Related Research Articles
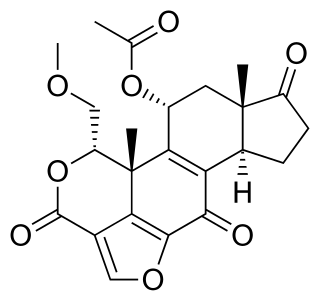
Wortmannin, a steroid metabolite of the fungi Penicillium funiculosum, Talaromyces wortmannii, is a non-specific, covalent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks). It has an in vitro inhibitory concentration (IC50) of around 5 nM, making it a more potent inhibitor than LY294002, another commonly used PI3K inhibitor. It displays a similar potency in vitro for the class I, II, and III PI3K members although it can also inhibit other PI3K-related enzymes such as mTOR, DNA-PKcs, some phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases, myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) at high concentrations Wortmannin has also been reported to inhibit members of the polo-like kinase family with IC50 in the same range as for PI3K. The half-life of wortmannin in tissue culture is about 10 minutes due to the presence of the highly reactive C20 carbon that is also responsible for its ability to covalently inactivate PI3K. Wortmannin is a commonly used cell biology reagent that has been used previously in research to inhibit DNA repair, receptor-mediated endocytosis and cell proliferation.

Protein kinase B (PKB), also known as Akt, is the collective name of a set of three serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that play key roles in multiple cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, transcription, and cell migration.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which in turn are involved in cancer.
Class I PI 3-kinases are a subgroup of the enzyme family, phosphoinositide 3-kinase that possess a common protein domain structure, substrate specificity, and method of activation. Class I PI 3-kinases are further divided into two subclasses, class IA PI 3-kinases and class IB PI 3-kinases.
Class III PI 3-kinase is a subgroup of the enzyme family, phosphoinositide 3-kinase that share a common protein domain structure, substrate specificity and method of activation.

The phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, catalytic subunit alpha, also called p110α protein, is a class I PI 3-kinase catalytic subunit. The human p110α protein is encoded by the PIK3CA gene.

Phosphatidylinositol (3,4)-bisphosphate is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes, yet an important second messenger. The generation of PtdIns(3,4)P2 at the plasma membrane activates a number of important cell signaling pathways.

Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform also known as phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) delta isoform or p110δ is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CD gene.

Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R1 gene.

Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit gamma isoform is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CG gene.

Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase C2 domain-containing alpha polypeptide is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3C2A gene.

Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase C2 domain-containing beta polypeptide is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3C2B gene.

PIKfyve, a FYVE finger-containing phosphoinositide kinase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIKFYVE gene.

Phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate 4-kinase type-2 alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIP4K2A gene.

Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase C2 domain-containing gamma polypeptide is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3C2G gene.

PKN3 is a protein kinase C-related molecule and thought to be an effector mediating malignant cell growth downstream of activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). It is thought that chronic activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/PTEN signal transduction pathway contributes to metastatic cell growth and that PKN3 may mediate that growth.1
The Akt signaling pathway or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway that promotes survival and growth in response to extracellular signals. Key proteins involved are PI3K and Akt.

In the field of biochemistry, PDPK1 refers to the protein 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1, an enzyme which is encoded by the PDPK1 gene in humans. It is implicated in the development and progression of melanomas.

Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors are a class of medical drugs that are mainly used to treat advanced cancers. They function by inhibiting one or more of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) enzymes, which are part of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. This signal pathway regulates cellular functions such as growth and survival. It is strictly regulated in healthy cells, but is always active in many cancer cells, allowing the cancer cells to better survive and multiply. PI3K inhibitors block the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and thus slow down cancer growth. They are examples of a targeted therapy. While PI3K inhibitors are an effective treatment, they can have very severe side effects and are therefore only used if other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
Lewis C. Cantley is an American cell biologist and biochemist who has made significant advances to the understanding of cancer metabolism. Among his most notable contributions are the discovery and study of the enzyme PI-3-kinase, now known to be important to understanding cancer and diabetes mellitus. He is currently Meyer Director and Professor of Cancer Biology at the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City. He was formerly a professor in the Departments of Systems Biology and Medicine at Harvard Medical School, and the Director of Cancer Research at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, in Boston, Massachusetts. In 2016, he was elected Chairman of the Board for the Hope Funds for Cancer Research.
References
- Stein RC (September 2001). "Prospects for phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibition as a cancer treatment". Endocrine-Related Cancer. 8 (3): 237–248. doi:10.1677/erc.0.0080237. PMID 11566615.
- Foster FM, Traer CJ, Abraham SM, Fry MJ (August 2003). "The phosphoinositide (PI) 3-kinase family". Journal of Cell Science. 116 (Pt 15): 3037–3040. doi:10.1242/jcs.00609. PMID 12829733.
- Vanhaesebroeck B, Waterfield MD (November 1999). "Signaling by distinct classes of phosphoinositide 3-kinases". Experimental Cell Research. 253 (1): 239–254. doi:10.1006/excr.1999.4701. PMID 10579926.