Related Research Articles
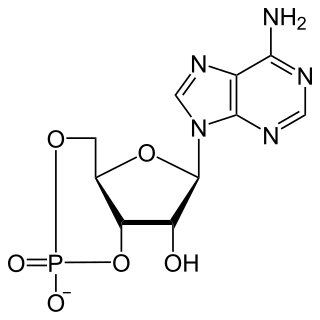
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway.

In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of serine-threonine kinase whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase. PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulation of glycogen, sugar, and lipid metabolism. It should not be confused with 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase.
In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins, or a member of this family. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in the concentration of diacylglycerol (DAG) or calcium ions (Ca2+). Hence PKC enzymes play important roles in several signal transduction cascades.

Phosphoinositide phospholipase C is a family of eukaryotic intracellular enzymes that play an important role in signal transduction processes. These enzymes belong to a larger superfamily of Phospholipase C. Other families of phospholipase C enzymes have been identified in bacteria and trypanosomes. Phospholipases C are phosphodiesterases.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which in turn are involved in cancer.
Class III PI 3-kinase is a subgroup of the enzyme family, phosphoinositide 3-kinase that share a common protein domain structure, substrate specificity and method of activation.

The phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, catalytic subunit alpha, also called p110α protein, is a class I PI 3-kinase catalytic subunit. The human p110α protein is encoded by the PIK3CA gene.
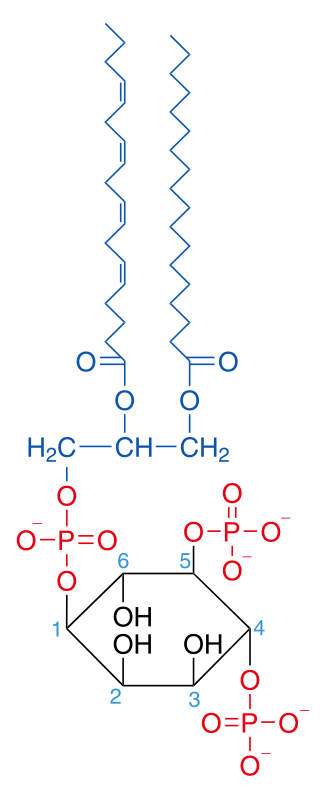
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)P2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)P2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of important signaling proteins. PIP2 also forms lipid clusters that sort proteins.

Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform also known as phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) delta isoform or p110δ is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CD gene.

Platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGF-R) are cell surface tyrosine kinase receptors for members of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) family. PDGF subunits -A and -B are important factors regulating cell proliferation, cellular differentiation, cell growth, development and many diseases including cancer. There are two forms of the PDGF-R, alpha and beta each encoded by a different gene. Depending on which growth factor is bound, PDGF-R homo- or heterodimerizes.

Phosphorylase kinase (PhK) is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase which activates glycogen phosphorylase to release glucose-1-phosphate from glycogen. PhK phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase at two serine residues, triggering a conformational shift which favors the more active glycogen phosphorylase “a” form over the less active glycogen phosphorylase b.
The IκB kinase is an enzyme complex that is involved in propagating the cellular response to inflammation, specifically the regulation of lymphocytes.

Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R1 gene.

Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R2 gene.

Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role in eukaryotic cell physiology, in particular signal transduction pathways. Phospholipase C's role in signal transduction is its cleavage of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacyl glycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), which serve as second messengers. Activators of each PLC vary, but typically include heterotrimeric G protein subunits, protein tyrosine kinases, small G proteins, Ca2+, and phospholipids.

Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit beta isoform is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CB gene.

Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit gamma is an enzyme, which in humans is encoded by the PIK3R3 gene.
The Akt signaling pathway or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway that promotes survival and growth in response to extracellular signals. Key proteins involved are PI3K and Akt.
Lewis C. Cantley is an American cell biologist and biochemist who has made significant advances to the understanding of cancer metabolism. Among his most notable contributions are the discovery and study of the enzyme PI-3-kinase, now known to be important to understanding cancer and diabetes mellitus. He is currently Meyer Director and Professor of Cancer Biology at the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City. He was formerly a professor in the Departments of Systems Biology and Medicine at Harvard Medical School, and the Director of Cancer Research at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, in Boston, Massachusetts. In 2016, he was elected Chairman of the Board for the Hope Funds for Cancer Research.
The insulin transduction pathway is a biochemical pathway by which insulin increases the uptake of glucose into fat and muscle cells and reduces the synthesis of glucose in the liver and hence is involved in maintaining glucose homeostasis. This pathway is also influenced by fed versus fasting states, stress levels, and a variety of other hormones.
References
- Stein RC (September 2001). "Prospects for phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibition as a cancer treatment". Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 8 (3): 237–48. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.324.8135 . doi:10.1677/erc.0.0080237. PMID 11566615. S2CID 568427. Archived from the original on 2008-05-21. Retrieved 2008-09-24.
- Foster FM, Traer CJ, Abraham SM, Fry MJ (August 2003). "The phosphoinositide (PI) 3-kinase family". J. Cell Sci. 116 (Pt 15): 3037–40. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00609 . PMID 12829733.
- Vanhaesebroeck B, Waterfield MD (November 1999). "Signaling by distinct classes of phosphoinositide 3-kinases" (PDF). Exp. Cell Res. 253 (1): 239–54. doi:10.1006/excr.1999.4701. PMID 10579926. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 2, 2006.