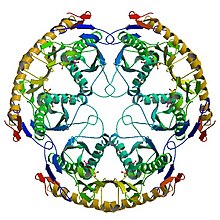
Ribonuclease is a type of nuclease that catalyzes the degradation of RNA into smaller components. Ribonucleases can be divided into endoribonucleases and exoribonucleases, and comprise several sub-classes within the EC 2.7 and 3.1 classes of enzymes.

Ribonuclease H is a family of non-sequence-specific endonuclease enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of RNA in an RNA/DNA substrate via a hydrolytic mechanism. Members of the RNase H family can be found in nearly all organisms, from bacteria to archaea to eukaryotes.

Dicer, also known as endoribonuclease Dicer or helicase with RNase motif, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DICER1 gene. Being part of the RNase III family, Dicer cleaves double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and pre-microRNA (pre-miRNA) into short double-stranded RNA fragments called small interfering RNA and microRNA, respectively. These fragments are approximately 20–25 base pairs long with a two-base overhang on the 3′-end. Dicer facilitates the activation of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which is essential for RNA interference. RISC has a catalytic component Argonaute, which is an endonuclease capable of degrading messenger RNA (mRNA).
Aquifex is a bacterial genus, belonging to phylum Aquificota. There is one species of Aquifex with a validly published name – A. pyrophilus – but "A. aeolicus" is sometimes considered as species though it has no standing as a name given it has not been validly or effectively published. Aquifex spp. are extreme thermophiles, growing best at temperature of 85 °C to 95 °C. They are members of the Bacteria as opposed to the other inhabitants of extreme environments, the Archaea.
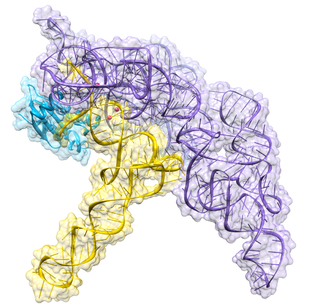
Ribonuclease P is a type of ribonuclease which cleaves RNA. RNase P is unique from other RNases in that it is a ribozyme – a ribonucleic acid that acts as a catalyst in the same way that a protein-based enzyme would. Its function is to cleave off an extra, or precursor, sequence of RNA on tRNA molecules. Further, RNase P is one of two known multiple turnover ribozymes in nature, the discovery of which earned Sidney Altman and Thomas Cech the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1989: in the 1970s, Altman discovered the existence of precursor tRNA with flanking sequences and was the first to characterize RNase P and its activity in processing of the 5' leader sequence of precursor tRNA. Recent findings also reveal that RNase P has a new function. It has been shown that human nuclear RNase P is required for the normal and efficient transcription of various small noncoding RNAs, such as tRNA, 5S rRNA, SRP RNA and U6 snRNA genes, which are transcribed by RNA polymerase III, one of three major nuclear RNA polymerases in human cells.
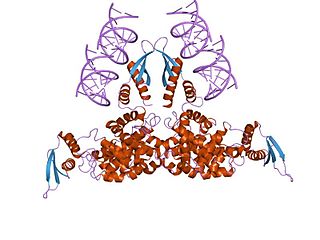
Ribonuclease III (RNase III or RNase C)(BRENDA 3.1.26.3) is a type of ribonuclease that recognizes dsRNA and cleaves it at specific targeted locations to transform them into mature RNAs. These enzymes are a group of endoribonucleases that are characterized by their ribonuclease domain, which is labelled the RNase III domain. They are ubiquitous compounds in the cell and play a major role in pathways such as RNA precursor synthesis, RNA Silencing, and the pnp autoregulatory mechanism.

The Argonaute protein family, first discovered for its evolutionarily conserved stem cell function, plays a central role in RNA silencing processes as essential components of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). RISC is responsible for the gene silencing phenomenon known as RNA interference (RNAi). Argonaute proteins bind different classes of small non-coding RNAs, including microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs). Small RNAs guide Argonaute proteins to their specific targets through sequence complementarity, which then leads to mRNA cleavage, translation inhibition, and/or the initiation of mRNA decay.
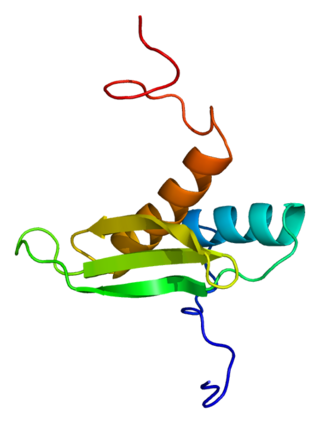
The microprocessor complex subunit DGCR8(DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DGCR8 gene. In other animals, particularly the common model organisms Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans, the protein is known as Pasha. It is a required component of the RNA interference pathway.

