
Piper excelsum, commonly known as kawakawa, is a small tree of which the subspecies P. excelsum subsp. excelsum is endemic to New Zealand; the subspecies P. e. subsp. psittacorum is found on Lord Howe Island, Norfolk Island and the Kermadec Islands.

Entandrophragma is a genus of twelve known species of deciduous trees in the family Meliaceae.
Centroscyllium is a genus of big-eyed, deepwater dogfishes with no anal fin, a grey or black-brown body, and dorsal spines, with the second one being much larger than the first. Seven extant species are described.

Jubaea is a genus of palms with one species, Jubaea chilensis or Jubaea spectabilis, commonly known in English as the "Chilean wine palm" or "Chile cocopalm", and "coquito" in Spanish. It is native to southwestern South America and is endemic to a small area of central Chile between 32°S and 35°S in southern Coquimbo, Valparaíso, Santiago, O'Higgins, and northern Maule regions.

Manglares de Tumbes National Sanctuary is a protected natural area located in the region of Tumbes, Peru. Established in 1988, it protects the largest area of mangrove forest in Peru.

The highfin dogfish is a sleeper shark of the family Etmopteridae, found in the northwest Pacific Ocean on the Emperor Seamount chain between latitudes 50 and 38°N, at depths between 800 and 1,000 m. It reaches a length of 63 cm.

Anacardium excelsum, the wild cashew or espavé, is a tree in the flowering plant family Anacardiaceae. The tree is common in the tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests of Pacific and Atlantic watersheds of Central and South America, extending as far north as Guatemala and south into Ecuador.
Dialium bipindense is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found in Cameroon and Gabon. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Dialium is a genus of plants in the family Fabaceae, subfamily Dialioideae. Velvet tamarind is a common name for several species.

Dialium cochinchinense, the velvet tamarind, is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found in Ghana, Sri Lanka, Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nigeria, Thailand, Vietnam and many west African countries. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Dialium holtzii is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found in Kenya, Mozambique, and Tanzania.
Dialium lopense is a species of legume in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in Gabon. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Dialium orientale is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae.It is found in Kenya, Somalia, and Tanzania. The fruit of this tree is a popular snack in Kenya and known as pepeta. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Dialium travancoricum is a critically endangered species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in Kerala India specifically around the Travancore range near Ponmudi and Ariankavu. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Euryodendron is a genus of plant in family Pentaphylacaceae. The genus currently contains a single species, Euryodendron excelsum. It is endemic to China. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Velvet tamarind is a common name for several trees in the genus Dialium and may refer to:
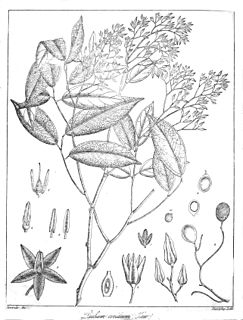
Dialium ovoideum is a tropical species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is endemic to Sri Lanka. The Sinhala name ගල් සියඹලා means "pebble tamarind". The Tamil name பட்டு புளியம் பழம் means "silky tamarind" which is named after the silky texture of the shell of the fruit..

Entandrophragma excelsum, is Africa's tallest indigenous tree native to tropical East Africa and occurs in eastern D.R.of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi, Uganda, Tanzania, Malawi and Zambia. This species is scattered in areas of upland semi-deciduous forest, in mid-altitude and montane rainforest, at 1280 – 2150 altitude. It is locally also found in riverine forest.
Arthrostylidium excelsum is a species of Arthrostylidium bamboo in the grass family.
Peter James de Lange is a New Zealand botanist. Schooled in Hamilton, he graduated from the University of Waikato as B.Sc. in biological and earth sciences then as M.Sc. in paleoecology and tephrochronostratigraphy. He has a PhD from the University of Auckland, the subject of his thesis, the biosystematics of Kunzea ericoides. From 1990 to 2017 he worked as a threatened plant scientist in the Ecosystems and Species Unit of Research and Development in the New Zealand Department of Conservation. He is an Adjunct Professor at the University of Sassari, Sardinia and now employed as an Associate Professor in the School of Environmental & Animal Sciences, Unitec Institute of Technology. He is a Fellow of the Linnean Society, recipient of the New Zealand Botanical Society Allan Mere award (2006) and also the Loder Cup (2017) for his botanical work. One plant, the Three Kings Islands endemic kawakawa (pepper) described as Macropiper excelsum subsp peltatum f. delangei and now placed in Piper, as P. excelsum subsp. delangei is named in his honour. He is the author of 30 books and 180 scientific papers.










