
The Dasyuridae are a family of marsupials native to Australia and New Guinea, including 71 extant species divided into 17 genera. Many are small and mouse-like or shrew-like, giving some of them the name marsupial mice or marsupial shrews, but the group also includes the cat-sized quolls, as well as the Tasmanian devil and the extinct thylacine. They are found in a wide range of habitats, including grassland, underground, forests, and mountains, and some species are arboreal or semiaquatic. The Dasyuridae are often called the 'marsupial carnivores', as most members of the family are insectivores.

The tiger quoll, also known as the spotted-tail quoll, the spotted quoll, the spotted-tail dasyure, native cat or the tiger cat, is a carnivorous marsupial of the quoll genus Dasyurus native to Australia. With males and females weighing around 3.5 and 1.8 kg, respectively, it is the world's second-largest extant carnivorous marsupial, behind the Tasmanian devil. Two subspecies are recognised; the nominate is found in wet forests of southeastern Australia and Tasmania, and a northern subspecies, D. m. gracilis, is found in a small area of northern Queensland and is endangered.

The Tasmanian pygmy possum, also known as the little pygmy possum or tiny pygmy possum, is the world's smallest possum. It was first described by Oldfield Thomas in 1888, after he identified that a museum specimen labelled as an eastern pygmy possum in fact represented a species then unknown to science. The holotype resides in the Natural History Museum in London.

The yellow-footed antechinus, also known as the mardo, is a shrew-like marsupial found in Australia. One notable feature of the species is its sexual behavior. The male yellow-footed antechinus engages in such frenzied mating that its immune system becomes compromised, resulting in stress related death before it is one year old.

The eastern quoll is a medium-sized carnivorous marsupial (dasyurid), and one of six extant species of quolls. Endemic to Australia, they occur on the island state of Tasmania, but were considered extinct on the mainland after 1963. The species has been reintroduced to fox-proof fenced sanctuaries Victoria in 2003 and to the Australian Capital Territory in 2016.

The tribe Dasyurini includes several genera of small carnivorous marsupials native to Australia: quolls, kowari, mulgara, kaluta, dibblers, neophascogales, pseudantechinuses, and the Tasmanian devil.

The fat-tailed dunnart is a species of mouse-like marsupial of the Dasyuridae, the family that includes the little red kaluta, quolls, and the Tasmanian devil.

The white-footed dunnart is a marsupial that occurs on Tasmania and mainland Australia. It occurs along the coast and in inner Gippsland and Alpine areas up to 400 metres near Narbethong. In southern New South Wales, the white-footed dunnart is known to occur at elevations at least as high as 1000 metres. The length from snout to tail tip is 14–20 cm (5.5–7.9 in) of which head and body are 7–11 cm (2.8–4.3 in) and the tail 7–9 cm (2.8–3.5 in) long. They weigh 19–27 g (0.67–0.95 oz).

The slender-tailed dunnart, also known as the common dunnart in Australia, is a dasyurid marsupial. It has an average body length of 7 to 12 centimeters (2.8–4.7 in) with a tail length of 5.5 to 13 centimetres (2.2–5.1 in). It weighs 25–40.8 grams for males and 16.5–25.4 grams for females.

The Carpentarian dunnart also known as Butler's dunnart is a marsupial with a puffy brown or mouse grey colour above and the underside of white, similar to its close relative the Kakadu dunnart. Head to anus length is 75-88mm with a tail of 72-90mm long for a total length of 147-178mm. Weight varies from 10-20g depending on a variety of factors including sex, food abundance, habitat etc.

The eastern pygmy possum is a diprotodont marsupial of south-eastern Australia. Occurring from southern Queensland to eastern South Australia and also Tasmania, it is found in a range of habitats, including rainforest, sclerophyll forest, woodland and heath.

The Alexandria false antechinus, also known as the Carpentarian false antechinus or Carpentarian pseudantechinus, is a small carnivorous marsupial, found only in a number of small, isolated localities in northern Australia. It is the smallest and rarest of the false antechinuses.
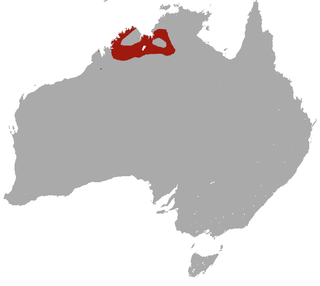
The Ningbing false antechinus, also known as the Ningbing pseudantechinus, is a small species of carnivorous marsupial found in north-western Australia. It is locally common throughout the Kimberley region of Western Australia and the Northern Territory.
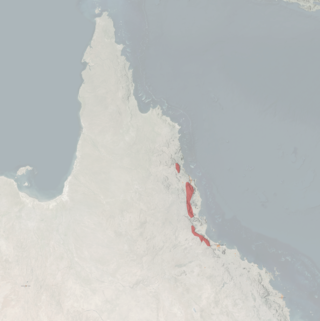
The tropical antechinus, also known as the rusty antechinus, is a species of small marsupial carnivore, particularly closely related to the brown antechinus.

The subtropical antechinus is a species of small carnivorous marsupial of the family Dasyuridae.

The agile antechinus is a species of small carnivorous marsupial of the family Dasyuridae. It is found in Australia.

The Atherton antechinus, also known as Godman's antechinus, is a species of small carnivorous, insectivorous marsupial native to Australia. It is one of the rarest members of its genus, and differs from other antechinuses in its more rufous body colour and small eyes.
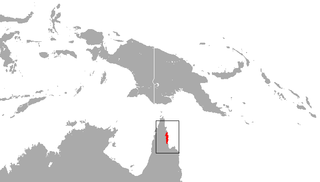
The cinnamon antechinus, also known as the Iron Ranges antechinus and the Cape York antechinus, is a species of small carnivorous marsupial of the family Dasyuridae. It is the only mammal endemic to Cape York Peninsula, being confined to semideciduous forest around the McIlraith and Iron Ranges. Along with the Atherton antechinus, it is the rarest in its genus.

The dusky antechinus, also known as Swainson's antechinus or the dusky marsupial mouse, is a species of small marsupial carnivore, a member of the family Dasyuridae. It is found in Australia.





















