
Christmas Island, officially known as the Territory of Christmas Island, is an Australian external territory comprising the island of the same name. It is located in the Indian Ocean, around 350 kilometres (220 mi) south of Java and Sumatra and around 1,550 km (960 mi) north-west of the closest point on the Australian mainland. It lies 2,600 km (1,600 mi) northwest of Perth and 1,327 km (825 mi) south of Singapore. It has an area of 135 square kilometres (52 sq mi).

Maclear's rat is an extinct large rat endemic to Christmas Island in the Indian Ocean. It was one of two species of rat native to Christmas Island, alongside the bulldog rat. Abundant, unfamiliar with and seemingly unafraid of humans, large numbers of the creatures emerged and foraged in all directions at night. Making querulous squeaks, the rats entered the Challenger Expedition's tents and shelters in 1886, ran over sleepers, and upset everything in the search and fight for food. Maclear's rat might have been responsible for keeping the population of the Christmas Island red crab in check, as recent numbers of the crab are greater than in the past. It is thought that black rats inadvertently introduced by the expedition infected the Maclear's rats with a disease, which in turn could have contributed to the species' decline. The last recorded sighting was in 1903, although it is possible that Maclear's rats hybridized with black rats. A hard tick, described as an ectoparasite of Maclear's rat, is also thought to be extinct.

The Christmas imperial pigeon, Black imperial pigeon, Dusky imperial pigeon, Wharton's imperial pigeon, or burong pergam, is a large imperial pigeon endemic to Christmas Island in the northeastern Indian Ocean. It has an overall grey-blue colouration, and juveniles are duller than adults. It makes a soft purring coo sound and a deeper whoo sound comparable to a cow mooing. It lays one glossy white egg per brood, and is possibly somewhat colonial.

John Fiot Lee Pearse Maclear was an admiral in the Royal Navy, known for his leadership in hydrography.
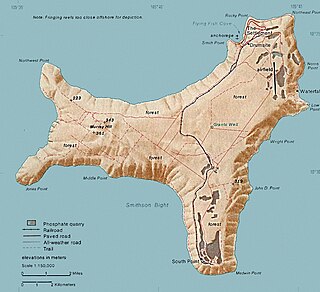
Murray Hill is the highest point of Christmas Island, at 357 metres (1,171 ft) above sea level. It was first scaled in 1857 even though the island had been located in 1615.

HMS Flying Fish was a Fantome-class sloop of the Royal Navy, built at Chatham Dockyard and launched on 27 November 1873. Originally intended to be named Daring, she was renamed Flying Fish before launch on 14 January 1873.

Hoya aldrichii , commonly known as the Christmas Island Waxvine is a species of flowering plant in the Apocynaceae or dogbane family. It is a vine that is endemic to Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the north-eastern Indian Ocean, where it is a common epiphyte in the shrublands of the island's coastal terraces. The specific epithet honours Captain Aldrich, commander of the survey vessel HMS Egeria, which visited Christmas Island in 1887.

Pandanus christmatensis is a dioecious tropical plant in the screwpine genus. It is endemic to Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the north-eastern Indian Ocean. The specific epithet, "christmatensis", comes from its native locality.
Pandanus elatus is a dioecious tropical plant in the screwpine genus. It is endemic to Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the north-eastern Indian Ocean. Its specific epithet comes from the Latin elatus (tall), in reference to its growth habit.
Abutilon listeri , commonly known as the lantern flower, is a tropical shrub in the Malvaceae or mallow family. It is endemic to Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the north-eastern Indian Ocean. Its specific epithet honours British zoologist and plant collector Joseph Jackson Lister, who visited the island on HMS Egeria in 1887.
Asystasia alba is a species of tropical herb in the family Acanthaceae. It is endemic to Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the north-eastern Indian Ocean. Its specific epithet comes from the Latin alba (white), referring to the colour of its flowers.
Colubrina pedunculata is a shrub in the family Rhamnaceae. It is endemic to Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the north-eastern Indian Ocean. Its specific epithet comes from the Latin pedunculatus, referring to the long and conspicuous peduncle of the inflorescence.
Peperomia rossii is a species of plant in the family Piperaceae. It is endemic to Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the northeastern Indian Ocean. Its specific epithet honours the Clunies-Ross family which established the Flying Fish Cove settlement on Christmas Island in 1888.
Brachypeza archytas, commonly known as the sage orchid, is an epiphytic orchid that is endemic to Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the north-eastern Indian Ocean. It has many cord-like roots, four or five leaves arranged like a fan and a large number of small, crowded, short-lived, white flowers.
Dendrobium nativitatis, commonly known as the Christmas Island crimp orchid, is a species of epiphytic orchid that is endemic to Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the north-eastern Indian Ocean. It has long, straggly stems, flattened pseudobulbs, a single leathery leaf and a single pale yellow flower.
Phreatia listeri, commonly known as the Christmas Island caterpillar orchid, is a plant in the orchid family and is an epiphyte with four to six flat, blunt leaves in a fan-like arrangement. A large number of tiny, greenish white flowers are arranged along a thin flowering stem. It is endemic to Christmas Island.

Cycas rumphii, commonly known as queen sago or the queen sago palm, is a dioecious gymnosperm, a species of cycad in the genus Cycas native to Indonesia, New Guinea and Christmas Island. Although palm-like in appearance, it is not a palm.
Claoxylon indicum is a dioecious flowering plant in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. The specific epithet comes from the Latin Indicus (Indian), referring to the locality of collection of the type specimen, which was probably Java, part of the Dutch East Indies at that time.

The Christmas Island flying fox or Christmas Island fruit bat, as the name suggests, is a flying fox endemic to Christmas Island. It is unclear if it should be considered a distinct species, or a subspecies of the black-eared flying fox. It may descend from a population of island flying foxes from Pulau Panjang near Java.

The wildlife of Christmas Island is composed of the flora and fauna of this isolated island in the tropical Indian Ocean. Christmas Island is the summit plateau of an underwater volcano. It is mostly clad in tropical rainforest and has karst, cliffs, wetlands, coasts and sea. It is a small island with a land area of 135 km2 (52 sq mi), 63% of which has been declared a National park. Most of the rainforest remains intact and supports a large range of endemic species of animals and plants.










