
VIA EPIA ( VIA Embedded Platform Innovative Architecture) is a series of mini-ITX, em-ITX, nano-ITX, pico-ITX and pico-ITXe motherboards with integrated VIA processors. They are small and consume less power than computers of comparable capabilities.

VIA EPIA ( VIA Embedded Platform Innovative Architecture) is a series of mini-ITX, em-ITX, nano-ITX, pico-ITX and pico-ITXe motherboards with integrated VIA processors. They are small and consume less power than computers of comparable capabilities.
The VIA EPIA motherboards have the following designators: [1]
| Code | Definition |
|---|---|
| A | Configured without TV-out |
| E | Fanless configuration |
| G | RoHS-compliant |
| L | Configured with Gigabit LAN (where this is optional) |
| T | With TPM |
All connections apart from the VGA and network connection are only onboard for reasons of space.

Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also retroactively called DDR1 SDRAM, has been superseded by DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM, DDR4 SDRAM and DDR5 SDRAM. None of its successors are forward or backward compatible with DDR1 SDRAM, meaning DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5 memory modules will not work on DDR1-equipped motherboards, and vice versa.

A DIMM, or Dual In-Line Memory Module, is a type of computer memory module used in desktop, laptop, and server computers. It is a circuit board that contains memory chips and connects to the computer's motherboard. A DIMM is often called a "RAM stick" due to its shape and size. A DIMM comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory integrated circuits that are mounted to its circuit board. DIMMs are the predominant method for adding memory into a computer system. The vast majority of DIMMs are standardized through JEDEC standards, although there are proprietary DIMMs. DIMMs come in a variety of speeds and sizes, but generally are one of two lengths - PC which are 133.35 mm (5.25 in) and laptop (SO-DIMM) which are about half the size at 67.60 mm (2.66 in).
Rambus DRAM (RDRAM), and its successors Concurrent Rambus DRAM (CRDRAM) and Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM), are types of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) developed by Rambus from the 1990s through to the early 2000s. The third-generation of Rambus DRAM, DRDRAM was replaced by XDR DRAM. Rambus DRAM was developed for high-bandwidth applications and was positioned by Rambus as replacement for various types of contemporary memories, such as SDRAM.

Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It is a JEDEC standard (JESD79-2); first published in September 2003. DDR2 succeeded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself succeeded by DDR3 SDRAM in 2007. DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR.

In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components on one or more integrated circuits that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. The chipset is usually found on the motherboard of computers. Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining system performance.
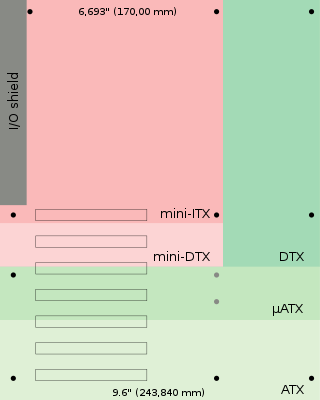
Mini-ITX is a 170 mm × 170 mm motherboard form factor developed by VIA Technologies in 2001. Mini-ITX motherboards have been traditionally used in small-configured computer systems. Originally, Mini-ITX was a niche standard designed for fanless cooling with a low power consumption architecture, which made them useful for home theater PC systems, where fan noise can detract from the cinema experience.

In computing, a northbridge is one of two chips comprising the core logic chipset architecture on motherboards for older personal computers. A northbridge is connected directly to a CPU via the front-side bus (FSB) to handle high-performance tasks, and is usually used in conjunction with a slower southbridge to manage communication between the CPU and other parts of the motherboard.

In computing, double data rate (DDR) describes a computer bus that transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in the context of NAND flash memory.
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed successor to DDR and DDR2 and predecessor to DDR4 synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) chips. DDR3 SDRAM is neither forward nor backward compatible with any earlier type of random-access memory (RAM) because of different signaling voltages, timings, and other factors.
The AMD 700 chipset series is a set of chipsets designed by ATI for AMD Phenom processors to be sold under the AMD brand. Several members were launched in the end of 2007 and the first half of 2008, others launched throughout the rest of 2008.

VIA CoreFusion is a line of low power x86 processors manufactured by VIA starting in 2003. The Corefusion integrates the Northbridge, graphics processing unit and a V-Link Interface

In computer design, Pico-ITX is a PC motherboard form factor announced by VIA Technologies in January 2007 and demonstrated later the same year at CeBIT. The formfactor was transferred over to SFF-SIG in 2008. The Pico-ITX form factor specifications call for the board to be 10 × 7.2 cm (3.9 × 2.8 in), which is half the area of Nano-ITX.

VIA Eden is a name of a variant of VIA's C3/C7 x86 processors, designed to be used in embedded devices. They have smaller package sizes, lower power consumption, and somewhat lower computing performance than their C equivalents, due to reduced clock rates. They are often used in EPIA mini-ITX, nano-ITX, and Pico-ITX motherboards. In addition to x86 instruction decoding, the processors have a second undocumented Alternate Instruction Set.
The IntelliStation is a family of workstations developed by IBM and first released in March 1997 as the follow-on to the PC Series 360 and 365. Certain IntelliStation M Pro Series were near hardware identical to low end IBM Netfinity 1000 Series network servers. In February 2002, POWER processor-based workstations, previously sold directly under the eServer pSeries brand, were also placed under the IntelliStation umbrella.
A memory divider is a ratio which is used to determine the operating clock frequency of computer memory in accordance with front side bus (FSB) frequency, if the memory system is dependent on FSB clock speed. Along with memory latency timings, memory dividers are extensively used in overclocking memory subsystems to find stable, working memory states at higher FSB frequencies. The ratio between DRAM and FSB is commonly referred to as "DRAM:FSB ratio".
The Digital Personal Workstation, code named "sports car", is a family of entry-level to mid-range workstation computers developed and manufactured by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). These workstations are based on the DEC Alpha and Intel Pentium Pro or Pentium II microprocessors. Members of this family can run the Digital UNIX, OpenVMS, and Windows NT operating systems. The i-Series, based on Pentium Pro, was introduced first, on September 23, 1996.

Pico-ITXe is a PC Pico-ITX motherboard specification created by VIA Technologies and SFF-SIG. It was announced by VIA Technologies on October 29, 2008, and released in December 2008. The Pico-ITXe specifications call for the board to be 10 × 7.2 cm (3.9 × 2.8 in), which is half the area of Nano-ITX, and 12 layers deep. The processor can be a VIA C7 that uses VIA's NanoBGA2 technology. It uses DDR2 667/533 SO-DIMM memory, with support for up to 2GB. Video is supplied by VIA's Chrome9 HC3 GPU with built-in MPEG-2, 4, WMV9, and VC1 decoding acceleration. The BIOS is a 4 or 8 Mbit Award BIOS.
Apollo VP3 is a x86 based Socket 7 chipset which was manufactured by VIA Technologies and was launched in 1997. On its time Apollo VP3 was a high performance, cost effective, and energy efficient chipset. It offered AGP support for Socket 7 processors which was not supported at that moment by Intel, SiS and ALi chipsets. In November 1997 FIC released motherboard PA-2012, which uses Apollo VP3 and has AGP bus. This was the first Socket 7 motherboard supporting AGP.