
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 is the primary law in the United States for protecting and conserving imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of economic growth and development untempered by adequate concern and conservation", the ESA was signed into law by President Richard Nixon on December 28, 1973. The Supreme Court of the United States described it as "the most comprehensive legislation for the preservation of endangered species enacted by any nation". The purposes of the ESA are two-fold: to prevent extinction and to recover species to the point where the law's protections are not needed. It therefore "protect[s] species and the ecosystems upon which they depend" through different mechanisms. For example, section 4 requires the agencies overseeing the Act to designate imperiled species as threatened or endangered. Section 9 prohibits unlawful 'take,' of such species, which means to "harass, harm, hunt..." Section 7 directs federal agencies to use their authorities to help conserve listed species. The Act also serves as the enacting legislation to carry out the provisions outlined in The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES).

The pallid sturgeon is an endangered species of ray-finned fish, endemic to the waters of the Missouri and lower Mississippi River basins of the United States. It may have even reached the St. Croix River before colonization.

The giant Palouse earthworm or Washington giant earthworm is a species of earthworm belonging to the genus Driloleirus inhabiting the Palouse region of Eastern Washington and North Idaho, in the United States. The worm was discovered in 1897 by Frank Smith near Pullman, Washington. It can burrow to a depth of 15 feet (4.6 m).

Fender's blue butterfly is a subspecies of Boisduval's blue endemic to the Willamette Valley of northwestern Oregon, United States. The potential range of the butterfly extends from south and west of Portland, OR to south of Eugene, OR. The butterfly is host-specific on the Kincaid's lupine, which it relies on for reproduction and growth. The male and female can be identified by their difference in wing color. The Fender's Blue Butterfly was added to the endangered species list in January 2000, but as of February of 2023, has been reclassified as "threatened". The Fender's blue butterfly population has increased over the past 20 years and projected to increase more through conservation efforts. In Willamette Valley, Oregon, there are currently 90 sites filled with Fender's blue.

Amaranthus brownii was an annual herb in the family Amaranthaceae. The plant was found only on the small island of Nihoa in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands, growing on rocky outcrops at altitudes of 120–215 m (394–705 ft). It was one of nine species of Amaranthus in the Hawaiian Islands, as well as the only endemic Hawaiian species of the genus. It is now considered extinct.

The Kanab ambersnail, formerly classified as Oxyloma haydeni kanabense or Oxyloma kanabense, is a small, air-breathing land snail belonging to the family Succineidae, the ambersnails. This terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusc was previously considered a critically endangered subspecies or species. In 2013, a scientific investigations report by the United States Geological Survey concluded that the Kanab ambersnail is not a genetically distinct species. In June 2021, the Fish and Wildlife Service removed the Kanab ambersnail from the United States Fish and Wildlife Service list of endangered mammals and birds and classified it with other common ambersnails within the same taxa, officially negating its status as a distinct subspecies.
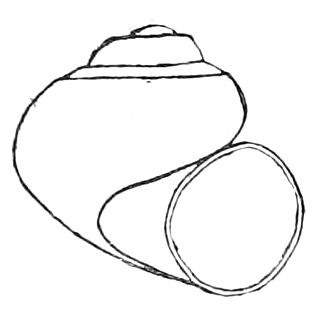
The Utah roundmouth snail, also known as the Utah valvata or desert valvata, scientific name Valvata utahensis, is a species of freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusc in the family Valvatidae, the valve snails.

Eleodes is a genus of darkling beetles, in the family Tenebrionidae. They are endemic to western North America ranging from southern Canada to central Mexico with many species found along the Mexico-United States border. Some species have been introduced to Colombia. The name pinacate is Mexican Spanish, derived from the Nahuatl (Aztec) name for the insect, pinacatl, which translates as "black beetle".
The Coffin Cave mold beetle, also known as the Inner Space Caverns mold beetle, is a small insect that is only found in caves. They are very small at 2.60–2.88 mm (0.102–0.113 in) and lack any form of eyes. They are found exclusively in caves in a single county in Texas, Williamson County. The United States Fish and Wildlife Service considers the Coffin Cave mold beetle to be an endangered species. Threats facing this species include urbanization.
The Death Valley June beetle is a scarab beetle in the subfamily Melolonthinae. It is only known to occur in the drainage basin of the Amargosa River in the southwestern United States. Saltgrass communities, such as those at Saratoga Springs in Death Valley, provide habitat for the insect at all stages of its life.

