
Cinnamaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula or C₆H₅CH=CHCHO. Occurring naturally as predominantly the trans (E) isomer, it gives cinnamon its flavor and odor. It is a phenylpropanoid that is naturally synthesized by the shikimate pathway. This pale yellow, viscous liquid occurs in the bark of cinnamon trees and other species of the genus Cinnamomum. It is an essential oil. The bark of cinnamon tree contains high concentrations of cinnamaldehyde.

Isobutyric acid, also known as 2-methylpropanoic acid or isobutanoic acid, is a carboxylic acid with structural formula (CH3)2CHCOOH. It is an isomer of butyric acid. It is classified as a short-chain fatty acid. Deprotonation or esterification gives derivatives called isobutyrates.

Cinnamic acid is an organic compound with the formula C6H5-CH=CH-COOH. It is a white crystalline compound that is slightly soluble in water, and freely soluble in many organic solvents. Classified as an unsaturated carboxylic acid, it occurs naturally in a number of plants. It exists as both a cis and a trans isomer, although the latter is more common.
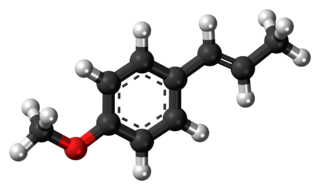
Anethole is an organic compound that is widely used as a flavoring substance. It is a derivative of the aromatic compound allylbenzene and occurs widely in the essential oils of plants. It is in the class of phenylpropanoid organic compounds. It contributes a large component of the odor and flavor of anise and fennel, anise myrtle (Myrtaceae), liquorice (Fabaceae), magnolia blossoms, and star anise (Schisandraceae). Closely related to anethole is its isomer estragole, which is abundant in tarragon (Asteraceae) and basil (Lamiaceae), and has a flavor reminiscent of anise. It is a colorless, fragrant, mildly volatile liquid. Anethole is only slightly soluble in water but exhibits high solubility in ethanol. This trait causes certain anise-flavored liqueurs to become opaque when diluted with water; this is called the ouzo effect.
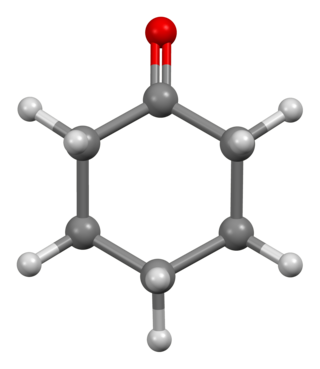
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has a sweet odor reminiscent of benzaldehyde. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Millions of tonnes are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon.

Carvone is a member of a family of chemicals called terpenoids. Carvone is found naturally in many essential oils, but is most abundant in the oils from seeds of caraway, spearmint, and dill.

Limonene is a colorless liquid aliphatic hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic monoterpene, and is the major component in the essential oil of citrus fruit peels. The (+)-isomer, occurring more commonly in nature as the fragrance of oranges, is a flavoring agent in food manufacturing. It is also used in chemical synthesis as a precursor to carvone and as a renewables-based solvent in cleaning products. The less common (-)-isomer has a piny, turpentine-like odor, and is found in the edible parts of such plants as caraway, dill, and bergamot orange plants.
Dodecanol, or lauryl alcohol, is an organic compound produced industrially from palm kernel oil or coconut oil. It is a fatty alcohol. Sulfate esters of lauryl alcohol, especially sodium lauryl sulfate, are very widely used as surfactants. Sodium lauryl sulfate and the related dodecanol derivatives ammonium lauryl sulfate and sodium laureth sulfate are all used in shampoos. Dodecanol is tasteless, colorless, and has a floral odor.

Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced in 2005.
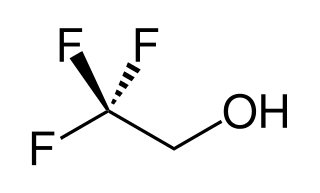
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol is the organic compound with the formula CF3CH2OH. Also known as TFE or trifluoroethyl alcohol, this colourless, water-miscible liquid has a smell reminiscent of ethanol. Due to the electronegativity of the trifluoromethyl group, this alcohol exhibits a stronger acidic character compared to ethanol.
Carvacrol, or cymophenol, C6H3(CH3)(OH)C3H7, is a monoterpenoid phenol. It has a characteristic pungent, warm odor of oregano.

Pulegone is a naturally occurring organic compound obtained from the essential oils of a variety of plants such as Nepeta cataria (catnip), Mentha piperita, and pennyroyal. It is classified as a monoterpene.

Bromoacetone is an organic compound with the formula CH3COCH2Br. It is a colorless liquid although impure samples appear yellow or even brown. It is a lachrymatory agent and a precursor to other organic compounds.
Salicylic aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4OH(CHO). Along with 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, it is one of the three isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde. This colorless oily liquid has a bitter almond odor at higher concentration. Salicylaldehyde is a precursor to coumarin and a variety of chelating agents.
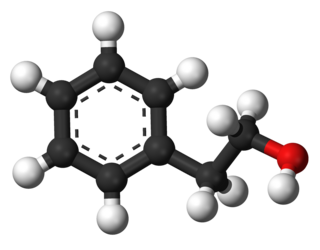
Phenethyl alcohol, or 2-phenylethanol, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2CH2OH. It is a colourless liquid with a pleasant floral odor. It occurs widely in nature, being found in a variety of essential oils. It is slightly soluble in water, but miscible with most organic solvents. The molecule of phenethyl alcohol consists of a phenethyl group attached to a hydroxyl group.

n-Butylamine is an organic compound (specifically, an amine) with the formula CH3(CH2)3NH2. This colourless liquid is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being sec-butylamine, tert-butylamine, and isobutylamine. It is a liquid having the fishy, ammonia-like odor common to amines. The liquid acquires a yellow color upon storage in air. It is soluble in all organic solvents. Its vapours are heavier than air and it produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion.

Furaneol, or strawberry furanone, is an organic compound used in the flavor and perfume industry. It is formally a derivative of furan. It is a white or colorless solid that is soluble in water and organic solvents.
Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is among the simplest aromatic aldehydes and one of the most industrially useful.
Fatty aldehydes are aliphatic, long-chain aldehydes which may be mono- or polyunsaturated. The fatty aldehydes include compounds such as octanal, nonanal, decanal or dodecanal. The nomenclature is derived from the nomenclature of the alkanes, the ending -al is added to indicate the aldehyde group.

4-Methylcyclohexanemethanol (MCHM, systematic name 4-methylcyclohexylmethanol) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H10CH2OH. Classified as a saturated higher alicyclic primary alcohol. Both cis and trans isomers exist, depending on the relative positions of the methyl (CH3) and hydroxymethyl (CH2OH) groups on the cyclohexane ring. Commercial samples of MCHM consists of a mixture of these isomers as well as other components that vary with the supplier.
















