Federal Telecommunications Institute.
Telecommunications in Nicaragua include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
The People's Republic of China possesses a diversified communications system that links all parts of the country by Internet, telephone, telegraph, radio, and television. The country is served by an extensive system of automatic telephone exchanges connected by modern networks of fiber-optic cable, coaxial cable, microwave radio relay, and a domestic satellite system; cellular telephone service is widely available, expanding rapidly, and includes roaming service to foreign countries. Fiber to the x infrastructure has been expanded rapidly in recent years.
Telecommunications in Peru include radio and television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
Telecommunications in Rwanda include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
Telecommunications is one of the most modern, diverse and fast-growing sectors in the economy of Ukraine. Unlike country's dominating export industries, the telecommunications, as well as the related Internet sector, remain largely unaffected by the global economic crisis, ranking high in European and global rankings.
Communications in the United States Virgin Islands
Telecommunications in Yemen provides information about the telephone, Internet, radio, and television infrastructure in Yemen.

Telecommunications in Armenia involves the availability and use of electronic devices and services, such as the telephone, television, radio or computer, for the purpose of communication. The various telecommunications systems found and used in Armenia includes radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the internet.
Telecommunications in Bahrain are provided by the Bahrain Telecommunications Company, trading as Batelco, as well as other companies such as Zain and Stc Bahrain.

Empresa de Telecomunicaciones de Cuba S.A. is the Cuban state company that provides telephony and communications services in Cuba. It is the sole lawful provider of telephony and telecommunications permitted by the Cuban penal code, constituting a communications state monopoly that has 8 million clients, both national and foreign.
Telecommunications in Panama includes radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
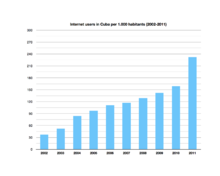
The internet in Cuba covers telecommunications in Cuba including the Cuban grassroots wireless community network and Internet censorship in Cuba.
Telecommunications in Angola include telephone, radio, television, and the Internet. The government controls all broadcast media with a nationwide reach.
Telecommunications in Ivory Coast include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
Telecommunications in Costa Rica include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.