
The Hampton Roads Bridge–Tunnel (HRBT) is a 3.5-mile-long (5.6 km) Hampton Roads crossing for Interstate 64 (I-64) and US Route 60 (US 60). It is a four-lane facility comprising bridges, trestles, artificial islands, and tunnels under the main shipping channels for Hampton Roads harbor in the southeastern portion of Virginia in the United States.
The Hampton Roads Beltway is a loop of Interstate 64 and Interstate 664, which links the communities of the Virginia Peninsula and South Hampton Roads which surround the body of water known as Hampton Roads and comprise much of the region of the same name in the southeastern portion of Virginia in the United States. It crosses the harbor of Hampton Roads at two locations on large four-laned bridge-tunnel facilities: the eastern half carries Interstate 64 and uses the Hampton Roads Bridge-Tunnel and the western half carries Interstate 664 and uses the Monitor-Merrimac Memorial Bridge-Tunnel. The beltway has the clockwise direction signed as the Inner Loop, and the counter-clockwise direction signed as the Outer Loop. The entire beltway, including the bridge-tunnels, is owned and operated by the Virginia Department of Transportation.

Interstate 264 (I-264) is an Interstate Highway in the US state of Virginia. It serves as the primary east–west highway through the South Hampton Roads region in southeastern Virginia. The route connects the central business districts of Chesapeake, Portsmouth, Norfolk, and Virginia Beach and serves as the most direct link between those cities and the resort beaches along Virginia's Atlantic coast.
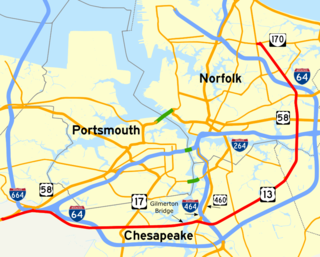
Military Highway is a four-to-eight-lane roadway built in the South Hampton Roads region of eastern Virginia, United States, during World War II. Carrying US 13 for most of its length, it also carries US 58, and US 460 while in Chesapeake. It is a major alternate route for the Hampton Roads Beltway, crossing four major freeways along its length.

The Interstate 264 Berkley Bridge is a double-leaf bascule bridge that crosses the Eastern Branch of the Elizabeth River in Norfolk, Virginia, United States. It carries Interstate 264 (I-264), U.S. Route 460 Alternate, and State Route 337 (SR 337) across the river, connecting the Berkley neighborhood south of the river with downtown Norfolk to the north. The toll-free facility is one of only a small number of movable bridges on the Interstate Highway System, and is the first of two in the Hampton Roads region, predating the High Rise Bridge. It is named for the former Town of Berkley that is now a part of the City of Norfolk.

Interstate 464 (I-464) is an Interstate Highway in the US state of Virginia. The highway runs 5.67 miles (9.12 km) from U.S. Route 17 (US 17) and State Route 168 (SR 168) in Chesapeake north to I-264 in Norfolk. I-464 connects two major highway junctions in the South Hampton Roads region. At its southern end, the Interstate meets two major highways that head toward North Carolina, US 17 and SR 168, and I-64, which follows the southern side of the Hampton Roads Beltway. At its northern terminus, I-464 has connections with Downtown Norfolk and Portsmouth via I-264.

Interstate 564 (I-564) is an Interstate Highway in the US state of Virginia. Known as Admiral Taussig Boulevard, after US Navy Rear Admiral Edward D. Taussig, the Interstate runs 3.03 miles (4.88 km) from State Route 337 (SR 337) east to I-64 within the city of Norfolk. I-564 is the primary access highway to Naval Station Norfolk, the world's largest naval base. The Interstate also links I-64 with Norfolk International Terminals via SR 406 and the Wards Corner area of Norfolk through connections with U.S. Route 460 (US 460) and SR 165.

Transportation in the Commonwealth of Virginia is by land, sea and air. Virginia's extensive network of highways and railroads were developed and built over a period almost 400 years, beginning almost immediately after the founding of Jamestown in 1607, and often incorporating old established trails of the Native Americans.

Transportation in Richmond, Virginia and its immediate surroundings include land, sea and air modes. This article includes the independent city and portions of the contiguous counties of Henrico and Chesterfield. While almost all of Henrico County would be considered part of the Richmond area, southern and eastern portions of Chesterfield adjoin the three smaller independent cities of Petersburg, Hopewell, and Colonial Heights, collectively commonly called the Tri-Cities area. A largely rural section of southwestern Chesterfield may be considered not a portion of either suburban area.

