| Dracontioides | |
|---|---|
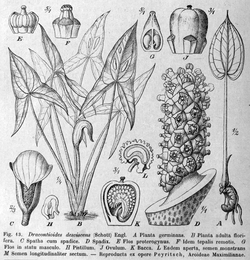 | |
| Dracontioides desciscens 1911 illustration [1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Alismatales |
| Family: | Araceae |
| Subfamily: | Lasioideae |
| Genus: | Dracontioides Engl. |
| Type species | |
| Dracontioides desciscens (Schott) Engl. | |
Dracontioides is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It was long thought to contain only a single species until a second species was described in 2005. Both are endemic to Brazil. [2] [3] [4]
The type species of the genus is Dracontioides desciscens, native to swamps in eastern Brazil. This species was originally classified by Heinrich Wilhelm Schott as belonging to Urospatha, but it was subsequently reassigned to its own genus Dracontioides by Adolf Engler. The genus is closely related to both Urospatha and Dracontium . The most notable feature of the species its glossy extremely sagittate leaves with oval fenestrations. The leaves are attached to 2 meter long stalks that are intern attached to a spongy rhizome. Additionally, the inflorescence produced has a smell of rotting meat. [5]
- Species
- Dracontioides desciscens (Schott) Engl. - Pernambuco, Bahia, Espírito Santo
- Dracontioides salvianii E.G.Gonç. - Bahia [6]