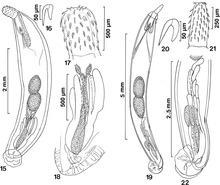
Acanthocephala is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described.

Eoacanthocephala is a class of parasitic worms, within the phylum Acanthocephala. They feed on any aquatic cold-blooded creature such as turtles and fish. Their proboscis spines arranged radially, no protonephridia, persistent ligament sacs in female. The only reliable way to identify the group is that they only have one cement gland. This is a primitive characteristic and hence the name. The class contains 2 orders:

Acanthocephalus is a genus of parasitic worms. One of the species in this genus is Acanthocephalus anguillae, a fish parasite. Acanthocephalans are also found in humans and primates, causing a common zoonotic infection called "human acanthocephaliasis". While pathogens can be transferred among animals and humans, the main source of human acanthocephaliasis is the diet of infected raw fish and insects.

The thorny-headed worm family Polymorphidae contains endoparasites which as adults feed mainly in fish and aquatic birds. When this taxon was erected by Meyer in 1931, a subfamily Polymorphinae was established in it. As the Polymorphidae as presently understood would then be monotypic, with no basal genera outside the Polymorphinae, the proposed subfamily is redundant for the time being and therefore most modern treatments simply omit it. Polymorphus minutus is an economically significant parasite in goose and duck farming.

Gigantorhynchus is a genus of Acanthocephala that parasitize marsupials, anteaters, and possibly baboons by attaching themselves to the intestines using their hook-covered proboscis. Their life cycle includes an egg stage found in host feces, a cystacanth (larval) stage in an intermediate host such as termites, and an adult stage where cystacanths mature in the intestines of the host. This genus is characterized by a cylindrical proboscis with a crown of robust hooks at the apex followed by numerous small hooks on the rest of the proboscis, a long body with pseudosegmentation, filiform lemnisci, and ellipsoid testes. The largest known specimen is the female G. ortizi with a length of around 240 millimetres (9.4 in) and a width of 2 millimetres (0.08 in). Genetic analysis on one species of Gigantorhynchus places it with the related genus Mediorhynchus in the family Gigantorhynchidae. Six species in this genus are distributed across Central and South America and possibly Zimbabwe. Infestation by a Gigantorhynchus species may cause partial obstructions of the intestines, severe lesions of the intestinal wall, and may lead to death.
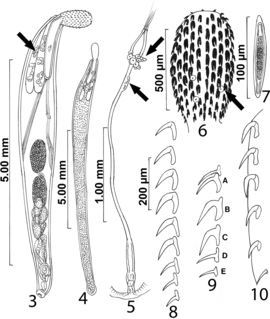
Echinorhynchus is a genus of acanthocephalan parasitic worms. They parasitize a wide variety of fishes from both marine and fresh waters. The intermediate host is usually a crustacean.

Oligacanthorhynchida is an order containing a single parasitic worm family, Oligacanthorhynchidae, that attach themselves to the intestinal wall of terrestrial vertebrates.
Arhythmacanthidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.

Cavisomidae are a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.

Pomphorhynchidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.

Illiosentidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.

Neoechinorhynchidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Neoechinorhynchida.
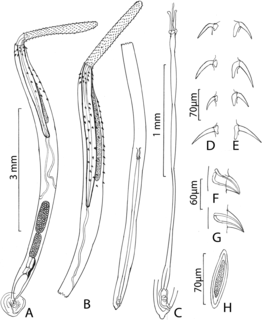
Rhadinorhynchidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.
Dactylosoma is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexia.

Philometra is a genus of nematodes, which are parasites of marine and freshwater fishes. The genus was erected by Oronzio Gabriele Costa in 1845.

Louis Euzet was a French parasitologist.

Transvenidae is a family of parasitic spiny-headed worms in the order Echinorhynchida. This family contains three species divided into two genera.

Neoandracantha is a genus of parasitic worms from the phylum Acanthocephala. The genus was created in 2017 by Amin & Heckmann for the single species Neoandracantha peruensis.
Pseudoacanthocephalus goodmani is a species of parasitic worm in the phylum Acanthocephala, first described in 2020.
Pseudoacanthocephalus is a genus of parasitic worms belonging to the family Echinorhynchidae.