The Tooth Cave ground beetle, Rhadine persephone, is an endemic beetle that lives only in karst caves in Texas. These arthropods belong to the family Carabidae. The United States government considers these beetles endangered because they are only found in a single cave system. If these caves are destroyed, this beetle will likely go extinct. The cave system is currently threatened by pollution, urban development, and invasion by fire ants.

Casey's June beetle, Dinacoma caseyi, is a beetle in the scarab family (Scarabaeidae). It is listed as an endangered species with approximately 587 acres of land as critical habitat in Riverside County, California. Their habitation range is limited to Palm Canyon Walsh and Tahquitz Creek in Palm Springs.
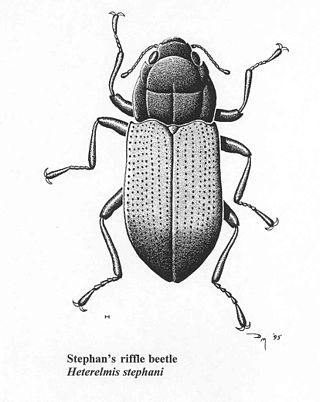
Heterelmis stephani was a rare species of aquatic beetle known by the common name Stephan's riffle beetle. It was endemic to Arizona in the United States, where it occurred in the Santa Rita Mountains before being declared presumed extinct. It was brown in color with small black dots on its wings.

Cartwrightia is a genus of scarab found in Latin America. It was named and circumscribed in 1958 by Federico Islas Salas. As of 2017, three species are recognized: C. intertribalis, C. cartwrighti, and C. islasi. They can be found in the nests of leafcutter ants or in dung.
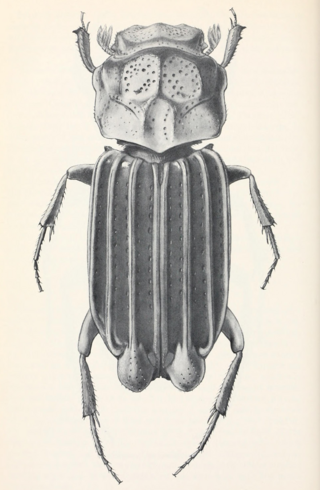
Cartwrightia cartwrighti is a species of aphodiine scarab found in South America. Oscar L. Cartwright named the species in 1967 after his brother. C. cartwrighti has been recorded in cow dung in pastures and forests.

Holcaspis brevicula, the Eyrewell ground beetle, is a species of carabid beetle native to New Zealand, one of a number of small black flightless beetles in the genus Holcaspis that inhabit the dry eastern lowlands of the South Island. H. brevicula is very rare—only ten specimens have ever been collected—and critically endangered: the species was found only in Eyrewell Forest, a single plantation of exotic pine trees currently being converted into dairy farms.

Sonorella neglecta is a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusc in the subfamily Helminthoglyptinae. Sonorella is a genus of large land snails consisting of over 80 species, with new ones continuing to be described. The shells typically differ only rather subtly, but proportions of the genitalia differentiate species. The genus is distributed in the southwestern USA and northern Mexico, with individual species often restricted to a single mountain massif or to a small part of one. Sonorella neglecta is such a narrow-range endemic from the Chiricahua Mountains. Its official vernacular name is the Portal Talussnail.

Horelophus walkeri is a small water scavenger beetle that is endemic to New Zealand. It is found in the South Island in the West Coast, Nelson, Buller and Marlborough regions. The preferred habitat of this species are the moss and crevices within the splash zone of waterfalls sourced from fast flowing, clear, cool waterways. The larvae of this species are carnivorous while the adults are herbivores or scavengers. In 2012 the Department of Conservation classified this beetle as Nationally Endangered.
Delphinium caseyi, also known as Casey's larkspur, is a flowering plant within the family Ranunculaceae.
















