Dachshund homolog 1, also known as DACH1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the DACH1 gene. [5] [6] [7] DACH1 has been shown to interact with Ubc9, [8] Smad4, [9] and NCoR. [9] [10]
Dachshund homolog 1, also known as DACH1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the DACH1 gene. [5] [6] [7] DACH1 has been shown to interact with Ubc9, [8] Smad4, [9] and NCoR. [9] [10]
Gene structure . This protein coding gene has 760 amino acid protein, and an observed molecular weight of 52 kDa. Dachshund Family transcription factor 1 is encoded by DACH gene, who spans 400kDa and is encoded by 12 exons. This gene is located, in humans, in chromosome 13 (13q22). It encodes a chromatin-associated protein that associates with other DNA-binding transcription factors to regulate gene expression, [9] [11] [12] [10] [13] [14] mRNA translation, [15] coactivator binding, [16] and cell fate determination during development. [17] [18]
Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Four alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene.DACH1 mRNA was detected in multiple human tissues, including kidney and heart. Dach1 is located in nuclear and cytoplasmic pools and is considered a cell fate determination factor. [17] [18] Dachshund domain 1 (DD1, also known as Box-N) has a predicted helix–turn–helix family structure. The X-ray crystal structure of the human DACH1 Box-N illustrates that the DACH1 protein contains a domain that is conserved with the pro-oncogenes ski/sno oncogenes, which form an α/β structure similar to that found in the winged helix/forkhead subgroup of DNA binding proteins. [14] This protein is widely expressed including bone marrow, brain, colon, eye, heart, kidney, leucocyte, liver, lung, pancreas, pineal gland, placenta, prostate, retina, skeletal muscle, small intestine, stromal/preosteoblasts and the spleen. [10] [19] [20]
Protein modification. DACH1 is modified by phosphorylation, [15] acetylation, [21] and SUMOYlation. [22] Acetylation of Dach1 determine binding to the p53 tumor suppressor, and thereby governs a subset of p53 functions involved in stem cell restraint and the inhibition of cellular proliferation. [21] SUMOYlation of DACH governs HDAC binding. [23] Phosphorylation of Dach1 contributes to YB-1 binding, subcellular distribution and the induction of EMT via translation of EMT regulatory genes. [15]

Organismal development. Dach1 is similar to the D. melanogaster dac gene, which encodes a nuclear factor essential for determining cell fates in the eye, leg, and nervous system of the fly. [6] Dach is a member of the Ski gene family and is involved in eye and organismal development. [18] [25] Dach1 deletion mice exhibit early postnatal death, although no developmental defects were detected in any organ system examined, including kidneys. DACH1 plays an important role on this precursor of cell proliferation in retinal and pituitary. [7] [17] [26]
Restrain of Cancer cell growth. DACH1 protein is able to prevent the proliferation of cancerous cells (lung, breast, prostate [11] [12] [10] [13] [14] ) and functions as a repressor of estrogen receptor activity in breast cancer cells. [11] [13]
Transcription. DACH1 conducts transcriptional function through interacting with transcription factors including c-Jun, [11] estrogen receptor alpha, [13] the androgen receptor, [10] and the basal transcription apparatus through binding to the co-integrator protein CA150. Curiously, DACH1 selectively bound to the delta domain of c-Jun, which was known to interact with an endogenous cellular repressor. DACH1 binds directly with a Forkhead-like DNA sequence to restrain oncogenic signals from a subset of FKHR proteins. [14] Dach1 governs mRNA translation of an EMT signature [15] and governs Snail1 transcription. [15]
Cell migration. DACH1 inhibits migration of vascular endothelial cells, [23] [27] fibroblasts [28] and prostate epithelial cells [27] wherein DACH1 maintains persistence of migratory directionality via heterotypic signals.
DACH1 has been implicated in suppression of tumor growth, and has been proposed as a putatative tumor suppressor although no formal in vivo evidence has been published to date. Supporting evidence includes the finding that Dach1 expression is reduced in human malignancies including breast, [26] [15] lung, [12] prostate [10] and brain tumors. [29] DACH1 inhibits Cyclin D1 expression and thereby reduces breast cancer cell line cell growth. [28] Normal cells and some breast cancer cells have receptors that bind estrogen and progesterone. These two hormones often promote the growth of breast cancer cells. Approximately 70% of breast cancers are ERa+, DACH1 expression decreases when the cancer is more invasive and the level of estrogen is high. [13]
Renal hypodysplasia (RHD) is characterized by small and/or disorganized kidneys following abnormal organogenesis. Double homozygous missense mutations of DACH1 and BMP4 occurred in a patient with bilateral cystic dysplasia. [30] Functional analysis of the DACH1 mutation (p.R684C). demonstrated enhanced suppression of the TGF-β pathway. Dach1 is highly expressed in the adult podocyte, with transcripts showing an approximate tenfold enrichment compared to total kidney cortex. It is also more widely expressed in the earlier developing kidney, but again including definite podocyte expression.
Hepatocyte the abundance of DACH1 Is Increased in the hepatocytes of Obese patients. Dach1 promotes hepatic insulin resistance via Nuclear Exclusion of HDAC4. [23]
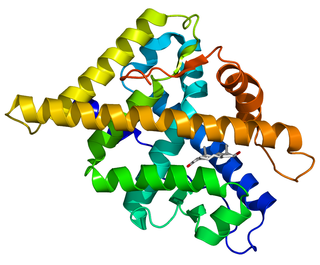
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4, is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.

