
Celia Thaxter was an American writer of poetry and stories. For most of her life, she lived with her father on the Isles of Shoals at his Appledore Hotel. How she grew up to become a writer is detailed in her early autobiography, and her book entitled Among the Isles of Shoals. Thaxter became one of America's favorite authors in the late 19th century. Among her best-known poems are "The Burgomaster Gull", "Landlocked", "Milking", "The Great White Owl", "The Kingfisher", and "The Sandpiper". Many of her romantic poems are addressed to women; as such, she has been identified by some scholars as a lesbian poet.

The Laboulbeniomycetes are a unique group of fungi that are obligatorily associated with arthropods, either as external parasites or for dispersal (Pyxidiophorales).

The Laboulbeniales is an order of fungi within the class Laboulbeniomycetes. They are also known by the colloquial name beetle hangers or labouls. The order includes around 2,325 species of obligate insect ectoparasites that produce cellular thalli from two-celled ascospores. Of the described Laboulbeniales, Weir and Hammond 1997 find 80% to be from Coleoptera and the next largest group to be the 10% from Diptera. Recently, the genus Herpomyces, traditionally considered a basal member of Laboulbeniales, was transferred to the order Herpomycetales based on molecular phylogenetic data. Laboulbeniales typically do not kill their hosts, although they may impair host fitness if the parasite density is high.

The Entomophthorales are an order of fungi that were previously classified in the class Zygomycetes. A new subdivision, Entomophthoromycotina, in 2007, was circumscribed for them.

Taphrina is a fungal genus within the Ascomycota that causes leaf and catkin curl diseases and witch's brooms of certain flowering plants. One of the more commonly observed species causes peach leaf curl. Taphrina typically grow as yeasts during one phase of their life cycles, then infect plant tissues in which typical hyphae are formed, and ultimately they form a naked layer of asci on the deformed, often brightly pigmented surfaces of their hosts. No discrete fruit body is formed outside of the gall-like or blister-like tissues of the hosts. The asci form a layer lacking paraphyses, and they lack croziers. The ascospores frequently bud into multiple yeast cells within the asci. Phylogenetically, Taphrina is a member of a basal group within the Ascomycota, and type genus for the subphylum Taphrinomycotina, the class Taphrinomycetes, and order Taphrinales.

Blakeslea trispora is a mould and member of the division Zygomycota. This species has been well studied for its ability to produce carotenoids, particularly, β-carotene and lycopene. β-carotene is a vitamin A precursor and both of β-carotene and lycopene play a significant role in the inhibition of oxidative stress. Blakeslea trispora is commonly isolated from soil samples throughout the Southern United States and Southern Asia. B. trispora is a pathogen of tropical plants. In vivo pathogenicity testing using animal models suggests this fungus is not a cause of animal or human disease.

Capnodiales is a diverse order of Dothideomycetes, initially based on the family Capnodiaceae, also known as sooty mold fungi. Sooty molds grow as epiphytes, forming masses of black cells on plant leaves and are often associated with the honeydew secreted by insects feeding on plant sap. This diverse order has been expanded by the addition of several families formerly thought unrelated and now also includes saprobes, endophytes, plant pathogens, lichens and rock-inhabiting fungi. The new additions include the genus Mycosphaerella containing the causal agents of several economically important crop and tree diseases. A small number of these fungi are also able to parasitise humans and animals, including species able to colonise human hair shafts.
Protogastraceae is a family of fungi in the order Boletales that contains the single genus Protogaster. The genus in turn contains the single species Protogaster rhizophilus, found on the roots of Viola in the USA. The family was described by American mycologist Sanford Myron Zeller in 1934, the genus and species by Roland Thaxter.

Mucoromycotina is a subphylum of uncertain placement in Fungi. It was considered part of the phylum Zygomycota, but recent phylogenetic studies have shown that it was polyphyletic and thus split into several groups, it is now thought to be a paraphyletic grouping. Mucoromycotina is currently composed of 3 orders, 61 genera, and 325 species. Some common characteristics seen throughout the species include: development of coenocytic mycelium, saprotrophic lifestyles, and filamentous.

The Basidiobolaceae are a family of fungi in the monotypic order Basidiobolales. All fungal cells of this family are exclusively uninucleate and their relatively large nuclei contain a nucleolus, but no heterochromatin.

The Mortierellaceae are a family of fungi in the order Mortierellales. The family contains six genera and 93 species.
Hydrophilomyces is a genus of fungi in the family Laboulbeniaceae. It was circumscribed by American mycologist Roland Thaxter in 1908. The genus contain 12 species.

Roland Thaxter was an American mycologist, plant pathologist, botanist, and entomologist, renowned for his contribution to the insect parasitic fungi—Laboulbeniales. His college education was completed at Harvard, where he dedicated forty years to mycological and botanical research. His five-volume series on fungi in the order Laboulbeniales laid a solid foundation of research on these insect ectoparasites. He also contributed to the field of Plant Pathology.

Wynnea is a genus of fungi in the family Sarcoscyphaceae. Circumscribed by Miles Joseph Berkeley and Moses Ashley Curtis in 1867, the genus contains seven species that have ear-shaped fruit bodies that grow on the ground. Wynnea species have a worldwide distribution and have been collected from the United States, Costa Rica, India, and China.

Wynnea americana, commonly known as moose antlers or rabbit ears, is a species of fungus in the family Sarcoscyphaceae. The uncommon species is recognizable by its spoon-shaped or rabbit ear–shaped fruit bodies that may reach up to 13 cm (5 in) tall. It has dark brown and warty outer surfaces, while the fertile spore-bearing inner surface is orange to pinkish to reddish brown. It is distinguished from other species in its genus by the pustules on the outer surface, and microscopically by the large asymmetrical longitudinally ribbed spores with a sharply pointed tip. The spores are made in structures called asci, which have thickened rings at one end that are capped by a hinged structure known as the operculum—a lid that opens to release spores from the ascus.

Endogone is a genus of fungi in the family Endogonaceae of the division Zygomycota. The genus has a widespread distribution, especially in temperate regions, and contains about 20 species.

Entomophthoromycota is a division of kingdom fungi. In 2007, it was placed at the taxonomic rank of subphylum in the most recent revision of the entire fungus kingdom. In 2012, it was raised to the rank of phylum as "Entomophthoromycota" in a scientific paper by Richard A. Humber 2012. Divided into three classes and six families, it contains over 250 species that are mostly arthropod pathogens or soil- and litter-borne saprobes.

Edward Angus Burt was an American mycologist and an authority on the resupinate fungus family Thelephoraceae. He received his M.A. in 1894 and PhD. in 1895, both from Harvard University under William G. Farlow and Roland Thaxter. He became a Professor of Natural History at Middlebury College in 1895, then both a Professor of Botany at the Henry Shaw School of Botany at Washington University in St. Louis, and a mycologist for the Missouri Botanical Garden in 1913. He also worked on a systematic description of basidiomycetes such as Merulius and fungi from Vermont, Siberia, and Java.
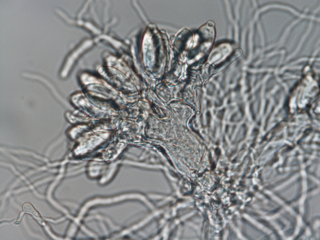
Blastocladia is a genus of aquatic fungi.

Basidiobolomycetes is one of the currently recognized classes within the kingdom Fungi, and subdivision Basidiobolomycotina.
















