
Echis carinatus, known as the saw-scaled viper, Indian saw-scaled viper, little Indian viper, and by other common names, is a viper species found in parts of the Middle East and Central Asia, and especially the Indian subcontinent. It is the smallest member of the "big four" Indian snakes that are responsible for causing the most snakebite cases and deaths, due to various factors including their frequent occurrence in highly populated regions, and their inconspicuous nature. Like all vipers, the species is venomous. Two subspecies are currently recognized, including the nominate subspecies described here.

Echis coloratus, known as the painted saw-scaled viper, painted carpet viper, Burton's carpet viper, and by other common names, is a highly venomous viper species endemic to the Middle East and Egypt. No subspecies are currently recognized.

The desert owl or desert tawny owl, formerly known as Hume's owl, is a species of owl. It is closely related to the more widespread tawny owl and to the range-restricted Omani owl.

The four venomous snake species responsible for causing the greatest number of medically significant human snake bite cases on the Indian subcontinent are sometimes collectively referred to as the Big Four. They are as follows:
- Russell's viper, Daboia russelii
- Common krait, Bungarus caeruleus
- Indian cobra, Naja naja
- Indian saw-scaled viper, Echis carinatus

Echis is a genus of vipers found in the dry regions of Africa, the Middle East, India, Sri Lanka and Pakistan. They have a characteristic threat display, rubbing sections of their body together to produce a "sizzling" warning sound. The name Echis is the Latin transliteration of the Greek word for "viper" (ἔχις). Like all vipers, they are venomous. Their common name is "saw-scaled vipers" and they include some of the species responsible for causing the most snakebite cases and deaths in the world. Twelve species are currently recognized.

Echis hughesi, known as the Hughes' carpet viper, Somali carpet viper, and Hughes' saw-scaled viper, is a species of venomous snake in the subfamily Viperinae of the family Viperidae. The species is endemic to Somalia. There are no subspecies which are currently recognized as being valid.
Echis leucogaster, also known as the white-bellied carpet viper or the Roman's saw-scaled viper, is a viper species endemic to West and Northwest Africa. Its scientific name derives from its white (leuco-), unmarked belly (gaster). like all other vipers, it is venomous. No subspecies are currently recognized.
Echis ocellatus, known by the common names West African carpet viper and ocellated carpet viper, is a highly venomous species of viper endemic to West Africa. No subspecies are currently recognized.

Echis pyramidum, known as the Northeast African carpet viper, Egyptian saw-scaled viper, and by other common names, is a species of viper endemic to Northeast Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. Like all other vipers, it is venomous. Three subspecies are currently recognized, including the nominate subspecies described here.

Echis carinatus sochureki is a venomous viper subspecies found in India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Iran, and parts of the Arabian Peninsula.
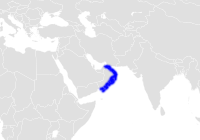
The Oman bullhead shark, Heterodontus omanensis, is a bullhead shark of the family Heterodontidae found in the tropical western Indian Ocean around central Oman, from the surface to a depth of 72 m (236 ft) on the continental shelf. This species has an average length of 56 cm (22 in) and can reach a maximum length of 61 cm (24 in). This shark was described in 2005, making it one of the most recently described of its genus. The Oman bullhead shark likely is accidentally caught as bycatch, putting the species at risk.

Iago is a genus of houndsharks in the family Triakidae. The name comes from the villain in William Shakespeare´s Othello. Also known as Iago omanensis is a small, placental viviparous shark that is found abundantly in the deep waters of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. It can be found at the depths of 150-1500 meters.

The bigeye houndshark is a species of houndshark, belonging to the family Triakidae. It is found in the deep waters of the continental shelves in the western Indian Ocean, from the Red Sea to southwestern India, between latitudes 30° N and 10° N, at depths between 110 and 2,200 m. Its length is up to 37 cm (15 in).

The Omani owl is an owl of the genus Strix found in shrubland and rocky areas of Oman, Iran and the United Arab Emirates. It was discovered in 2013.

Amphiprion omanensis is a marine fish belonging to the family Pomacentridae, the clownfishes and damselfishes.

Echis khosatzkii is a species of viper. Like all other vipers, it is venomous.

Echis borkini is a species of viper. Like all vipers, it is venomous. It was originally described as subspecies of Echis varius.
Lobulogobius omanensis, the Oman goby, is a species of goby found in the Indo-West Pacific.
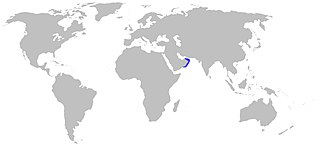
Acroteriobatus omanensis, the Oman guitarfish, is a type of guitarfish of the family Rhinobatidae found in Gulf of Oman and Arabian Sea. There has only been a handful of specimens discovered in fish landings in Muscat. Therefore, its population and potential threats are not specifically known to scientists.


