Histone acetyltransferase p300 also known as p300 HAT or E1A-associated protein p300 also known as EP300 or p300 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the EP300 gene. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription of genes via chromatin remodeling by allowing histone proteins to wrap DNA less tightly. This enzyme plays an essential role in regulating cell growth and division, prompting cells to mature and assume specialized functions (differentiate), and preventing the growth of cancerous tumors. The p300 protein appears to be critical for normal development before and after birth.
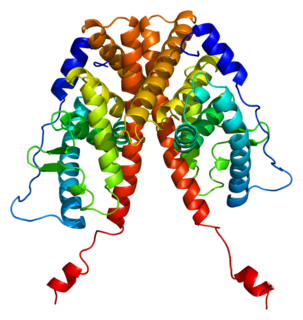
Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), also known as NR3A1, is one of two main types of estrogen receptor, a nuclear receptor that is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans, ERα is encoded by the gene ESR1.
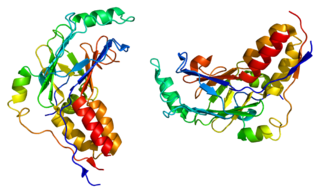
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 also known as SMAD family member 3 or SMAD3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD3 gene.
Myc is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The Myc family consists of three related human genes: c-myc (MYC), l-myc (MYCL), and n-myc (MYCN). c-myc was the first gene to be discovered in this family, due to homology with the viral gene v-myc.

The SKI protein is a nuclear proto-oncogene that is associated with tumors at high cellular concentrations. SKI has been shown to interfere with normal cellular functioning by both directly impeding expression of certain genes inside the nucleus of the cell as well as disrupting signaling proteins that activate genes.

Cyclin D1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCND1 gene.

Forkhead box protein P1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXP1 gene. FOXP1 is necessary for the proper development of the brain, heart, and lung in mammals. It is a member of the large FOX family of transcription factors.
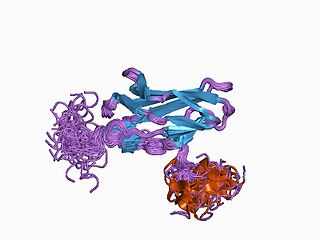
Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) also known as acute myeloid leukemia 1 protein (AML1) or core-binding factor subunit alpha-2 (CBFA2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RUNX1 gene.
TEAD2, together with TEAD1, defines a novel family of transcription factors, the TEAD family, highly conserved through evolution. TEAD proteins were notably found in Drosophila (Scalloped), C. elegans, S. cerevisiae and A. nidulans. TEAD2 has been less studied than TEAD1 but a few studies revealed its role during development.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PAK1 gene.

Caveolin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAV1 gene.

Nuclear respiratory factor 1, also known as Nrf1, Nrf-1, NRF1 and NRF-1, encodes a protein that homodimerizes and functions as a transcription factor which activates the expression of some key metabolic genes regulating cellular growth and nuclear genes required for respiration, heme biosynthesis, and mitochondrial DNA transcription and replication. The protein has also been associated with the regulation of neurite outgrowth. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, which encode the same protein, have been characterized. Additional variants encoding different protein isoforms have been described but they have not been fully characterized. Confusion has occurred in bibliographic databases due to the shared symbol of NRF1 for this gene and for "nuclear factor -like 1" which has an official symbol of NFE2L1.
Four and a half LIM domains protein 2 also known as FHL-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FHL2 gene. LIM proteins contain a highly conserved double zinc finger motif called the LIM domain.

Sal-like protein 4(SALL4) is a transcription factor encoded by a member of the Spalt-like (SALL) gene family, SALL4. The SALL genes were identified based on their sequence homology to Spalt, which is a homeotic gene originally cloned in Drosophila melanogaster that is important for terminal trunk structure formation in embryogenesis and imaginal disc development in the larval stages. There are four human SALL proteins with structural homology and playing diverse roles in embryonic development, kidney function, and cancer. The SALL4 gene encodes at least three isoforms, termed A, B, and C, through alternative splicing, with the A and B forms being the most studied. SALL4 can alter gene expression changes through its interaction with many co-factors and epigenetic complexes. It is also known as a key embryonic stem cell (ESC) factor.

TATA box-binding protein-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBPL1 gene.

Transcription factor AP-2 gamma also known as AP2-gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFAP2C gene. AP2-gamma is a member of the activating protein 2 family of transcription factors.

The Hippo signaling pathway, also known as the Salvador-Warts-Hippo (SWH) pathway, is a signaling pathway that controls organ size in animals through the regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis. The pathway takes its name from one of its key signaling components—the protein kinase Hippo (Hpo). Mutations in this gene lead to tissue overgrowth, or a "hippopotamus"-like phenotype.
dachshund (dac) is a gene involved in the development of the arthropod compound eye which also plays a role in leg development. It is activated by the Distal-less (Dll) gene.

Dachshund homolog 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DACH2 gene.