
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleotide that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, it is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" for intracellular energy transfer.
A salvage pathway is a pathway in which a biological product is produced from intermediates in the degradative pathway of its own or a similar substance. The term often refers to nucleotide salvage in particular, in which nucleotides are synthesized from intermediates in their degradative pathway.
A nucleoside triphosphate is a nucleoside containing a nitrogenous base bound to a 5-carbon sugar, with three phosphate groups bound to the sugar. They are the molecular precursors of both DNA and RNA, which are chains of nucleotides made through the processes of DNA replication and transcription. Nucleoside triphosphates also serve as a source of energy for cellular reactions and are involved in signalling pathways.
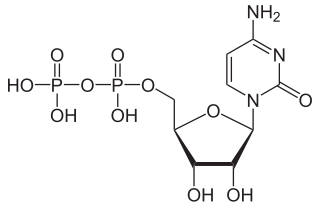
Cytidine diphosphate, abbreviated CDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside cytidine. CDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase cytosine.
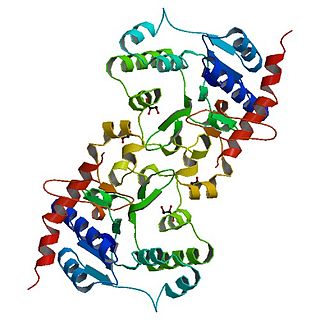
Glycogenin is an enzyme involved in converting glucose to glycogen. It acts as a primer, by polymerizing the first few glucose molecules, after which other enzymes take over. It is a homodimer of 37-kDa subunits and is classified as a glycosyltransferase.
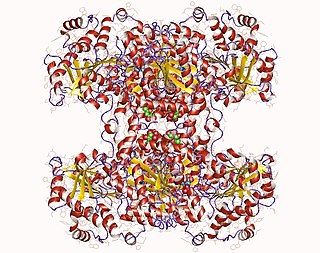
Glycogen synthase is a key enzyme in glycogenesis, the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase that catalyses the reaction of UDP-glucose and n to yield UDP and n+1.
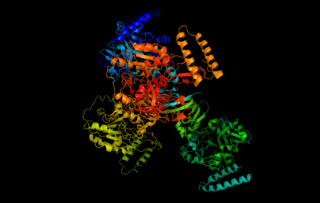
UTP—glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase also known as glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase is an enzyme involved in carbohydrate metabolism. It synthesizes UDP-glucose from glucose-1-phosphate and UTP; i.e.,
Ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase is an enzyme that converts ribose 5-phosphate into phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP). It is classified under EC 2.7.6.1.
CDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxyglucose reductase (EC 1.17.1.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Nucleotide sugars are the activated forms of monosaccharides. Nucleotide sugars act as glycosyl donors in glycosylation reactions. Those reactions are catalyzed by a group of enzymes called glycosyltransferases.

Guanosine diphosphate mannose or GDP-mannose is a nucleotide sugar that is a substrate for glycosyltransferase reactions in metabolism. This compound is a substrate for enzymes called mannosyltransferases.

In enzymology, a 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-ribitol-5-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ethanolamine-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycerol-3-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase (CDS) is the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol from cytidine triphosphate and phosphatidate.
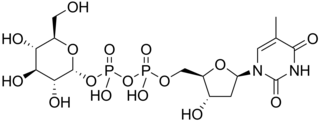
Thymidine diphosphate glucose is a nucleotide-linked sugar consisting of deoxythymidine diphosphate linked to glucose. It is the starting compound for the syntheses of many deoxysugars.