State Route 168 is a primary state highway in the South Hampton Roads region of the U.S. state of Virginia. It runs from the border with North Carolina through the independent cities of Chesapeake and Norfolk where it ends in the Ocean View area near the Hampton Roads Bridge-Tunnel.
The Gilmerton Bridge, originally a twin bascule drawbridge, is now a vertical-lift bridge which spans the Southern Branch Elizabeth River in the City of Chesapeake in South Hampton Roads in southeastern Virginia. Completed in 1938, it carries U.S. Route 13 and US 460 and is part of Military Highway. The Gilmerton Bridge is operated by the City of Chesapeake.

U.S. Route 17 (US 17) is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that runs from Punta Gorda, Florida, to Winchester, Virginia. In Virginia, the U.S. Highway runs 255.83 miles (411.72 km) from the North Carolina state line in Chesapeake north to its northern terminus at US 11, US 50, and US 522 in Winchester. US 17 is a major highway in the eastern half of Virginia. The U.S. Highway connects the Albemarle Region of North Carolina with the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. Within the urban area, US 17 passes through the South Hampton Roads cities of Chesapeake, Portsmouth, and Suffolk and the Virginia Peninsula city of Newport News. Between Yorktown and Fredericksburg, the U.S. Highway serves as the primary highway of the Middle Peninsula. At Fredericksburg, US 17 leaves the Atlantic Plain; the highway passes through the Piedmont town of Warrenton and crosses the Blue Ridge Mountains on its way to Winchester in the Shenandoah Valley. The route from Tappahannock to Winchester roughly follows the Confederate march during the Civil War to Gettysburg.

State Route 165 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 39.75 miles (63.97 km) from U.S. Route 17 Business in Chesapeake north to SR 337 in Norfolk. SR 165 is a C-shaped route that connects Chesapeake and Norfolk in the Hampton Roads metropolitan area indirectly via Virginia Beach. The highway's east–west segment connects the Chesapeake communities of Deep Creek and Great Bridge with the Princess Anne part of Virginia Beach. SR 165's northwest–southeast portion connects the Princess Anne area with Virginia Beach's Salem and Kempsville communities and with Norfolk. Within Norfolk, the state highway parallels Interstate 64 (I-64) while passing through the eastern and northern areas of the city near Norfolk International Airport and Naval Station Norfolk. Much of SR 165 is a multi-lane divided highway, but there are significant two-lane stretches in all three of the independent cities the highway serves.

State Route 166 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 15.47 miles (24.90 km) from U.S. Route 17 in Chesapeake north to US 60 in Virginia Beach.

State Route 190 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 15.43 miles (24.83 km) from SR 166 in Chesapeake east and north to SR 225 in Virginia Beach. SR 190 is a J-shaped route that connects the central part of Chesapeake with the western part of Virginia Beach.

Interstate 64 (I-64) in the US state of Virginia runs east–west through the middle of the state from West Virginia to the Hampton Roads region, for a total of 299 miles (481 km). From the West Virginia state line to Chesapeake, it passes through the major cities of Lexington, Staunton, Charlottesville, the state capital of Richmond, Newport News, Hampton, and Norfolk. It is notable for crossing the mouth of the harbor of Hampton Roads on the Hampton Roads Bridge–Tunnel (HRBT), the first bridge–tunnel to incorporate artificial islands, concurrent with U.S. Route 60 (US 60). Also noteworthy is a section through Rockfish Gap, a wind gap in the Blue Ridge Mountains, which was equipped with an innovative system of airport-style runway lighting embedded into the pavement to aid motorists during periods of poor visibility due to fog or other conditions.

State Route 247 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 5.31 miles (8.55 km) from SR 337 east to SR 165 within the independent city of Norfolk. SR 247 is a major east–west thoroughfare that connects U.S. Route 460 and Interstate 64 (I-64) with Norfolk International Airport.
Located in the southeastern corner of the state, Norfolk is economically and culturally important to Virginia. A variety of transportation modes have developed around the city's importance and somewhat unusual geography.

Historically, the harbor was the key to the Hampton Roads area's growth, both on land and in water-related activities and events. Ironically, the harbor and its tributary waterways were both important transportation conduits and obstacles to other land-based commerce and travel. For hundreds of years, state and community leaders have worked to develop solutions to accommodate both.
The Veterans Bridge is a fixed span concrete bridge that spans the Southern Branch of the Elizabeth River in the Deep Creek neighborhood of Chesapeake in southeastern Virginia, USA. The bridge, which partially opened in 2014, currently carries two lanes of U.S. Route 17 on each direction across its northbound and southbound spans. The corridor frequently acts as a bypass route for congested I-64 High Rise Bridge traffic. It replaces the much shorter and smaller Dominion Boulevard Steel Bridge, which because of its 11-foot underwater clearance opened on average of 16 times per day.
















