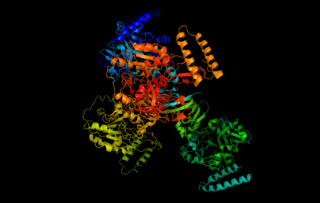
UTP—glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase also known as glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase is an enzyme involved in carbohydrate metabolism. It synthesizes UDP-glucose from glucose-1-phosphate and UTP; i.e.,
Nucleotide sugars are the activated forms of monosaccharides. Nucleotide sugars act as glycosyl donors in glycosylation reactions. Those reactions are catalyzed by a group of enzymes called glycosyltransferases.

Guanosine diphosphate mannose or GDP-mannose is a nucleotide sugar that is a substrate for glycosyltransferase reactions in metabolism. This compound is a substrate for enzymes called mannosyltransferases.

In enzymology, a 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a 3-deoxy-manno-octulosonate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-ribitol-5-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ethanolamine-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
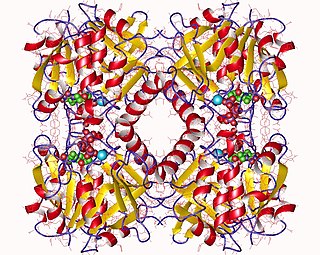
In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycerol-3-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a N-acylneuraminate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase (CDS) is the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol from cytidine triphosphate and phosphatidate.
CCA tRNA nucleotidyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name CTP,CTP,ATP:tRNA cytidylyl,cytidylyl,adenylyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine diphosphorylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
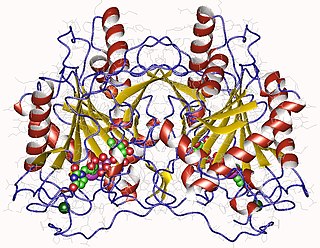
In enzymology, an UTP—hexose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
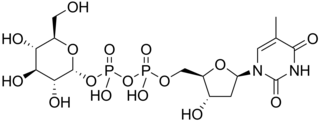
Thymidine diphosphate glucose is a nucleotide-linked sugar consisting of deoxythymidine diphosphate linked to glucose. It is the starting compound for the syntheses of many deoxysugars.

Cytidine diphosphate glucose, often abbreviated CDP-glucose, is a nucleotide-linked sugar consisting of cytidine diphosphate and glucose. This nucleotide saccharide participates in the synthesis of deoxy sugars such as paratose and tyvelose.










