
The family Fulgoridae is a large group of hemipteran insects, especially abundant and diverse in the tropics, containing over 125 genera worldwide. They are mostly of moderate to large size, many with a superficial resemblance to Lepidoptera due to their brilliant and varied coloration. Various genera and species are sometimes referred to as lanternflies or lanthorn flies, but neither do their heads emit light, nor are they even distantly related to flies.

The Auchenorrhyncha suborder of the Hemiptera contains most of the familiar members of what was called the "Homoptera" – groups such as cicadas, leafhoppers, treehoppers, planthoppers, and spittlebugs. The aphids and scale insects are the other well-known "Homoptera", and they are in the suborder Sternorrhyncha.

A planthopper is any insect in the infraorder Fulgoromorpha, in the suborder Auchenorrhyncha, a group exceeding 12,500 described species worldwide. The name comes from their remarkable resemblance to leaves and other plants of their environment and that they often "hop" for quick transportation in a similar way to that of grasshoppers. However, planthoppers generally walk very slowly. Distributed worldwide, all members of this group are plant-feeders, though few are considered pests. The infraorder contains 2 superfamily, Fulgoroidea and Delphacoidea. Fulgoroids are most reliably distinguished from the other Auchenorrhyncha by two features; the bifurcate (Y-shaped) anal vein in the forewing, and the thickened, three-segmented antennae, with a generally round or egg-shaped second segment (pedicel) that bears a fine filamentous arista.

Dictyopharidae is a family of planthoppers, related to the Fulgoridae. The family comprises nearly 760 species in more than 150 genera which are grouped into two subfamilies, Dictyopharinae and Orgeriinae.

The subfamily Aphaeninae is a group of hemipteran insects, especially abundant and diverse in the tropics, in the family Fulgoridae, or "lanternflies".

Acanalonia is a genus of planthopper and contains the majority of the species within the family Acanaloniidae. Species have been recorded from southern Europe and the Americas.

Ordralfabetix is an extinct genus of planthoppers in the family Lophopidae and containing the single species Ordralfabetix sirophatanis. The species is known only from the Early Eocene, Ypresian stage Oise amber from the Quesnoy locality, Oise Department, France.

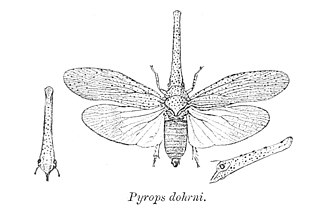
Pyrops clavatus is a species of true bug in the family Fulgoridae, in the genus Pyrops which are sometimes called "lanternflies". This species is found in parts of northern and northeastern India, Myanmar, northern Thailand, southern China and northern Vietnam. The tip of the elongated head capsule is spheroidal, shiny and chestnut in colour while the remainder of the process is black with fine white spotting. The forewing has a variable patterning of black, grey and white. The hindwing is purplish white with the apical half black. Specimens have been obtained along the Himalayas west to Mussoorie but more often in Assam, Sikkim, Shillong and the Khasi Hills.
Zanna is a genus of tropical planthoppers found in Asia and Africa, now belonging to the monotypic subfamily Zanninae.

The spotted lanternfly is a planthopper indigenous to parts of China and Vietnam. It has spread invasively to Japan, South Korea, and the United States, where it is often referred to by the acronym "SLF". Its preferred host is tree of heaven, but it infests crops including soybean, grapes, stone fruits, and Malus spp. In its native habitat, L. delicatula populations are regulated by parasitic wasps.

Penthicodes is a genus of planthoppers belonging to the family Fulgoridae, subfamily Aphaeninae: found in South-East Asia. The genus name was formerly treated as feminine, but in 2022 it was revised to masculine in accordance with ICZN Article 30.1.4.4, changing the spelling of several species' names.

Lycorma is a genus of planthoppers native to Asia. The first species within the genus was described by Frederick William Hope in 1843 and the genus was formally established by Carl Stål in 1863.

The Fulgorinae are a sub-family of insects in the Auchenorrhyncha: which include the spectacular "lantern-bugs" and allied insects.

Rhynchomitra is a genus of dictyopharid planthoppers in the family Dictyopharidae. There are about five described species in Rhynchomitra.

The subfamily Poiocerinae include Hemipteran insects in the family Fulgoridae, found especially in the tropics.

Dictyophara europaea, is the type species of planthoppers belonging to the subgenus Dictyophara (Dictyophara): in the family Dictyopharidae, and tribe Dictyopharini.

Florissantia is an extinct monotypic genus of planthopper in the dictyopharid subfamily Dictyopharinae. The single species, Florissantia elegans, was described by Samuel Hubbard Scudder (1890) from fossils found in the Florissant Formation of Colorado.

Lycorma imperialis is a planthopper indigenous to parts of China and Indo-Malaysia. L. imperialis was originally discovered in 1846 by Adam White and has one recognized non-nominate subspecies, L. i. punicea. L. imperialis has undergone a number of reclassifications since its discovery and is one of four species in the genus Lycorma. L. imperialis follows a hemimetabolous life cycle and will undergo a series of nymphal stages (instars) before maturing to an adult.

Lycorma meliae is a planthopper species endemic to Taiwan, with multiple, dramatically different color morphs depending on the life stage. The species was described by Masayo Kato in Taiwan in 1929, and is the only member of its genus confirmed to be native to the island. In 1929, a specimen of L. meliae was originally described as a separate species, L. olivacea, also by Kato. These two taxon names were declared synonymous in 2023. L. meliae undergoes four instar stages before achieving adulthood and generally only survive until the winter.

Scaralina marmorata is a species of planthopper in the family Fulgoridae, found throughout the southeastern United States. It is one of four species that were, for several decades, erroneously grouped together under a single name, Alphina glauca; this name is now treated as a synonym of S. marmorata.





















