Related Research Articles

Cotransporters are a subcategory of membrane transport proteins (transporters) that couple the favorable movement of one molecule with its concentration gradient and unfavorable movement of another molecule against its concentration gradient. They enable cotransport and include antiporters and symporters. In general, cotransporters consist of two out of the three classes of integral membrane proteins known as transporters that move molecules and ions across biomembranes. Uniporters are also transporters but move only one type of molecule down its concentration gradient and are not classified as cotransporters.
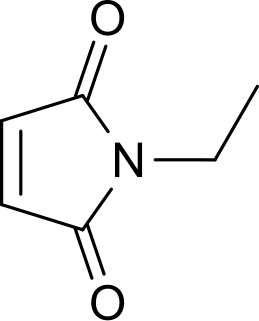
N-Ethylmaleimide (NEM) is an organic compound that is derived from maleic acid. It contains the amide functional group, but more importantly it is an alkene that is reactive toward thiols and is commonly used to modify cysteine residues in proteins and peptides.
The solute carrier (SLC) group of membrane transport proteins include over 400 members organized into 66 families. Most members of the SLC group are located in the cell membrane. The SLC gene nomenclature system was originally proposed by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) and is the basis for the official HGNC names of the genes that encode these transporters. A more general transmembrane transporter classification can be found in TCDB database.
The Na-K-Cl cotransporter (NKCC) is a protein that aids in the secondary active transport of sodium, potassium, and chloride into cells. In humans there are two isoforms of this membrane transport protein, NKCC1 and NKCC2, encoded by two different genes. Two isoforms of the NKCC1/Slc12a2 gene result from keeping or skipping exon 21 in the final gene product.

The sodium-chloride symporter (also known as Na+-Cl− cotransporter, NCC or NCCT, or as the thiazide-sensitive Na+-Cl− cotransporter or TSC) is a cotransporter in the kidney which has the function of reabsorbing sodium and chloride ions from the tubular fluid into the cells of the distal convoluted tubule of the nephron. It is a member of the SLC12 cotransporter family of electroneutral cation-coupled chloride cotransporters. In humans, it is encoded by the SLC12A3 gene (solute carrier family 12 member 3) located in 16q13.
The sodium/phosphate cotransporter is a member of the phosphate:Na+ symporter (PNaS) family within the TOG Superfamily of transport proteins as specified in the Transporter Classification Database (TCDB).

The sulfate transporter is a solute carrier family protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC26A2 gene. SLC26A2 is also called the diastrophic dysplasia sulfate transporter (DTDST), and was first described by Hästbacka et al. in 1994. A defect in sulfate activation described by Superti-Furga in achondrogenesis type 1B was subsequently also found to be caused by genetic variants in the sulfate transporter gene. This sulfate (SO42−) transporter also accepts chloride, hydroxyl ions (OH−), and oxalate as substrates. SLC26A2 is expressed at high levels in developing and mature cartilage, as well as being expressed in lung, placenta, colon, kidney, pancreas and testis.

WNK , also known as WNK1, is an enzyme that is encoded by the WNK1 gene. WNK1 is serine-threonine kinase and part of the "with no lysine/K" kinase WNK family. The predominant role of WNK1 is the regulation of cation-Cl− cotransporters (CCCs) such as the sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC), basolateral Na-K-Cl symporter (NKCC1), and potassium chloride cotransporter (KCC1) located within the kidney. CCCs mediate ion homeostasis and modulate blood pressure by transporting ions in and out of the cell. WNK1 mutations as a result have been implicated in blood pressure disorders/diseases; a prime example being familial hyperkalemic hypertension (FHHt).

Electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 1 (NBCe1) is a membrane transport protein that in humans is encoded by the 'SLC4A4' gene.

Neutral amino acid transporter A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC1A4 gene.

Potassium-chloride transporter member 5 is a neuron-specific chloride potassium symporter responsible for establishing the chloride ion gradient in neurons through the maintenance of low intracellular chloride concentrations. It is a critical mediator of synaptic inhibition, cellular protection against excitotoxicity and may also act as a modulator of neuroplasticity. Potassium-chloride transporter member 5 is also known by the names: KCC2 for its ionic substrates, and SLC12A5 for its genetic origin from the SLC12A5 gene in humans.

Potassium-chloride transporter, member 4 is a chloride potassium symporter protein. It is encoded by the gene SLC12A4.

