
Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other types of material. As a method of printmaking, it is, along with engraving, the most important technique for old master prints, and remains in wide use today. In a number of modern variants such as microfabrication etching and photochemical milling, it is a crucial technique in much modern technology, including circuit boards.

Sir Francis Seymour Haden PPRE, was an English surgeon, better known as an original etcher who championed original printmaking. He was at the heart of the Etching Revival in Britain, and one of the founders of the Society of Painter-Etchers, now the Royal Society of Painter-Printmakers, as its first president. He was also a collector and scholar of Rembrandt's prints.

The etching revival was the re-emergence and invigoration of etching as an original form of printmaking during the period approximately from 1850 to 1930. The main centres were France, Britain and the United States, but other countries, such as the Netherlands, also participated. A strong collector's market developed, with the most sought-after artists achieving very high prices. This came to an abrupt end after the 1929 Wall Street crash wrecked what had become a very strong market among collectors, at a time when the typical style of the movement, still based on 19th-century developments, was becoming outdated.

Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn, usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker and draughtsman. An innovative and prolific master in three media, he is generally considered one of the greatest visual artists in the history of art and the most important in Dutch art history. It is estimated Rembrandt produced a total of about three hundred paintings, three hundred etchings and two thousand drawings.

An old master print is a work of art produced by a printing process within the Western tradition. The term remains current in the art trade, and there is no easy alternative in English to distinguish the works of "fine art" produced in printmaking from the vast range of decorative, utilitarian and popular prints that grew rapidly alongside the artistic print from the 15th century onwards. Fifteenth-century prints are sufficiently rare that they are classed as old master prints even if they are of crude or merely workmanlike artistic quality. A date of about 1830 is usually taken as marking the end of the period whose prints are covered by this term.

In printmaking, a state is a different form of a print, caused by a deliberate and permanent change to a matrix such as a copper plate or woodblock.

The Hundred Guilder Print is an etching by Rembrandt. The etching's popular name derives from the large sum of money supposedly once paid for an example. It is also called Christ healing the sick, Christ with the Sick around Him, Receiving Little Children, or Christ preaching, since the print depicts multiple events from Matthew 19 in the New Testament, including Christ healing the sick, debating with scholars and calling on children to come to him. The rich young man mentioned in the chapter is leaving through the gateway on the right.

Joseph and Potiphar's Wife is a 1634 etching by Rembrandt. It depicts a story from the Bible, wherein Potiphar's Wife attempts to seduce Joseph. It is signed and dated "Rembrandt f. 1634", and exists in two states.

The dozens of self-portraits by Rembrandt were an important part of his oeuvre. Rembrandt created approaching one hundred self-portraits including over forty paintings, thirty-one etchings and about seven drawings; some remain uncertain as to the identity of either the subject or the artist, or the definition of a portrait.

The Raising of Lazarus is an oil-on-panel painting by the Dutch artist Rembrandt from early in his career; it was probably painted between 1630 and 1632. The work depicts the Raising of Lazarus as told in the Gospel of John, Chapter 11. It is in the collection of the Los Angeles County Museum of Art.

The Three Crosses is a 1653 print in etching and drypoint by the Dutch artist Rembrandt van Rijn, which depicts the crucifixion of Jesus Christ. Most of his prints are mainly in etching and this one is a drypoint with burin adjustments from the third state onwards. It is considered "one of the most dynamic prints ever made".

The Goldweigher's Field is a 1651 etching by Rembrandt now held by many museums, including the British Museum, the Rijksmuseum, and the Metropolitan Museum of Art. It is based on a landscape drawing in the collection of the Museum Boijmans van Beuningen.

The Artist and his Model is a print by Rembrandt, known in two states, both incomplete. Copies of the work are in the British Museum, the Rijksmuseum, the Mikkel Museum, the Saint Louis Art Museum and many other collections. It was numbered B. 1921 by.
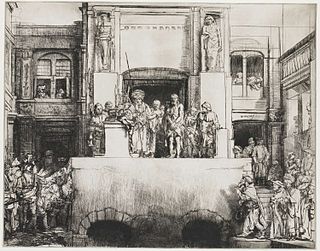
Christ Presented to the People, also known as Ostentatio Christi or Ecce Homo, is a drypoint print by Rembrandt van Rijn which exists in eight states, all c.1655. It is one of the two largest prints made by Rembrandt, about 15 by 18 inches, similar to his 1653 engraving of The Three Crosses. It has been described by Christie's as "at the summit of the western printmaking tradition".

The Mill is a 1641 print by Rembrandt, only known in a single state. Copies of it are in the Rijksmuseum, the Metropolitan Museum of Art, and most large print rooms.

Portrait of Jan Six is a 1647 etching by Rembrandt, known in five states. It shows Jan Six, also the subject of a painted portrait by the same artist.

The State Bed is a 1646 print by Rembrandt in etching and drypoint. It is also known as Le Lit à la française, a title first given to it in Edme-François Gersaint's 1751 Catalogue raisonné de toutes les pièces qui forment l’œuvre de Rembrandt.

The Shell, also known as Rembrandt's Shell or Conus Marmoreus, or in Dutch as De schelp or Het schelpje, is a 1650 drypoint and etching by Rembrandt van Rijn. Catalogued as B.159, it is Rembrandt's only still life etching. Only a handful of original prints are known, in three states.

In printmaking, surface tone, or surface-tone, is produced by deliberately or accidentally not wiping all the ink off the surface of the printing plate, so that parts of the image have a light tone from the film of ink left. Tone in printmaking meaning areas of continuous colour, as opposed to the linear marks made by an engraved or drawn line. The technique can be used with all the intaglio printmaking techniques, of which the most important are engraving, etching, drypoint, mezzotint and aquatint. It requires individual attention on the press before each impression is printed, and is mostly used by artists who print their own plates, such as Rembrandt, "the first master of this art", who made great use of it.

Rembrandt Laughing is a c. 1628 oil on copper painting by the Dutch painter Rembrandt van Rijn. It is an elaborate study of a laughing face, a tronie, and, since it represents the painter himself, one of over 40 self-portraits by Rembrandt, probably the earliest elaborate one. The painting, which was only recently discovered, is now in the J. Paul Getty Museum, California.


















