Rink history
First rink
The first rink was opened on December 20, 1884, and was located on the Rideau Canal at Waller Street and Theodore Street (today's Laurier Avenue), next to the Dey Family boat works. [1] The natural ice rink surface was 150 feet (46 m) by 60 feet (18 m). This location is today occupied by the Canadian Department of Defence headquarters, just south of the Federal Conference Centre, the old Union Station railway station. The rink was torn down in the fall of 1895 to make way for the Canada Atlantic Railway, which opened a station at Rideau Street and the Canal and laid rail tracks alongside the eastern bank of the Canal. The last hockey game at the rink was held on March 30, 1895. [1] The boat works moved to Patterson Creek at Bank Street in Ottawa.

Dey's Skating Rink: Second rink, first arena
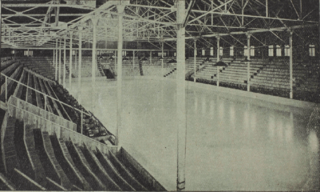
The second rink, an arena, opened on December 17, 1896. 'Dey's Skating Rink', [2] its proper name, held an estimated 3,500 spectators. The ice rink measured 200 feet (61 m) by 81 feet (25 m), one of the largest indoor ice surfaces in Canada at the time. The arena featured a bandstand that could be used as a press box, and elevated seats. This was possibly the first arena designed for ice hockey in Canada, the second in North America after the St. Nicholas Rink, which opened in New York one month earlier. Dey's Skating Rink was located at Bay and Ann (now Gladstone) Streets, the location at the time being on the city outskirts, but served by city streetcars. [3]
The first hockey game at the arena was between the Capitals of Ottawa and Cornwall on December 19, 1896. [4] The arena was the site of the first Stanley Cup win by the Ottawa Hockey Club, in 1903, and the site of numerous Stanley Cup challenge matches during the 'Silver Seven's' reign from 1903–1907, including the famous 1905 challenge of Dawson City. [3]

The arena was the site of the final game of the 1906 championship playoff between Ottawa and the Montreal Wanderers, a game labelled the "Greatest Hockey Game in History." by The Sporting News. [5] The Toronto Globe called it the "greatest game of hockey ever played on Canadian ice, or any other." [6] Although Ottawa entered the game nine goals down in a two-game playoff, fan interest was exceptional. For the game, the rink was modified to hold more spectators, including setting up temporary bleachers, removing the grandstand which had been used as a press box, and the installation of a press box attached to the rafters. Over 5,400 would attend the game and the top $2 tickets were being sold for $10. Betting interest was high, including one $12,000 bet. [7] Remarkably, Ottawa tied the series with ten minutes to play before two power play goals in the last two minutes by Lester Patrick would win it for the Wanderers. [5]
The rink was destroyed twice. In 1902, a violent summer windstorm flattened the building. It was rebuilt in time for the 1902–03 hockey season. The replacement rink followed the ice dimensions of the Montreal Arena and had semi-circular ends, rather than squared with rounded corners. [8] In 1920, fire destroyed the rink, after which it was not rebuilt. Today, the city block it occupied is mostly single-family houses. Nearby, the McNabb arena and community centre was built one block west at Percy Street and Gladstone and is operated by the City of Ottawa.
In 1997, a commemorative plaque was unveiled at the rink's location at the corner of Bay and Gladstone. The plaque was stolen on April 14, 2008, and its pedestal destroyed. [9] A new memorial marker was installed and dedicated on November 17, 2008. [10] [11]
The Arena: Third rink, second arena
The third rink was built in 1907 and was built because audiences for hockey matches had out-grown the previous arena. The spectator capacity was 7,000, of which 2,500 was standing room. At the time, it was Canada's largest arena. 'The Arena', as it was called, [12] was built on leased land on the north side of Laurier Avenue next to Rideau Canal, on the location of today's Confederation Park, across the street from the current Ottawa city hall. This is very close to the location of the first rink, on the opposite bank of the Canal. It was leased from landowner Esther Sherwood for the rate of $166.66 per month, for twenty years.
The Arena opened on January 11, 1908 for a game between Ottawa and the Montreal Wanderers, the top rivalry of the day. The last Senators game at the arena was held on March 10, 1923, after which the team moved to the Ottawa Auditorium. The Ottawa Auditorium was also built by the Deys, who were part owners of the Ottawa Senators. This third rink was torn down by the federal government at the end of the lease in 1927 to make way for the Driveway along the Rideau Canal.
The Arena was used for the sports of ice skating and figure skating as well as hockey. The 1912 Canadian Figure Skating Championships were held in February 1912 at the Arena. [13]