| riboflavin kinase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
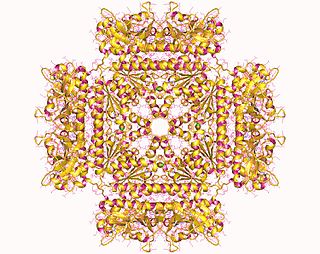
 Crystal structure of riboflavin kinase from Thermoplasma acidophilum . [1] | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 2.7.1.26 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9032-82-0 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Riboflavin Kinase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
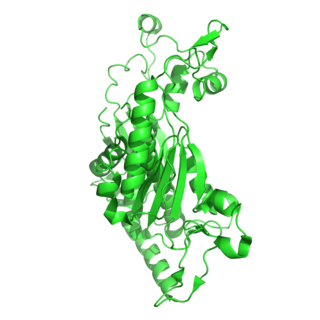
 crystal structure of flavin binding to fad synthetase from thermotoga maritina | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Flavokinase | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01687 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR015865 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1mrz / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Riboflavin kinase | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | Riboflavin_kinase | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF01687 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR015865 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
In enzymology, a riboflavin kinase (EC 2.7.1.26) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Contents
- ATP + riboflavin ADP + FMN
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and riboflavin, whereas its two products are ADP and FMN.
Riboflavin is converted into catalytically active cofactors (FAD and FMN) by the actions of riboflavin kinase (EC 2.7.1.26), which converts it into FMN, and FAD synthetase (EC 2.7.7.2), which adenylates FMN to FAD. Eukaryotes usually have two separate enzymes, while most prokaryotes have a single bifunctional protein that can carry out both catalyses, although exceptions occur in both cases. While eukaryotic monofunctional riboflavin kinase is orthologous to the bifunctional prokaryotic enzyme, [2] the monofunctional FAD synthetase differs from its prokaryotic counterpart, and is instead related to the PAPS-reductase family. [3] The bacterial FAD synthetase that is part of the bifunctional enzyme has remote similarity to nucleotidyl transferases and, hence, it may be involved in the adenylylation reaction of FAD synthetases. [4]
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, to be specific, those transferring phosphorus-containing groups (phosphotransferases) with an alcohol group as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ATP:riboflavin 5'-phosphotransferase. This enzyme is also called flavokinase. This enzyme participates in riboflavin metabolism.
However, archaeal riboflavin kinases (EC 2.7.1.161) in general utilize CTP rather than ATP as the donor nucleotide, catalyzing the reaction
- CTP + riboflavin CDP + FMN [5]
Riboflavin kinase can also be isolated from other types of bacteria, all with similar function but a different number of amino acids.