
Myliobatiformes is one of the four orders of batoids, cartilaginous fishes related to sharks. They were formerly included in the order Rajiformes, but more recent phylogenetic studies have shown the myliobatiforms to be a monophyletic group, and its more derived members evolved their highly flattened shapes independently of the skates.

Scyliorhinus is a genus of catsharks in the family Scyliorhinidae. This genus is known in the fossil records from the Cretaceous period, late Albian age to the Pliocene epoch.

The guitarfish, also referred to as shovelnose rays, are a family, Rhinobatidae, of rays. The guitarfish are known for an elongated body with a flattened head and trunk and small, ray-like wings. The combined range of the various species is tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate waters worldwide.

River stingrays or freshwater stingrays are Neotropical freshwater fishes of the family Potamotrygonidae in the order Myliobatiformes, one of the four orders of batoids, cartilaginous fishes related to sharks. They are found in rivers in tropical and subtropical South America. A single marine genus, Styracura, of the tropical West Atlantic and East Pacific are also part of Potamotrygonidae. They are generally brownish, greyish or black, often with a mottled, speckled or spotted pattern, have disc widths ranging from 31 to 200 centimetres (1.0–6.6 ft) and venomous tail stingers. River stingrays feed on a wide range of smaller animals and the females give birth to live young. There are more than 35 species in five genera.
Squalus is a genus of dogfish sharks in the family Squalidae. Commonly known as spurdogs, these sharks are characterized by smooth dorsal fin spines, teeth in upper and lower jaws similar in size, caudal peduncle with lateral keels; upper precaudal pit usually present, and caudal fin without subterminal notch. In spurdogs, the hyomandibula is oriented at a right angle to the neurocranium, while in other sharks, the hyomandibula runs more parallel to the body. This led some to think that the upper jaw of Squalus would not be as protractile as the jaws of other sharks. However, a study that compared different jaw suspension types in sharks showed that this is not the case and that Squalus is quite capable of protruding its upper jaw during feeding.

Apristurus is a genus of catsharks, the family Scyliorhinidae, commonly known as the ghost or demon catsharks.

Etmopterus is a genus of lantern sharks in the squaliform family Etmopteridae. They are found in deep sea ecosystems of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Potamotrygon is a genus of freshwater stingrays in the family Potamotrygonidae native to the rivers of South America, and sometimes seen in the aquarium trade. It inhabits rivers of tropical and subtropical climates, especially those of the Amazon basin and is virtually present in all South American countries, except for Chile.

Dipturus is a large genus of skates native to the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans. They were formerly included in Raja. Some species initially moved to Dipturus were later placed in Dentiraja, Spiniraja, and Zearaja.

Pristiophorus is a genus of sawsharks found in the Pacific, Atlantic and Indian oceans. Members of this genus differ from the Sixgill Sawshark (Pliotrema warreni) in having five gill slits. Their rostral sawteeth lack prominent transverse ridges on the basal ledges, and the large teeth are not posteriorly serrated.
Welcommia is an extinct genus of shark. It contains only three species :-

Debeerius is a genus of chondrichthyan from the Mississippian age Bear Gulch Limestone of Montana, United States. It is named after Gavin de Beer. One species, D. ellefseni, is known.

Sclerorhynchoidei is an extinct suborder of rajiform rays that had long rostra with large denticles similar to sawfishes and sawsharks. This feature was convergently evolved, recently proposed as 'pristification', and their closest living relatives are actually skates. While they are often called "sawfishes", sawskates is a more accurate common name proposed in 2021 for sclerorhynchoids, which has been subsequently used by other researchers.

Paracestracion is an extinct genus of heterodontiform sharks from Early Jurassic to Early Cretaceous-aged rocks of England, France, Germany and Luxembourg. The genus was first described in 1911 by Ernst Hermann Friedrich von Koken in Karl Alfred von Zittel.
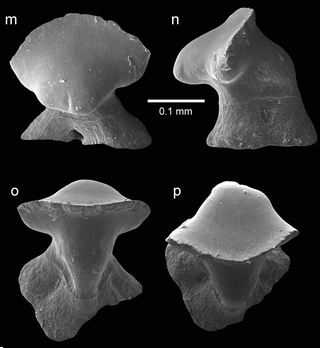
Antiquaobatis is an extinct genus of ray from the Early Jurassic of Europe, containing the single species A. grimmenensis. It is the oldest known described member of the Rajiformes, and is based on a single tooth from Pliensbachian of Northern Germany. It was recovered from the Grimmen Clay Pit, on Spinatum strata that belongs in the region to the Komorowo Formation. The holotype is a single antero-lateral tooth, very small and slightly asymmetrical, measuring 0.25 mm in maximum height and 0.26 mm in maximum width, that has an overall morphology, that suggests a consistent referral to Batoidea, encompassing all skates and rays. The tooth has an overall rather gracile crown morphology, different from any other know jurassic batomorphs, indicating closest affinities to the monotypic genus Engaibatis schultzei from the Kimmeridgian-Tithonian of Tanzania.
This list of fossil fish research presented in 2022 is a list of new fossil taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes, and other fishes that were described during the year, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoichthyology that occurred in 2022.
Toarcibatidae is a family of extinct rays that lived in the Early Jurassic in what would become Europe and North America. The family includes two genera, Cristabatis and Toarcibatis, and was originally named "Archaeobatidae", but that name did not conform to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature and was replaced. Doliobatis was originally included in this family as well, but it has since been reassigned to the Rhinobatidae.
Toarcibatis is an extinct genus of rays that lived during the Early Jurassic. It contains four valid species which have been found in Belgium, France, Luxembourg, and Spain. It was originally referred to the family "Archaeobatidae", but the family would eventually be renamed "Toarcibatidae" to conform with ICZN rules..
Cristabatis is an extinct genus of rays that lived during the Early Jurassic. It contains two valid species, C. exundans and C. crescentiformis, which have been found in Belgium and France. It was originally referred to the family "Archaeobatidae", but was later reassigned to the family Toarcibatidae.
Arthrobatis is an extinct genus of possible rays that lived during the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic in the United Kingdom. It contains one species, A. rileyi, and is the only member of the family Arthrobatidae. It might be the oldest known batoid, but its exact age and affinities are uncertain.












