| ketohexokinase (fructokinase) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Ketohexokinase homodimer, Human | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | KHK | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 3795 | ||||||
| HGNC | 6315 | ||||||
| OMIM | 229800 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_006488 | ||||||
| UniProt | P50053 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| EC number | 2.7.1.3 | ||||||
| Locus | Chr. 2 p23.3-23.2 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Ketohexokinase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 2.7.1.3 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9030-50-6 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Hepatic fructokinase (or ketohexokinase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructose to produce fructose-1-phosphate.
Contents
- ATP +
 ADP +
ADP + 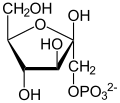
- ATP + D-fructose → ADP + D-fructose-1-phosphate [1]


