
Salmon is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera Salmo and Oncorhynchus of the family Salmonidae, native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (Salmo) and North Pacific (Oncorhynchus) basins. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, char, grayling, whitefish, lenok and taimen, all coldwater fish of the subarctic and cooler temperate regions with some sporadic endorheic populations in Central Asia.

Trout is a generic common name for numerous species of carnivorous freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the genera Oncorhynchus, Salmo and Salvelinus, all of which are members of the subfamily Salmoninae in the family Salmonidae. The word trout is also used for some similar-shaped but non-salmonid fish, such as the spotted seatrout/speckled trout.

In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist guest (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms, cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, or a bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner.

Mayflies are aquatic insects belonging to the order Ephemeroptera. This order is part of an ancient group of insects termed the Palaeoptera, which also contains dragonflies and damselflies. Over 3,000 species of mayfly are known worldwide, grouped into over 400 genera in 42 families.

Diphyllobothrium is a genus of tapeworms which can cause diphyllobothriasis in humans through consumption of raw or undercooked fish. The principal species causing diphyllobothriasis is D. latum, known as the broad or fish tapeworm, or broad fish tapeworm. D. latum is a pseudophyllid cestode that infects fish and mammals. D. latum is native to Scandinavia, western Russia, and the Baltics, though it is now also present in North America, especially the Pacific Northwest. In Far East Russia, D. klebanovskii, having Pacific salmon as its second intermediate host, was identified.
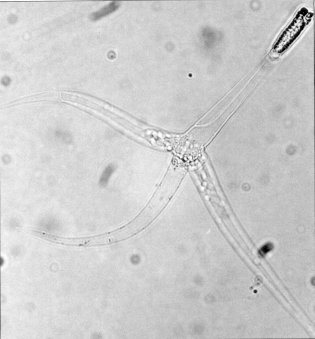
Myxobolus cerebralis is a myxosporean parasite of salmonids that causes whirling disease in farmed salmon and trout and also in wild fish populations. It was first described in rainbow trout in Germany in 1893, but its range has spread and it has appeared in most of Europe, the United States, South Africa, Canada and other countries from shipments of cultured and wild fish. In the 1980s, M. cerebralis was found to require a tubificid oligochaete to complete its life cycle. The parasite infects its hosts with its cells after piercing them with polar filaments ejected from nematocyst-like capsules. This infects the cartilage and possibly the nervous tissue of salmonids, causing a potentially lethal infection in which the host develops a black tail, spinal deformities, and possibly more deformities in the anterior part of the fish.
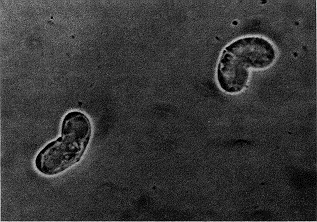
Ceratonova shasta is a myxosporean parasite that infects salmonid fish on the Pacific coast of North America. It was first observed at the Crystal Lake Hatchery, Shasta County, California, and has now been reported from Idaho, Oregon, Washington, British Columbia and Alaska.

Sea lice are copepods of the family Caligidae within the order Siphonostomatoida. They are marine ectoparasites that feed on the mucus, epidermal tissue, and blood of host fish. The roughly 559 species in 37 genera include around 162 Lepeophtheirus and 268 Caligus species.

The common river galaxias or Canterbury galaxias is a galaxiid fish of the genus Galaxias, found only in Canterbury, New Zealand.

A gapeworm, also known as a red worm and forked worm, is a parasitic nematode worm that infects the tracheas of certain birds. The resulting disease, known as "gape", occurs when the worms clog and obstruct the airway. The worms are also known as "red worms" or "forked worms" due to their red color and the permanent procreative conjunction of males and females. Gapeworms are common in young, domesticated chickens and turkeys.
Gyrinicola batrachiensis are nematode parasites that are members of the order Oxyurida. Members of this order are also known as pinworms. These organisms are nematodes that feed on micro-particles in the gut of vertebrates and invertebrates. Oxyurida is further separated into two superfamilies: Oxyuroidea and Thelastomatoidea, which are parasites of vertebrates and invertebrates respectively. Oxyuroidea is composed on three families: Pharyngodonidae; parasites of herbivorous vertebrates, and Oxyuridae and Heteroxynematidae; parasites of mammals and some birds.
Trichostrongylus tenuis, also known as the strongyle worm, is a gut nematode found in the United Kingdom, sensitive to Pyrantel pamoate. Larvae have a short migration inside the mucosa of the intestine and return quickly to the digestive tract.

Nanophyetus salmincola is a food-borne intestinal trematode parasite prevalent on the Pacific Northwest coast. The species may be the most common trematode endemic to the United States.

Linguatula serrata is a species of cosmopolitan zoonotic parasite, belonging to the tongueworm order Pentastomida. They are wormlike parasites of the respiratory systems of vertebrates. They live in the nasopharyngeal region of mammals. Cats, dogs, foxes, and other carnivores are normal hosts of this parasite. Apparently, almost any mammal is a potential intermediate host.

The aquaculture of salmonids is the farming and harvesting of salmonid fish under controlled conditions for both commercial and recreational purposes. Salmonids, along with carp and tilapia, are the three most important fish groups in aquaculture. The most commonly commercially farmed salmonid is the Atlantic salmon.

Like humans and other animals, fish suffer from diseases and parasites. Fish defences against disease are specific and non-specific. Non-specific defences include skin and scales, as well as the mucus layer secreted by the epidermis that traps microorganisms and inhibits their growth. If pathogens breach these defences, fish can develop inflammatory responses that increase the flow of blood to infected areas and deliver white blood cells that attempt to destroy the pathogens.

Diseases and parasites in salmon, trout and other salmon-like fishes of the family Salmonidae are also found in other fish species. The life cycle of many salmonids is anadromous, so such fish are exposed to parasites in fresh water, brackish water and saline water.

Argulus foliaceus, also known as the common fish louse, is a species of fish lice in the family Argulidae. It is "the most common and widespread native argulid in the Palaearctic" and "one of the most widespread crustacean ectoparasites of freshwater fish in the world", considering its distribution and range of hosts. It can cause the severe disease state argulosis in a wide variety of fish species. It is responsible for epizootic outbreaks that have led to the collapse of aquaculture operations. Fish lice are not related to lice, which are insects.
Eustrongylidosis is a parasitic disease that mainly affects wading birds worldwide; however, the parasite's complex, indirect lifecycle involves other species, such as aquatic worms and fish. Moreover, this disease is zoonotic, which means the parasite can transmit disease from animals to humans. Eustrongylidosis is named after the causative agent Eustrongylides, and typically occurs in eutrophicated waters where concentrations of nutrients and minerals are high enough to provide ideal conditions for the parasite to thrive and persist. Because eutrophication has become a common issue due to agricultural runoff and urban development, cases of eustrongylidosis are becoming prevalent and hard to control. Eustrongylidosis can be diagnosed before or after death by observing behavior and clinical signs, and performing fecal flotations and necropsies. Methods to control it include preventing eutrophication and providing hosts with uninfected food sources in aquaculture farms. Parasites are known to be indicators of environmental health and stability, so should be studied further to better understand the parasite's lifecycle and how it affects predator-prey interactions and improve conservation efforts.

Leptophlebia marginata, the sepia dun, is a species of mayfly in the family Leptophlebiidae. It is native to Europe and North America where it is distributed widely near lakes, ponds and slow-moving streams. The larvae, which are known as nymphs, are aquatic.
















