
ECHELON, originally a secret government code name, is a surveillance program operated by the five signatory states to the UKUSA Security Agreement: Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States, also known as the Five Eyes.

The National Security Agency (NSA) is a national-level intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the Director of National Intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collection, and processing of information and data for foreign and domestic intelligence and counterintelligence purposes, specializing in a discipline known as signals intelligence (SIGINT). The NSA is also tasked with the protection of U.S. communications networks and information systems. The NSA relies on a variety of measures to accomplish its mission, the majority of which are clandestine. The existence of the NSA was not revealed until 1975. The NSA has roughly 32,000 employees.

The Government Communications Security Bureau is the public-service department of New Zealand charged with promoting New Zealand's national security by collecting and analysing information of an intelligence nature. The GCSB is considered to be New Zealand's most powerful intelligence agency, and has been alleged to have conducted more espionage and data collection than the country's primary intelligence agency, the less funded NZSIS. This has at times proven controversial, although the GCSB does not have the baggage of criticism attached to it for a perceived failure to be effective like the NZSIS does. The GCSB is considered an equivalent of GCHQ in the United Kingdom or the NSA in the United States.

The United Kingdom – United States of America Agreement is a multilateral agreement for cooperation in signals intelligence between Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The alliance of intelligence operations is also known as the Five Eyes. In classification markings this is abbreviated as FVEY, with the individual countries being abbreviated as AUS, CAN, NZL, GBR, and USA, respectively.
Spying on the United Nations refers to acts of espionage committed by states against the United Nations.

The Five Eyes (FVEY) is an intelligence alliance comprising Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States. These countries are parties to the multilateral UKUSA Agreement, a treaty for joint cooperation in signals intelligence. Informally, Five Eyes can also refer to the group of intelligence agencies of these countries.

"Stellar Wind" was the code name of a warrantless surveillance program begun under the George W. Bush administration's President's Surveillance Program (PSP). The National Security Agency (NSA) program was approved by President Bush shortly after the September 11, 2001 attacks and was revealed by Thomas Tamm to The New York Times in 2004. Stellar Wind was a prelude to new legal structures that allowed President Bush and President Barack Obama to reproduce each of those programs and expand their reach.
This is a list of notable content from the United States diplomatic cables leak that reveals the United States' political opinion towards a variety of international affairs. Beginning on November 28, 2010, WikiLeaks had been publishing classified documents of detailed correspondence—diplomatic cables—between the United States Department of State and its diplomatic missions around the world. On 1 September 2011, it released all of the Cablegate documents in its possession without redaction.
Spying on United Nations leaders by United States diplomats was confirmed by a 2009 confidential directive from the United States Department of State directly instructing US diplomats to spy on top officials of the United Nations. The intelligence information to be gathered included biometric information and passwords and other authentication keys used in official communications. The directives were revealed as part of the United States diplomatic cables leak in late 2010. While spying by the US on the UN was not new, the directive's aggressive goals for information gathering and desire for use of regular diplomats in the gathering was seen by some as new, and caused a strain in relations between the US and UN.

PRISM is a code name for a program under which the United States National Security Agency (NSA) collects internet communications from various U.S. internet companies. The program is also known by the SIGAD US-984XN. PRISM collects stored internet communications based on demands made to internet companies such as Google LLC under Section 702 of the FISA Amendments Act of 2008 to turn over any data that match court-approved search terms. Among other things, the NSA can use these PRISM requests to target communications that were encrypted when they traveled across the internet backbone, to focus on stored data that telecommunication filtering systems discarded earlier, and to get data that is easier to handle.

Edward Joseph Snowden is an American and naturalized Russian former computer intelligence consultant and whistleblower who leaked highly classified information from the National Security Agency (NSA) in 2013, when he was an employee and subcontractor. His disclosures revealed numerous global surveillance programs, many run by the NSA and the Five Eyes intelligence alliance with the cooperation of telecommunication companies and European governments and prompted a cultural discussion about national security and individual privacy.

