
Dasyuromorphia is an order comprising most of the Australian carnivorous marsupials, including quolls, dunnarts, the numbat, the Tasmanian devil, and the extinct thylacine. In Australia, the exceptions include the omnivorous bandicoots and the marsupial moles. Numerous South American species of marsupials are also carnivorous, as were some extinct members of the order Diprotodontia, including extinct kangaroos and thylacoleonids, and some members of the partially extinct clade Metatheria and all members of the extinct superorder Sparassodonta.

The Dasyuridae are a family of marsupials native to Australia and New Guinea, including 71 extant species divided into 17 genera. Many are small and mouse-like or shrew-like, giving some of them the name marsupial mice or marsupial shrews, but the group also includes the cat-sized quolls, as well as the Tasmanian devil. They are found in a wide range of habitats, including grassland, underground, forests, and mountains, and some species are arboreal or semiaquatic. The Dasyuridae are often called the 'marsupial carnivores', as most members of the family are insectivores.
The former subfamily Planigalinae contained the planigales and the ningauis: very small marsupial carnivores native to Australia which are, like the quolls, antechinuses, dibblers, Tasmanian devil, and many others, part of the biological order Dasyuromorphia: the carnivorous marsupials. The subfamily is now contained in the Sminthopsinae subfamily, and the two genera are split between two different tribes; the planigales are by themselves in their own tribe, while the ningaui are lumped with the dunnarts and the Kultarr.

The tiger quoll, also known as the spotted-tailed quoll, spotted quoll, spotted-tailed dasyure, or tiger cat, is a carnivorous marsupial of the quoll genus Dasyurus native to Australia. With males and females weighing around 3.5 and 1.8 kg, respectively, it is the world's second-largest extant carnivorous marsupial, behind the Tasmanian devil. Two subspecies are recognised; the nominate is found in wet forests of southeastern Australia and Tasmania, and a northern subspecies, D. m. gracilis, is found in a small area of northern Queensland and is endangered.

Quolls are carnivorous marsupials native to Australia and New Guinea. They are primarily nocturnal and spend most of the day in a den. Of the six species of quoll, four are found in Australia and two in New Guinea. Another two species are known from fossil remains in Pliocene and Pleistocene deposits in Queensland. Genetic evidence indicates that quolls evolved around 15 million years ago in the Miocene, and that the ancestors of the six species had all diverged by around four million years ago. The six species vary in weight and size, from 300 g (11 oz) to 7 kg (15 lb). They have brown or black fur and pink noses. They are largely solitary, but come together for a few social interactions such as mating which occurs during the winter season. A female gives birth to up to 30 pups, but the number that can be raised to adulthood is limited by the number of teats (6–7). They have a life span of 1–5 years.

The kowari, also known by its Diyari name kariri, is a small carnivorous marsupial native to the gibber deserts of central Australia. It is the sole member of the genus Dasyuroides.

Mulgaras are the six small rat-sized species in the genus Dasycercus. They are marsupial carnivores, closely related to the Tasmanian devil and the quolls, that live in deserts and spinifex grasslands of arid Australia. They are nocturnal, but occasionally "sunbathe" in the entrance of the burrow in which they dwell. Their kidneys are highly developed to excrete extremely concentrated urine to preserve water, as the animals rarely drink. They feed mostly on insects, but also eat reptiles and small mammals. They are seasonal breeders and breed from June to September. The pouch comprises two lateral folds of skin.
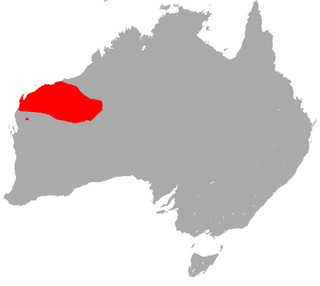
The little red kaluta is a small, reddish-brown, shrew-like mammal native to dry grasslands of northwest Western Australia. It is active at night, feeding on insects and other small animals. The kaluta is a marsupial and is the only member of its genus, Dasykaluta. Individuals are around 10 cm (3.9 in) long and weigh from 20 to 40 g. They live for about four years in captivity. Other common names include little red antechinus, russet antechinus and spinifex antechinus.

The tribe Dasyurini includes several genera of small carnivorous marsupials native to Australia: quolls, kowari, mulgara, kaluta, dibblers, neophascogales, pseudantechinuses, and the Tasmanian devil.

The Phascogalini are a tribe in the family Dasyuridae, comprising seven genera of small marsupials native to Australia and New Guinea.

The New Guinean quoll, also known as the New Guinea quoll or New Guinea native cat, is a carnivorous marsupial mammal native to New Guinea. It is the second-largest surviving marsupial carnivore of New Guinea. It is known as suatg in the Kalam language of Papua New Guinea.

The crest-tailed mulgara is a small to medium-sized Australian carnivorous marsupial and a member of the family Dasyuridae which includes quolls, dunnarts, numbats, the endangered Tasmanian devil and the extinct thylacine. The crest-tailed mulgara is among a group of native predatory mammals or mesopredators endemic to arid Australia.











