
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles starting with Cuba, to the east by the Lesser Antilles, and to the south by the northern coast of South America. The Gulf of Mexico lies to the northwest.

Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life, organisms in the sea. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy.

Marine mammals are mammals that rely on marine (saltwater) ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as cetaceans, pinnipeds, sirenians, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine environments for feeding and survival.

Pinnipeds, commonly known as seals, are a widely distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semi-aquatic, mostly marine mammals. They comprise the extant families Odobenidae, Otariidae, and Phocidae, with 34 extant species and more than 50 extinct species described from fossils. While seals were historically thought to have descended from two ancestral lines, molecular evidence supports them as a monophyletic lineage. Pinnipeds belong to the suborder Caniformia of the order Carnivora; their closest living relatives are musteloids, having diverged about 50 million years ago.

Sea turtles, sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, Kemp's ridley, and olive ridley. Six of the seven sea turtle species, all but the flatback, are present in U.S. waters, and are listed as endangered and/or threatened under the Endangered Species Act. All but the flatback turtle are listed as threatened with extinction globally on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. The flatback turtle is found only in the waters of Australia, Papua New Guinea, and Indonesia.

The Philippine Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean east of the Philippine Archipelago and the largest sea in the world, occupying an estimated surface area of 5 million square kilometers. The Philippine Sea Plate forms the floor of the sea. Its western border is the first island chain to the west, comprising the Ryukyu Islands in the northwest and Taiwan in the west. Its southwestern border comprises the Philippine islands of Luzon, Catanduanes, Samar, Leyte, and Mindanao. Its northern border comprises the Japanese islands of Honshu, Shikoku and Kyūshū. Its eastern border is the second island chain to the east, comprising the Bonin Islands and Iwo Jima in the northeast, the Mariana Islands in the due east, and Halmahera, Palau, Yap and Ulithi in the southeast. Its southern border is Indonesia's Morotai Island.

The Coral Sea is a marginal sea of the South Pacific off the northeast coast of Australia, and classified as an interim Australian bioregion. The Coral Sea extends 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) down the Australian northeast coast. Most of it is protected by the French Natural Park of the Coral Sea and the Australian Coral Sea Marine Park. The sea was the location for the Battle of the Coral Sea, a major confrontation during World War II between the navies of the Empire of Japan, and the United States and Australia.
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word pelagic is derived from Ancient Greek πέλαγος (pélagos) 'open sea'. The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients all change. Somewhat analogous to stratification in the Earth's atmosphere, but depending on how deep the water is, the water column can be divided vertically into up to five different layers.

Sea slug is a common name for some marine invertebrates with varying levels of resemblance to terrestrial slugs. Most creatures known as sea slugs are gastropods, i.e. they are sea snails that over evolutionary time have either completely lost their shells, or have seemingly lost their shells due to having a greatly reduced or internal shell. The name "sea slug" is most often applied to nudibranchs, as well as to a paraphyletic set of other marine gastropods without obvious shells.

Marine ecosystems are the largest of Earth's aquatic ecosystems and exist in waters that have a high salt content. These systems contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have a lower salt content. Marine waters cover more than 70% of the surface of the Earth and account for more than 97% of Earth's water supply and 90% of habitable space on Earth. Seawater has an average salinity of 35 parts per thousand of water. Actual salinity varies among different marine ecosystems. Marine ecosystems can be divided into many zones depending upon water depth and shoreline features. The oceanic zone is the vast open part of the ocean where animals such as whales, sharks, and tuna live. The benthic zone consists of substrates below water where many invertebrates live. The intertidal zone is the area between high and low tides. Other near-shore (neritic) zones can include mudflats, seagrass meadows, mangroves, rocky intertidal systems, salt marshes, coral reefs, lagoons. In the deep water, hydrothermal vents may occur where chemosynthetic sulfur bacteria form the base of the food web.

Provannidae is a family of deep water sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the superfmaily Abyssochrysoidea.

Diastomatidae is a family of sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the superfamily Cerithioidea.

Abyssochrysos melanioides is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Abyssochrysidae.
Desbruyeresia cancellata is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae.
Desbruyeresia marianensis is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae.
Desbruyeresia marisindica is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae.
Desbruyeresia spinosa is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae.

Abyssochrysos is a genus of bathyal sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Abyssochrysidae.
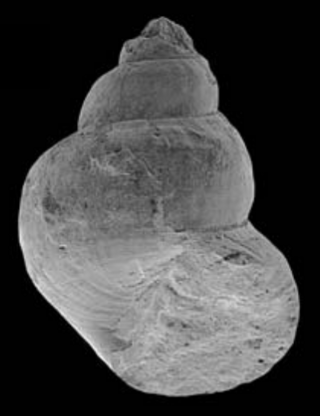
Provanna is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Provannidae.

Margarya melanioides is a species of large operculate freshwater snail, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Viviparidae, the river snails.