Sodium- and chloride-dependent glycine transporter 2, also known as glycine transporter 2 (GlyT2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A5 gene.
The chloride potassium symporter is a membrane transport protein of the solute carrier family 12 that is present in the S3-segment of the renal proximal tubule and in the neuron. It functions in renal chloride reabsorption to transport chloride across the basolateral membrane. Chloride potassium symporter can lower intracellular chloride concentrations below the electrochemical equilibrium potential.
Electroneutral sodium bicarbonate exchanger 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC4A8 gene.

Solute carrier family 12 member 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC12A6 gene.

Solute carrier family 12 member 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC12A7 gene.
The cation-chloride cotransporter (CCC) family is part of the APC superfamily of secondary carriers. Members of the CCC family are found in animals, plants, fungi and bacteria. Most characterized CCC family proteins are from higher eukaryotes, but one has been partially characterized from Nicotiana tabacum, and homologous ORFs have been sequenced from Caenorhabditis elegans (worm), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast) and Synechococcus sp.. The latter proteins are of unknown function. These proteins show sequence similarity to members of the APC family. CCC family proteins are usually large, and possess 12 putative transmembrane spanners (TMSs) flanked by large N-terminal and C-terminal hydrophilic domains.
The anion exchanger family is a member of the large APC superfamily of secondary carriers. Members of the AE family are generally responsible for the transport of anions across cellular barriers, although their functions may vary. All of them exchange bicarbonate. Characterized protein members of the AE family are found in plants, animals, insects and yeast. Uncharacterized AE homologues may be present in bacteria. Animal AE proteins consist of homodimeric complexes of integral membrane proteins that vary in size from about 900 amino acyl residues to about 1250 residues. Their N-terminal hydrophilic domains may interact with cytoskeletal proteins and therefore play a cell structural role. Some of the currently characterized members of the AE family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.

Andermann syndrome, also known as agenesis of corpus callosum with neuronopathy (ACCPN) and Charlevoix disease, among other names, is a very rare neurodegenerative genetic disorder that damages the nerves used to control muscles and related to sensation and is often associated with agenesis of the corpus collosum.
References
- ↑ Gillen CM, Brill S, Payne JA, Forbush B (July 1996). "Molecular cloning and functional expression of the K-Cl cotransporter from rabbit, rat, and human. A new member of the cation-chloride cotransporter family". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (27): 16237–44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.27.16237 . PMID 8663127.
- ↑ Payne JA, Stevenson TJ, Donaldson LF (July 1996). "Molecular characterization of a putative K-Cl cotransporter in rat brain. A neuronal-specific isoform". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (27): 16245–52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.27.16245 . PMID 8663311.
- ↑ Rivera C, Voipio J, Payne JA, Ruusuvuori E, Lahtinen H, Lamsa K, Pirvola U, Saarma M, Kaila K (January 1999). "The K+/Cl− co-transporter KCC2 renders GABA hyperpolarizing during neuronal maturation". Nature. 397 (6716): 251–5. Bibcode:1999Natur.397..251R. doi:10.1038/16697. PMID 9930699. S2CID 7687596.
- ↑ Race JE, Makhlouf FN, Logue PJ, Wilson FH, Dunham PB, Holtzman EJ (December 1999). "Molecular cloning and functional characterization of KCC3, a new K-Cl cotransporter". Am. J. Physiol. 277 (6 Pt 1): C1210–9. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.1999.277.6.C1210. PMID 10600773.
- ↑ Singhvi, Aakanksha; Liu, Bingqian; Friedman, Christine J.; Fong, Jennifer; Lu, Yun; Huang, Xin-Yun; Shaham, Shai (May 2016). "A Glial K/Cl Transporter Controls Neuronal Receptive Ending Shape by Chloride Inhibition of an rGC". Cell. 165 (4): 936–948. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.026. PMC 4860081 . PMID 27062922.
- ↑ Howard HC, Mount DB, Rochefort D, Byun N, Dupre N, Lu J, Fan X, Song L, Riviere JB, Prevost C, Horst J, Simonati A, Lemcke B, Welch R, England R, Zhan FQ, Mercado A, Siesser WB, George AL, McDonald MP, Bouchard JP, Mathieu J, Delpire E, Rouleau GA (November 2002). "The K-Cl cotransporter KCC3 is mutant in a severe peripheral neuropathy associated with agenesis of the corpus callosum". Nat. Genet. 32 (3): 384–92. doi:10.1038/ng1002. PMID 12368912. S2CID 23820724.