
A hopping mouse is any of about ten different Australian native mice in the genus Notomys. They are rodents, not marsupials, and their ancestors are thought to have arrived from Asia about 5 million years ago.

The dusky hopping mouse, is a small rodent endemic to Australia, inhabiting desert regions characterised by sand dunes. Populations have experienced significant declines since the arrival of Europeans, and continue to be subject to threatening processes. It is currently listed as a threatened species.
The big-eared hopping mouse is an extinct species of mouse, which lived in the Moore River area of south-western Australia. The big-eared hopping mouse was a small, rat-sized animal resembling a tiny kangaroo. It had large eyes and ears with a brush-tipped tail. It moved on its four legs when traveling at a slower pace, or by bounding upon its enlarged, padded, hind feet when traveling quickly. They mainly lived in sand dunes and made nests of leaves and other organic materials. The big-eared hopping-mouse was last collected in July 1843 near the Moore River, Western Australia, close to where New Norcia is now situated, and has not been seen since.

The lesser bilby, also known as the yallara, the lesser rabbit-eared bandicoot or the white-tailed rabbit-eared bandicoot, was a rabbit-like marsupial. The species was first described by Oldfield Thomas as Peregale leucura in 1887 from a single specimen from a collection of mammals of the British Museum. Reaching the size of a young rabbit, this species lived in the deserts of Central Australia. Since the 1950s–1960s, it has been believed to be extinct.

Mitchell's hopping mouse also known as the pankot, is the largest extant member of the genus Notomys, weighing between 40 and 60 g. N. mitchellii is a bipedal rodent with large back legs, similar to a jerboa or kangaroo rat. The species occurs throughout much of semi-arid Southern Australia, and appears to be particularly common on the Eyre Peninsula, South Australia. Typical habitat for N. mitchellii appears to be mallee shrublands on sandy dune systems. The species is currently considered to be unthreatened, but its range has been reduced through habitat disturbance and destruction associated with European settlement in Australia.

The eastern long-eared bat, species Nyctophilus bifax, is a small flying mammal, a vespertilionid bat. It is found in eastern Australia and Papua New Guinea.

The New Guinea long-eared bat, species Nyctophilus microtis, is a small flying mammal. It is found only in Papua New Guinea.

The pygmy long-eared bat is a vespertilionid bat, found in the north of the Australian continent. An insectivorous flying hunter, they are one of the tiniest mammals in Australia, weighing only a few grams and one or two inches long.
The northern cave bat is a vespertilionid bat that occurs in most of Australia.

The northern hopping mouse is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found only in coastal northern Australia, from Arnhem Land to the Cobourg Peninsula.
The blue-gray mouse is an Australian rodent species that is only known by a few specimens found in Eastern Australia, and since presumed to have become extinct.
Hotson's jerboa or the Iranian jerboa, is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is found in Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan.

The velvety fruit-eating bat, also known as Hart's little fruit bat, is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is monotypic within the genus Enchisthenes. It is found in Central America, Mexico, the United States, and northern South America.
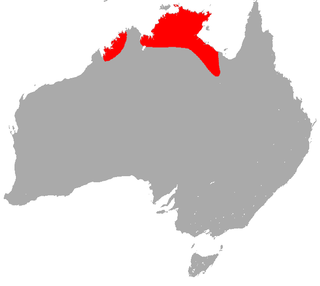
The northern leaf-nosed bat is a micro-bat of the family Hipposideridae, known as "leaf-nosed" bats. The species is endemic to northern regions of Australia. They are highly manoeuvrable in flight, and use echolocation to forage for insect prey.
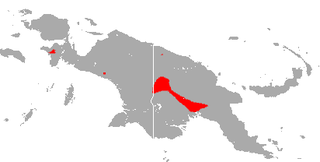
Wollaston's roundleaf bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is found in West Papua, Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. It was named after the explorer Sandy Wollaston.
Nyctophilus daedalus is a species of bat in the family Vespertilionidae, a flying mammal endemic to northern Australia. They are also referred to as the pallid long-eared bat or northern long-eared bat.

Hydromyini is a very large, diverse tribe of muroid rodents in the subfamily Murinae. They are the dominant native rodents in Australasia and one of only two native rodent groups there, the other being the genus Rattus in the tribe Rattini. They are also found in parts of Southeast Asia.