The practice of mass surveillance in the United States dates back to wartime monitoring and censorship of international communications from, to, or which passed through the United States. After the First and Second World Wars, mass surveillance continued throughout the Cold War period, via programs such as the Black Chamber and Project SHAMROCK. The formation and growth of federal law-enforcement and intelligence agencies such as the FBI, CIA, and NSA institutionalized surveillance used to also silence political dissent, as evidenced by COINTELPRO projects which targeted various organizations and individuals. During the Civil Rights Movement era, many individuals put under surveillance orders were first labelled as integrationists, then deemed subversive, and sometimes suspected to be supportive of the communist model of the United States' rival at the time, the Soviet Union. Other targeted individuals and groups included Native American activists, African American and Chicano liberation movement activists, and anti-war protesters.

The Australia–Indonesia spying scandal developed from allegations made in 2013 by The Guardian and the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC), based on leaked documents, that the Australian Signals Directorate had in 2009 attempted to monitor the mobile phone calls of Indonesian President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono, his wife Kristiani Herawati, and senior officials.

Ongoing news reports in the international media have revealed operational details about the Anglophone cryptographic agencies' global surveillance of both foreign and domestic nationals. The reports mostly emanate from a cache of top secret documents leaked by ex-NSA contractor Edward Snowden, which he obtained whilst working for Booz Allen Hamilton, one of the largest contractors for defense and intelligence in the United States. In addition to a trove of U.S. federal documents, Snowden's cache reportedly contains thousands of Australian, British, Canadian and New Zealand intelligence files that he had accessed via the exclusive "Five Eyes" network. In June 2013, the first of Snowden's documents were published simultaneously by The Washington Post and The Guardian, attracting considerable public attention. The disclosure continued throughout 2013, and a small portion of the estimated full cache of documents was later published by other media outlets worldwide, most notably The New York Times, the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation, the Australian Broadcasting Corporation, Der Spiegel (Germany), O Globo (Brazil), Le Monde (France), L'espresso (Italy), NRC Handelsblad, Dagbladet (Norway), El País (Spain), and Sveriges Television (Sweden).

The origins of global surveillance can be traced back to the late 1940s, when the UKUSA Agreement was jointly enacted by the United Kingdom and the United States, whose close cooperation eventually culminated in the creation of the global surveillance network, code-named "ECHELON", in 1971.

The global surveillance disclosure released to media by Edward Snowden has caused tension in the bilateral relations of the United States with several of its allies and economic partners as well as in its relationship with the European Union. In August 2013, U.S. President Barack Obama announced the creation of "a review group on intelligence and communications technologies" that would brief and later report to him. In December, the task force issued 46 recommendations that, if adopted, would subject the National Security Agency (NSA) to additional scrutiny by the courts, Congress, and the president, and would strip the NSA of the authority to infiltrate American computer systems using "backdoors" in hardware or software. Geoffrey R. Stone, a White House panel member, said there was no evidence that the bulk collection of phone data had stopped any terror attacks.
This is a category of disclosures related to global surveillance.

Global mass surveillance can be defined as the mass surveillance of entire populations across national borders.
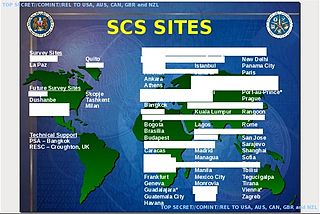
STATEROOM is the code name of a highly secretive signals intelligence collection program involving the interception of international radio, telecommunications and internet traffic. It is operated out of the diplomatic missions of the signatories to the UKUSA Agreement and the members of the ECHELON network including Australia, New Zealand, United Kingdom, Canada and the United States.

This timeline of global surveillance disclosures from 2013 to the present day is a chronological list of the global surveillance disclosures that began in 2013. The disclosures have been largely instigated by revelations from the former American National Security Agency contractor Edward Snowden.












