Proportional representation (PR) characterizes electoral systems in which divisions in an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. If n% of the electorate support a particular political party, then roughly n% of seats will be won by that party. The essence of such systems is that all votes contribute to the result - not just a plurality, or a bare majority. The most prevalent forms of proportional representation all require the use of multiple-member voting districts, as it is not possible to fill a single seat in a proportional manner. In fact, the implementations of PR that achieve the highest levels of proportionality tend to include districts with large numbers of seats.
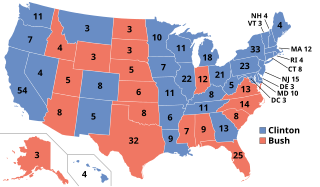
The 1992 United States presidential election was the 52nd quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 3, 1992. Democratic Governor Bill Clinton of Arkansas defeated incumbent Republican President George H. W. Bush, independent businessman Ross Perot of Texas, and a number of minor candidates.
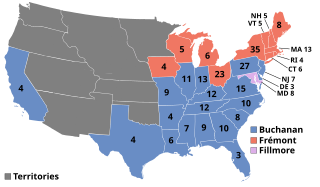
The United States presidential election of 1856 was the 18th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 1856. In a three-way election, Democrat James Buchanan defeated Republican nominee John C. Frémont and American Party nominee Millard Fillmore.

The 1860 United States presidential election was the nineteenth quadrennial presidential election to select the President and Vice President of the United States. The election was held on Tuesday, November 6, 1860. In a four-way contest, the Republican Party ticket of Abraham Lincoln and Hannibal Hamlin emerged triumphant. The election of Lincoln served as the primary catalyst of the American Civil War.
A primary election is the process by which voters, either the general public or members of a political party, can indicate their preference for a candidate in an upcoming general election or by-election, thus narrowing the field of candidates.

The Election for the 6th Legislative Yuan (第六屆立法委員選舉) of Taiwan was held on December 11, 2004. All 225 seats of the Legislative Yuan were up for election: 168 elected by popular vote, 41 elected on the basis of the proportion of nationwide votes received by participating political parties, eight elected from overseas Chinese constituencies on the basis of the proportion of nationwide votes received by participating political parties, eight elected by popular vote among the aboriginal populations. Members served three-year terms beginning on February 1, 2005, and ending January 31, 2008. The next term served four years.

Elections in the United States are held for government officials at the federal, state, and local levels. At the federal level, the nation's head of state, the President, is elected indirectly by the people of each state, through an Electoral College. Today, these electors almost always vote with the popular vote of their state. All members of the federal legislature, the Congress, are directly elected by the people of each state. There are many elected offices at state level, each state having at least an elective Governor and legislature. There are also elected offices at the local level, in counties, cities, towns, townships, boroughs, and villages. According to a study by political scientist Jennifer Lawless, there were 519,682 elected officials in the United States as of 2012.
Regular elections in Croatia are mandated by the Constitution and legislation enacted by Parliament. The presidency, Parliament, county prefects and assemblies, city and town mayors, and city and municipal councils are all elective offices. Since 1990, five presidential elections have been held. During the same period, nine parliamentary elections were also held. In addition, there were six nationwide local elections. Croatia has held two elections to elect 11 members of the European Parliament following its accession to the EU on 1 July 2013.

Elections in Cuba involve nomination of municipal candidates by voters in nomination assemblies, nomination of provincial and national candidates by candidacy commissions, voting by secret ballot, and recall elections. Cuba is a one-party state with the Communist Party of Cuba as the "leading force of society and of the state" under the national constitution, although elections are nominally non-partisan.

Elections in Jordan are for the lower house, known as the House of Representatives, of the bicameral parliament of Jordan, as well as for local elections. They take place within a political system where the King has extensive legislative and executive powers, retaining ultimate political control. The Prime Minister is selected by the King, the PM is then free to choose his own Cabinet. The parliament has quotas: three seats for Circassians and Chechens, nine for Christians and fifteen for women. The electoral system favours rural tribes and those of East Bank origin over urban areas that are primarily inhabited by those of Palestinian descent.

Elections in Lithuania gives information on elections and election results in Lithuania.

Parliamentary elections were held in Zimbabwe on 31 March 2005 to elect members to the Zimbabwe House of Assembly. All of the 120 elected seats in the 150-seat House of Assembly were up for election.
Welsh Labour is the part of the United Kingdom Labour Party that operates in Wales. Labour is the largest and most successful political party in modern Welsh politics, having won the largest share of the vote at every UK General Election since 1922, every Welsh Assembly election since 1999, and each European Parliament election from 1979 until 2004, as well as the 2014 one.

The 2000 United States presidential election in Florida took place on November 7, 2000, as part of the nationwide presidential election. Florida, a swing state, had a major recount dispute that took center stage in the election. The outcome of the 2000 United States presidential election was not known for more than a month after balloting because of the extended process of counting and recounting Florida's presidential ballots. State results tallied on election night gave 246 electoral votes to Republican nominee Texas Governor George W. Bush and 255 to Democratic nominee Vice President Al Gore, with New Mexico (5), Oregon (7), and Florida (25) too close to call that evening. Gore won New Mexico and Oregon over the following few days, but the result in Florida would have been decisive however those two states had voted.

The Conservative and Unionist Party, also known as Northern Ireland Conservatives is a section of the United Kingdom's Conservative Party that operates in Northern Ireland. The party won 0.4% of the vote in the Northern Ireland Assembly election, 2016, and 0.3% of the vote in the Northern Ireland Assembly election, 2017.

The election of president and vice president of the United States is an indirect election in which citizens of the United States who are registered to vote in one of the 50 U.S. states or in Washington, D.C. cast ballots not directly for those offices, but instead for members of the U.S. Electoral College, known as electors. These electors then in turn cast direct votes, known as electoral votes, for president, and for vice president. The candidate who receives an absolute majority of electoral votes is then elected to that office. If no candidate receives an absolute majority of the votes for President, the House of Representatives chooses the winner; if no one receives an absolute majority of the votes for Vice President, then the Senate chooses the winner.

The Communist Party of Britain is a communist and Marxist–Leninist political party organised in Great Britain. The party emerged from a dispute between Eurocommunists and Marxist-Leninists in the Communist Party of Great Britain in 1988.
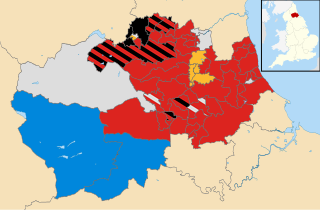
An election to Durham County Council took place on 2 May 2013 as part of the United Kingdom local elections, 2013. Following a boundary review, 126 councillors were elected from 63 electoral divisions which returned either one, two or three councillors each by first-past-the-post voting for a four-year term of office. The previous election took place in 2008 in advance of the council becoming a unitary authority after the 2009 changes to local government. The election saw the Labour Party increase their majority on the council.

The Socialist Party is a Trotskyist political party in England and Wales which adopted its current name in 1997 after being formerly known as Militant, an entryist group in the Labour Party from 1964 until it abandoned that tactic in 1991. The party stands under the electoral banner of the Trade Unionist and Socialist Coalition (TUSC).




















