
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At 508 million years old, it is one of the earliest fossil beds containing soft-part imprints.

Lysithea is a prograde irregular satellite of Jupiter. It was discovered by Seth Barnes Nicholson in 1938 at Mount Wilson Observatory and is named after the mythological Lysithea, daughter of Oceanus and one of Zeus' lovers.

A prion is a misfolded protein that can induce misfolding of normal variants of the same protein and trigger cellular death. Prions cause prion diseases known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) that are fatal transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and animals. The proteins may misfold sporadically, due to genetic mutations, or by exposure to an already misfolded protein. The consequent abnormal three-dimensional structure confers on them the ability to cause misfolding of other proteins.

Isobel Gowdie was a Scottish woman who confessed to witchcraft at Auldearn near Nairn during 1662. Scant information is available about her age or life and, although she was probably executed in line with the usual practice, it is uncertain whether this was the case or if she was allowed to return to the obscurity of her former life as a cottar’s wife. Her detailed testimony, apparently achieved without the use of violent torture, provides one of the most comprehensive insights into European witchcraft folklore at the end of the era of witch-hunts.

Pterobranchia, members of which are often called pterobranchs, is a class of small worm-shaped animals. They belong to the Hemichordata, and live in secreted tubes on the ocean floor. Pterobranchia feed by filtering plankton out of the water with the help of cilia attached to tentacles. There are about 25 known living pterobranch species in three genera, which are Rhabdopleura, Cephalodiscus, and Atubaria. On the other hand, there are several hundred extinct genera, some of which date from the Cambrian Period.
The Early Anthropocene Hypothesis is a stance concerning the beginning of the Anthropocene first proposed by William Ruddiman in 2003. It posits that the Anthropocene, a proposed geological epoch coinciding with the most recent period in Earth's history when the activities of the human race first began to have a significant global impact on Earth's climate and ecosystems, did not begin during European colonization of the Americas, as numerous scholars posit, nor the eighteenth century with advent of coal-burning factories and power plants of the industrial era, as originally argued by Paul Crutzen, nor in the 1950s as claimed by the Anthropocene Working Group, but dates back to 8,000 years ago, triggered by intense farming activities after agriculture became widespread. It was at that time that atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations stopped following the periodic pattern of rises and falls that had accurately characterized their past long-term behavior, a pattern that is explained by natural variations in Earth's orbit known as Milankovitch cycles.

Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 7, also known as TRPM7, is a human gene encoding a protein of the same name.

Gap junction alpha-5 protein (GJA5), also known as connexin 40 (Cx40) — is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GJA5 gene.

The external sphincter muscle of female urethra is a muscle which controls urination in females. The muscle fibers arise on either side from the margin of the inferior ramus of the pubis. They are directed across the pubic arch in front of the urethra, and pass around it to blend with the muscular fibers of the opposite side, between the urethra and vagina.

The Morchellaceae are a family of ascomycete fungi in the order Pezizales. According to a standard reference work, the family has contained at least 49 species distributed among four genera. However, in 2012, five genera that produce ascoma that are sequestrate and hypogeous were added. The best-known members are the highly regarded and commercially picked true morels of the genus Morchella, the thimble morels of the genus Verpa, and a genus of cup-shaped fungi Disciotis. The remaining four genera produce the sequestrate fruit bodies.
The Burgess Shale of British Columbia is famous for its exceptional preservation of mid-Cambrian organisms. Around 69 other sites have been discovered of a similar age, with soft tissues preserved in a similar, though not identical, fashion. Additional sites with a similar form of preservation are known from the Ediacaran and Ordovician periods.

Geoglossaceae is a family of fungi in the order Geoglossales, class Geoglossomycetes. These fungi are broadly known as earth tongues. The ascocarps of most species in the family Geoglossaceae are terrestrial and are generally small, dark in color, and club-shaped with a height of 2–8 cm. The ascospores are typically light-brown to dark-brown and are often multiseptate. Other species of fungi have been known to parasitize ascocarps. The use of a compound microscope is needed for accurate identification.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1873.

CDPPB is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a positive allosteric modulator selective for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. It has antipsychotic effects in animal models, and mGluR5 modulators are under investigation as potential drugs for the treatment of schizophrenia, as well as other applications.

Primocandelabrum is a genus of rangeomorph known from the Avalon-type Ediacaran biota. It makes up the brunt of some bedding plane assemblages. Primocandelabrum was described by Hofmann, O'Brien, and King in 2008.

Dawsonia is a genus of acrocarpous mosses. Dawsonia, along with other members of the order Polytrichales, are taller than most mosses and have thicker leaves. Their sporophytes have conducting systems analogous to those of vascular plants. Dawsonia superba is found in New Zealand, Australia and New Guinea. D. longifolia is found in the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Australia. There is uncertainty as to whether D. superba and D. longifolia are actually distinct species.

Tetragraptus approximatus is a species of dichograptid graptolite belonging to the genus Tetragraptus. It existed during the Floian Age of the Ordovician. It is an important index fossil in biostratigraphy.

Dawsonia superba is a moss in the family Polytrichaceae that is found in Australia, New Guinea, Malaysia and New Zealand. D. superba is the tallest self-supporting moss in the world, reaching heights of 60 cm (24 in). It has analogous structures to those in vascular plants that support large size, including hydroid and leptoid cells to conduct water and photosynthate, and lamellae that provide gas chambers for more efficient photosynthesis. D. superba is a member of the class Polytrichopsida, although it has a sporophyte that is unique from other hair-cap mosses.
The Anthropocene Working Group (AWG) is an interdisciplinary research group dedicated to the study of the Anthropocene as a geological time unit. It was established in 2009 as part of the Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy (SQS), a constituent body of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). As of 2021, the research group features 37 members, with the physical geographer Simon Turner as Secretary and the geologist Colin Neil Waters as chair of the group. The late Nobel Prize-winning Paul Crutzen, who popularized the word 'Anthropocene' in 2000, had also been a member of the group until he died on January 28, 2021. The main goal of the AWG is providing scientific evidence robust enough for the Anthropocene to be formally ratified by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) as an epoch within the Geologic time scale.
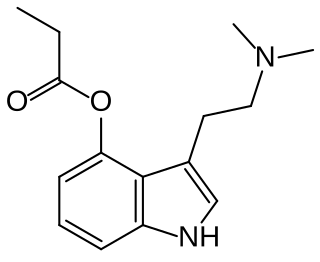
4-Propionoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine is a synthetic psychedelic drug from the tryptamine family with psychedelic effects, and is believed to act as a prodrug for psilocin. It produces a head-twitch response in mice. It has been sold online as a designer drug since May 2019. It was first identified as a new psychoactive substance in Sweden, in July 2019. A number of related derivatives have been synthesised as prodrugs of psilocin for medical applications.















