| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name Dichloro[1,3-propanediylbis(diphenylphosphanuide-κP)]nickel | |
| Other names 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propanenickel(II) chloride; NiCl2(dppp) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.132.628 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H26Cl2NiP2 | |
| Molar mass | 542.05 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange to red-orange powder |
| Melting point | 213 °C (415 °F; 486 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  [1] [1] | |
| Danger [1] | |
| H315, H317, H319, H334, H335, H350 [1] | |
| P201, P261, P280, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313 [1] | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External SDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
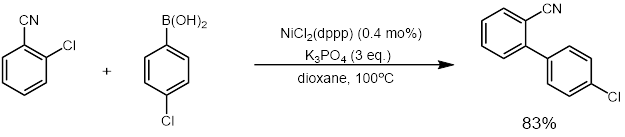
Dichloro[1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane]nickel a coordination complex with the formula NiCl2(dppp); where dppp is the diphosphine 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane. It is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. The compound is a bright orange-red crystalline powder.