The exosome complex is a multi-protein intracellular complex capable of degrading various types of RNA molecules. Exosome complexes are found in both eukaryotic cells and archaea, while in bacteria a simpler complex called the degradosome carries out similar functions.

An exoribonuclease is an exonuclease ribonuclease, which are enzymes that degrade RNA by removing terminal nucleotides from either the 5' end or the 3' end of the RNA molecule. Enzymes that remove nucleotides from the 5' end are called 5'-3' exoribonucleases, and enzymes that remove nucleotides from the 3' end are called 3'-5' exoribonucleases.
In biochemistry, an endoribonuclease is a class of enzyme which is a type of ribonuclease, itself a type of endonuclease. It cleaves either single-stranded or double-stranded RNA, depending on the enzyme. Example includes both single proteins such as RNase III, RNase A, RNase T1, RNase T2 and RNase H and also complexes of proteins with RNA such as RNase P and the RNA-induced silencing complex. Further examples include endoribonuclease XendoU found in frogs (Xenopus).
RNase R, or Ribonuclease R, is a 3'-->5' exoribonuclease, which belongs to the RNase II superfamily, a group of enzymes that hydrolyze RNA in the 3' - 5' direction. RNase R has been shown to be involved in selective mRNA degradation, particularly of non stop mRNAs in bacteria. RNase R has homologues in many other organisms.
The degradosome is a multiprotein complex present in most bacteria that is involved in the processing of ribosomal RNA and the degradation of messenger RNA and is regulated by Non-coding RNA. It contains the proteins RNA helicase B, RNase E and Polynucleotide phosphorylase.
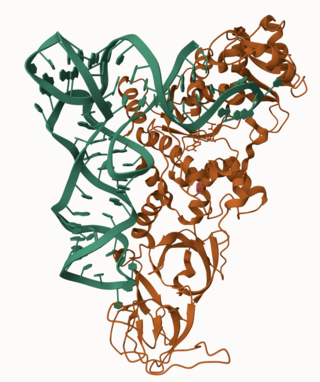
Glutamine—tRNA ligase or glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase (GlnRS) is an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, also called tRNA-ligase. is an enzyme that attaches the amino acid glutamine onto its cognate tRNA.

Hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase is a hepatitis B viral protein. It is a DNA polymerase that can use either DNA or RNA templates and a ribonuclease H that cuts RNA in the duplex. Both functions are supplied by the reverse transcriptase (RT) domain.

Cas9 is a 160 kilodalton protein which plays a vital role in the immunological defense of certain bacteria against DNA viruses and plasmids, and is heavily utilized in genetic engineering applications. Its main function is to cut DNA and thereby alter a cell's genome. The CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique was a significant contributor to the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2020 being awarded to Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna.
tRNA (guanine37-N1)-methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.228, TrmD, tRNA (m1G37) methyltransferase, transfer RNA (m1G37) methyltransferase, Trm5p, TRMT5, tRNA-(N1G37) methyltransferase, MJ0883 (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:tRNA (guanine37-N1)-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Ribonuclease E is a bacterial ribonuclease that participates in the processing of ribosomal RNA and the chemical degradation of bulk cellular RNA.
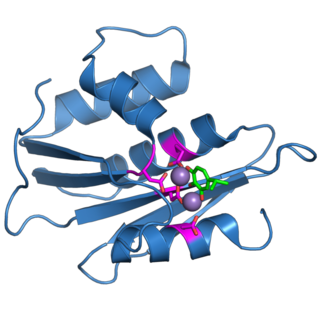
The retroviral ribonuclease H is a catalytic domain of the retroviral reverse transcriptase (RT) enzyme. The RT enzyme is used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from the retroviral RNA genome. This process is called reverse transcription. To complete this complex process, the retroviral RT enzymes need to adopt a multifunctional nature. They therefore possess 3 of the following biochemical activities: RNA-dependent DNA polymerase, ribonuclease H, and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities. Like all RNase H enzymes, the retroviral RNase H domain cleaves DNA/RNA duplexes and will not degrade DNA or unhybridized RNA.

Ribonuclease T is a ribonuclease enzyme involved in the maturation of transfer RNA and ribosomal RNA in bacteria, as well as in DNA repair pathways. It is a member of the DnaQ family of exonucleases and non-processively acts on the 3' end of single-stranded nucleic acids. RNase T is capable of cleaving both DNA and RNA, with extreme sequence specificity discriminating against cytosine at the 3' end of the substrate.